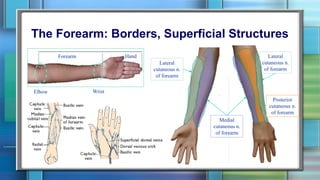
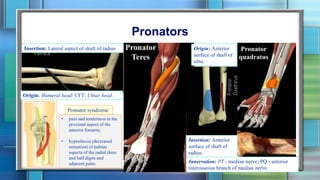
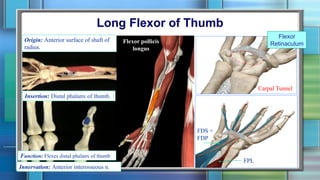
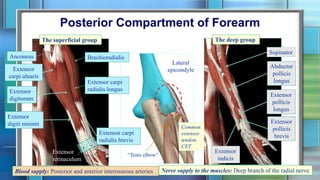
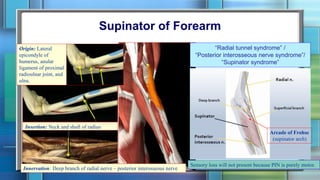
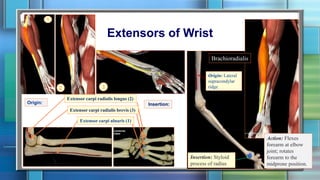
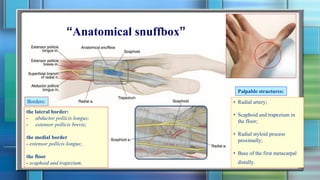
The document summarizes the anatomy of the forearm, including its bony framework, fascia, compartments, muscles, nerves and blood vessels. The forearm has two compartments - anterior and posterior. The anterior compartment contains flexor muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves and supplied by the ulnar and radial arteries. The posterior compartment contains extensor muscles innervated by the radial nerve's deep branch and posterior interosseous nerve. Common injuries include fractures of the distal forearm bones like the scaphoid.