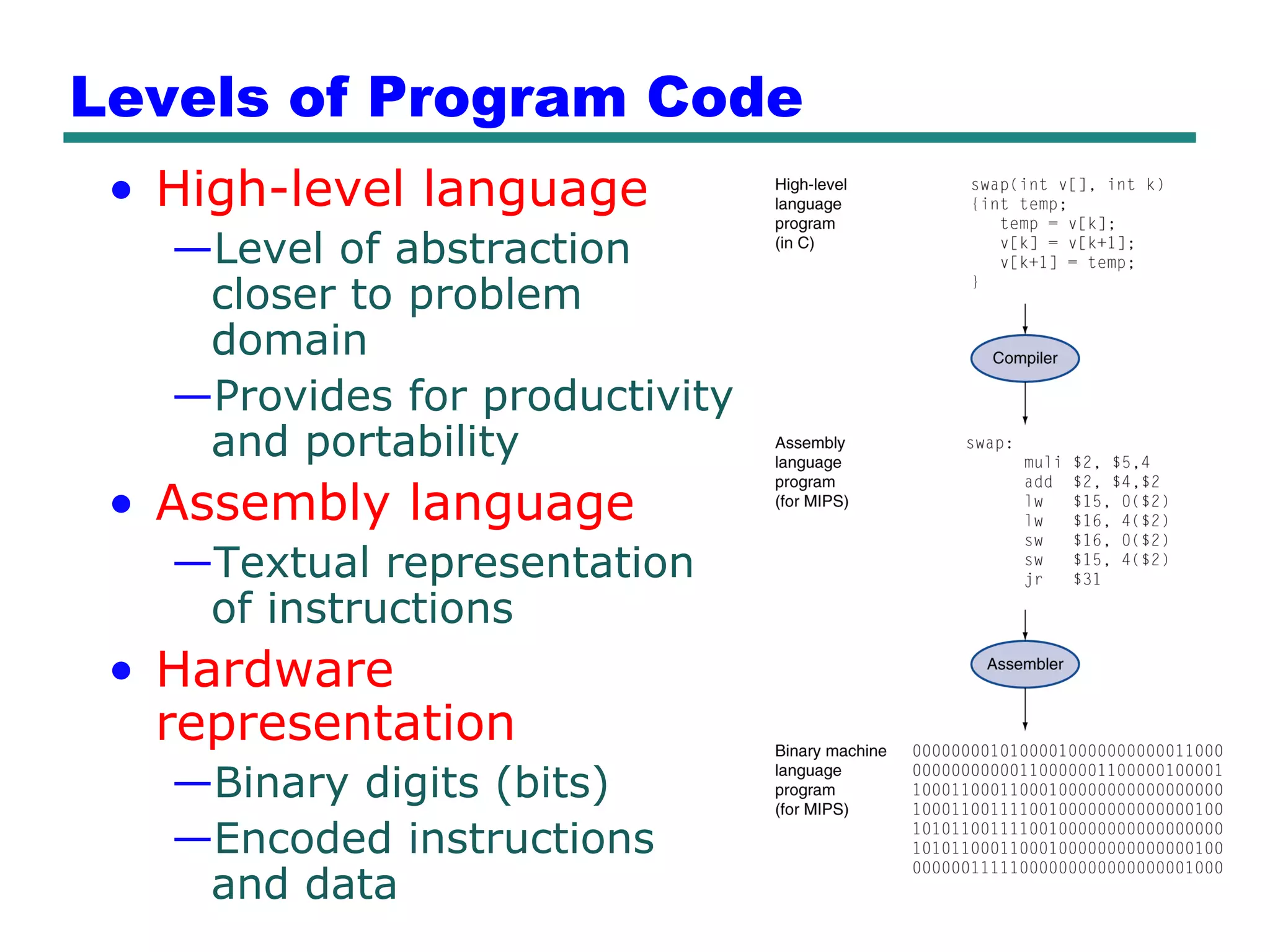
