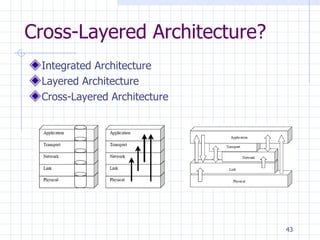
The document discusses network models and layers. It covers the layered architecture of the Internet model and OSI model. The key points are:
1. The Internet and OSI models use a layered approach to break down the complex process of network communication into smaller, well-defined functions.
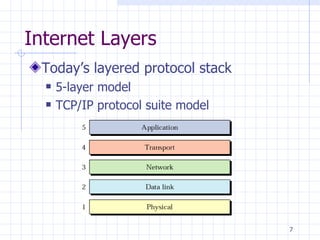
2. The Internet model has 5 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, and application. The OSI model adds an additional session layer and presentation layer.
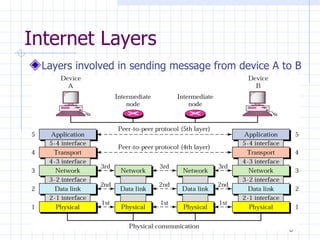
3. Each layer only interacts with the layers directly above and below it, performing specific tasks like physical addressing, routing, and providing end-user services.
![Ch.2 Network Models Lecturer: Tae-Hyong Kim (D132) [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02networkmodels-091020211449-phpapp02/85/02-Network-Models-1-320.jpg)