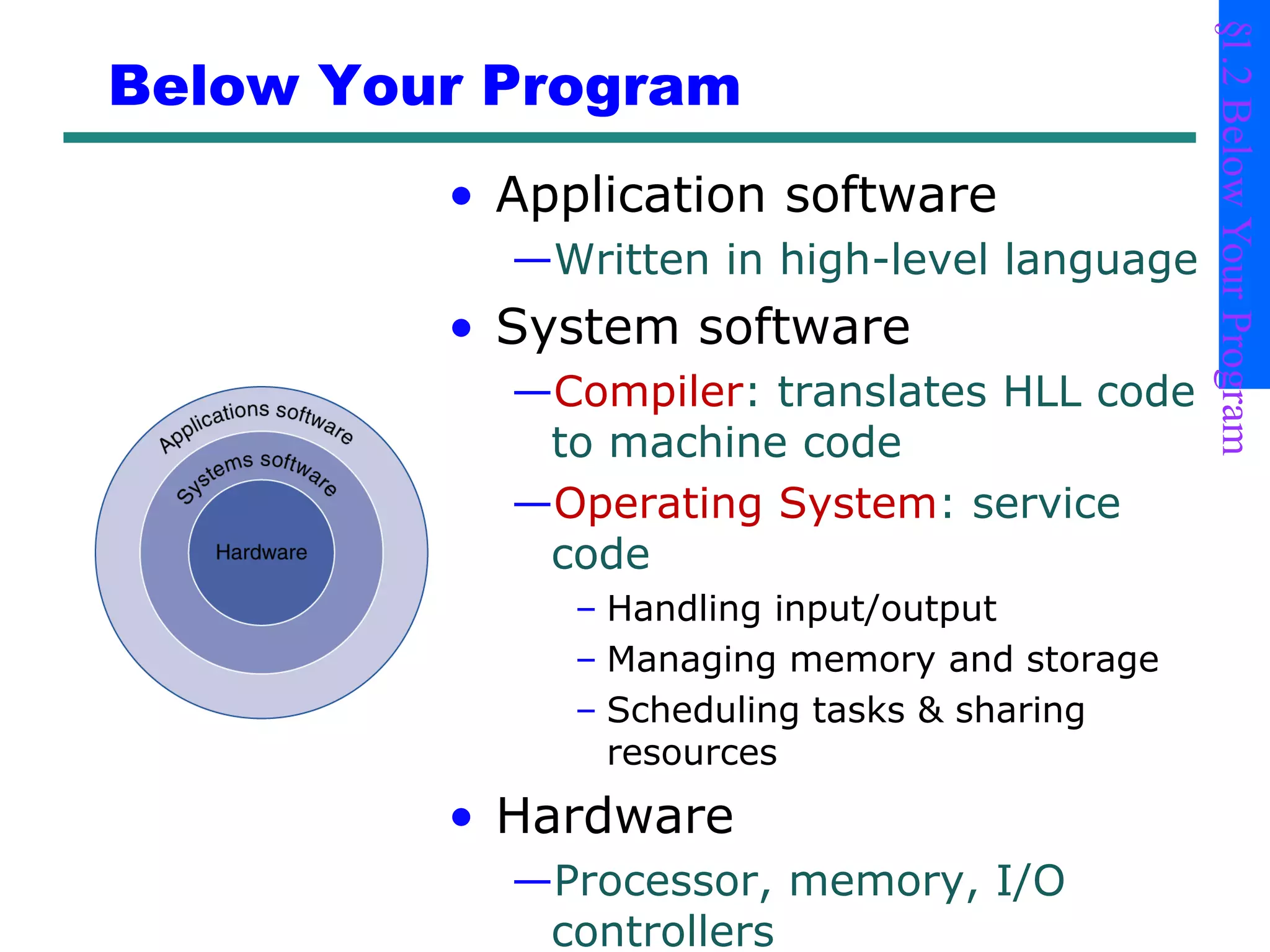
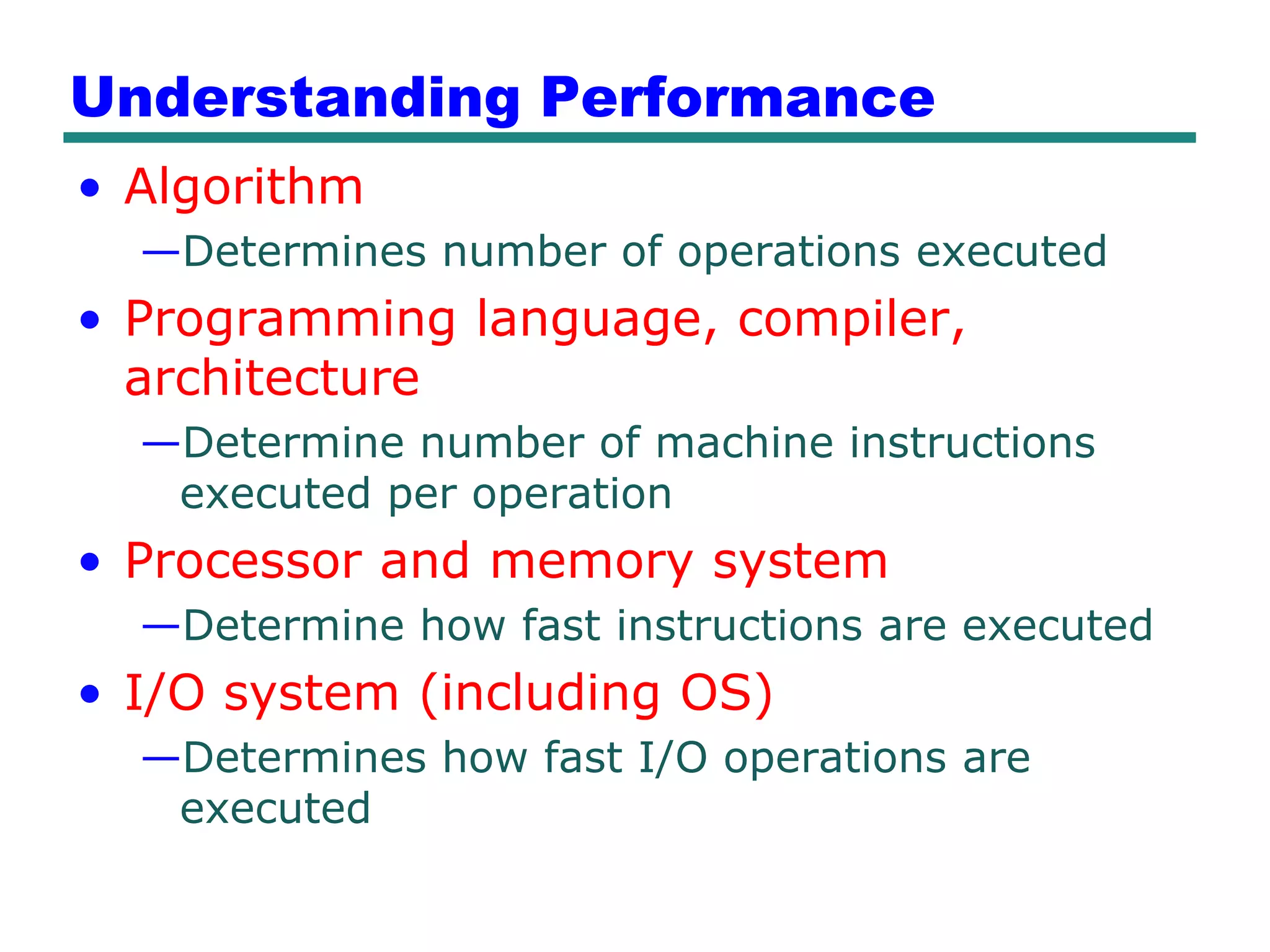
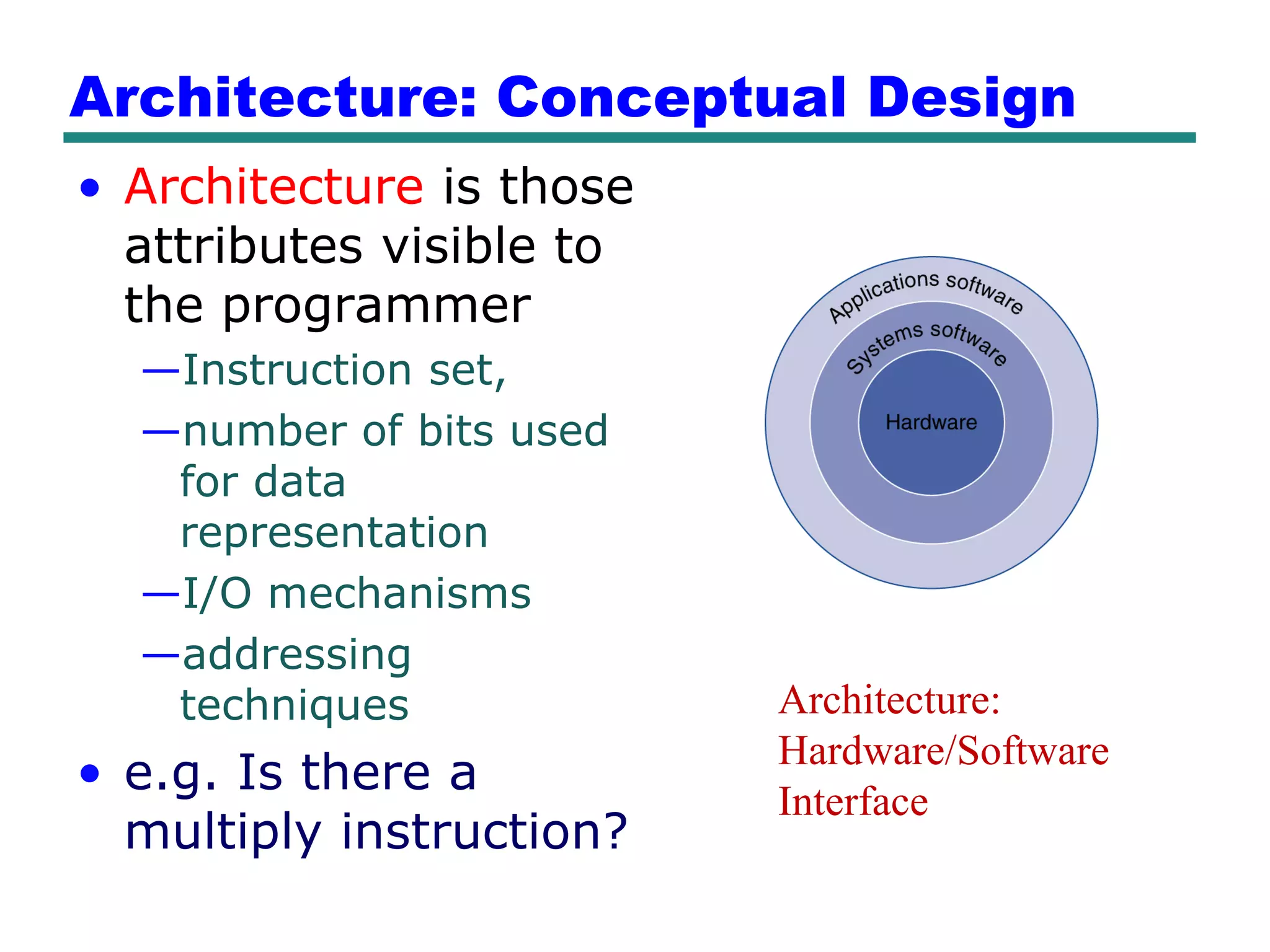
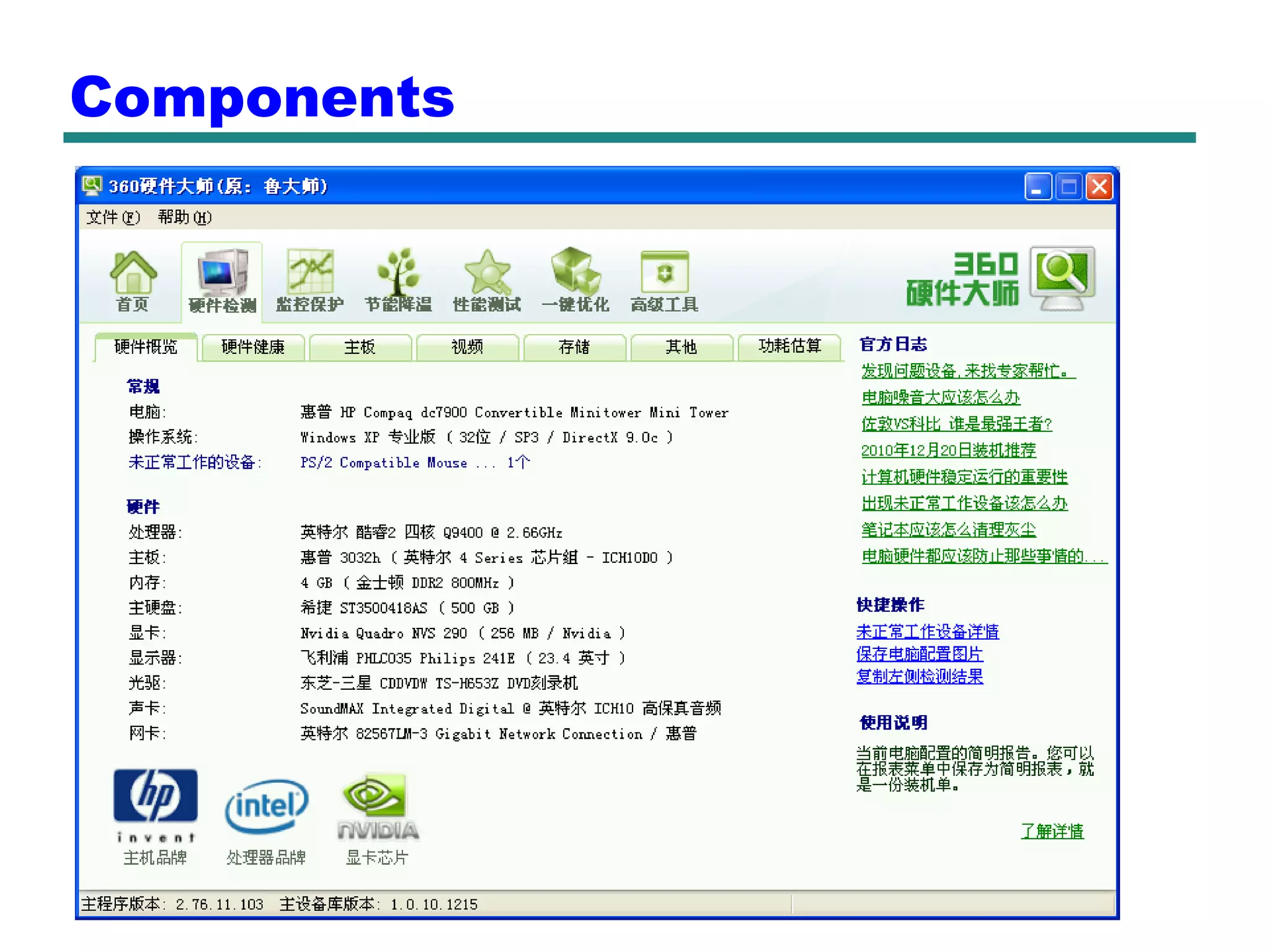
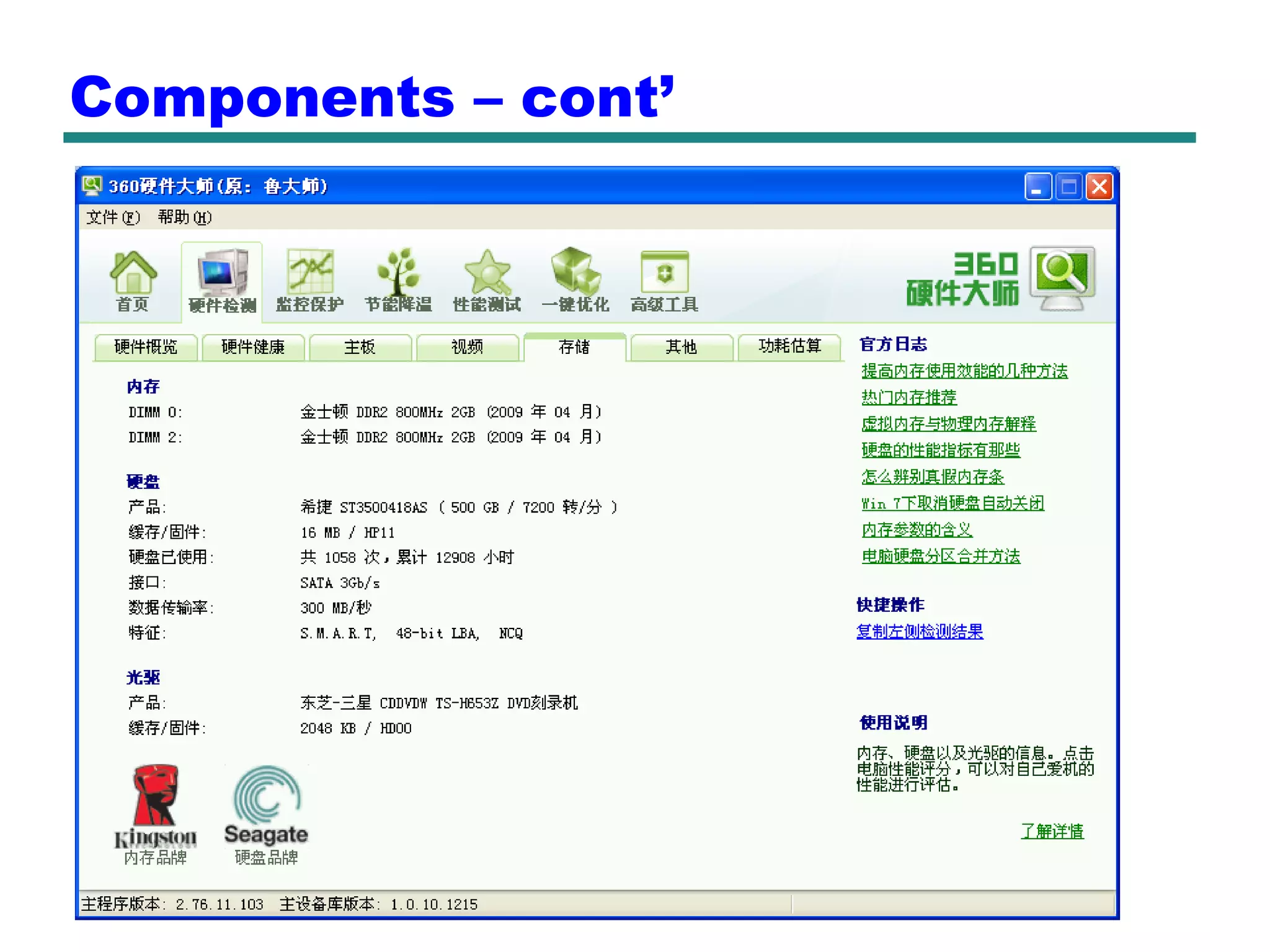
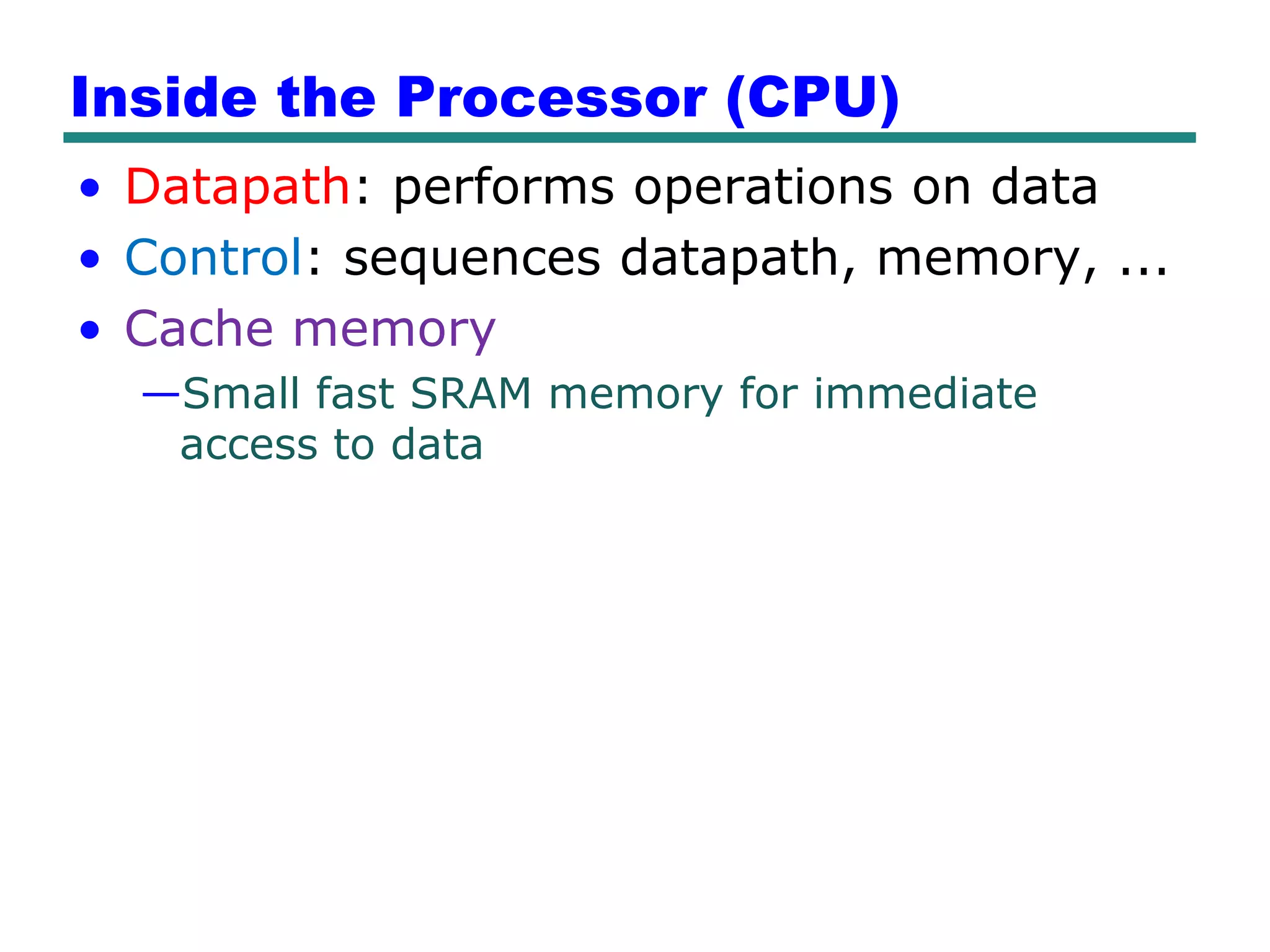
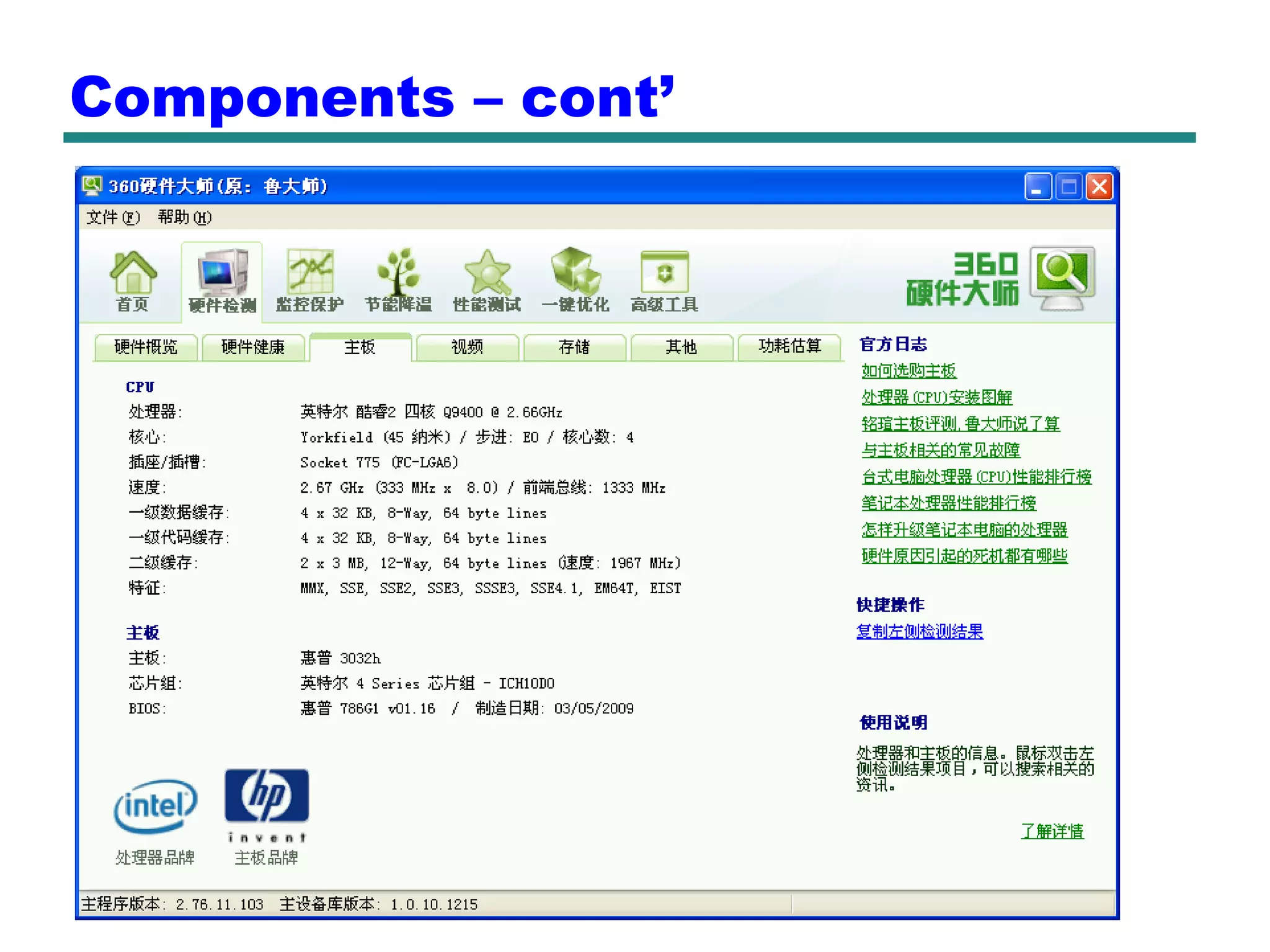
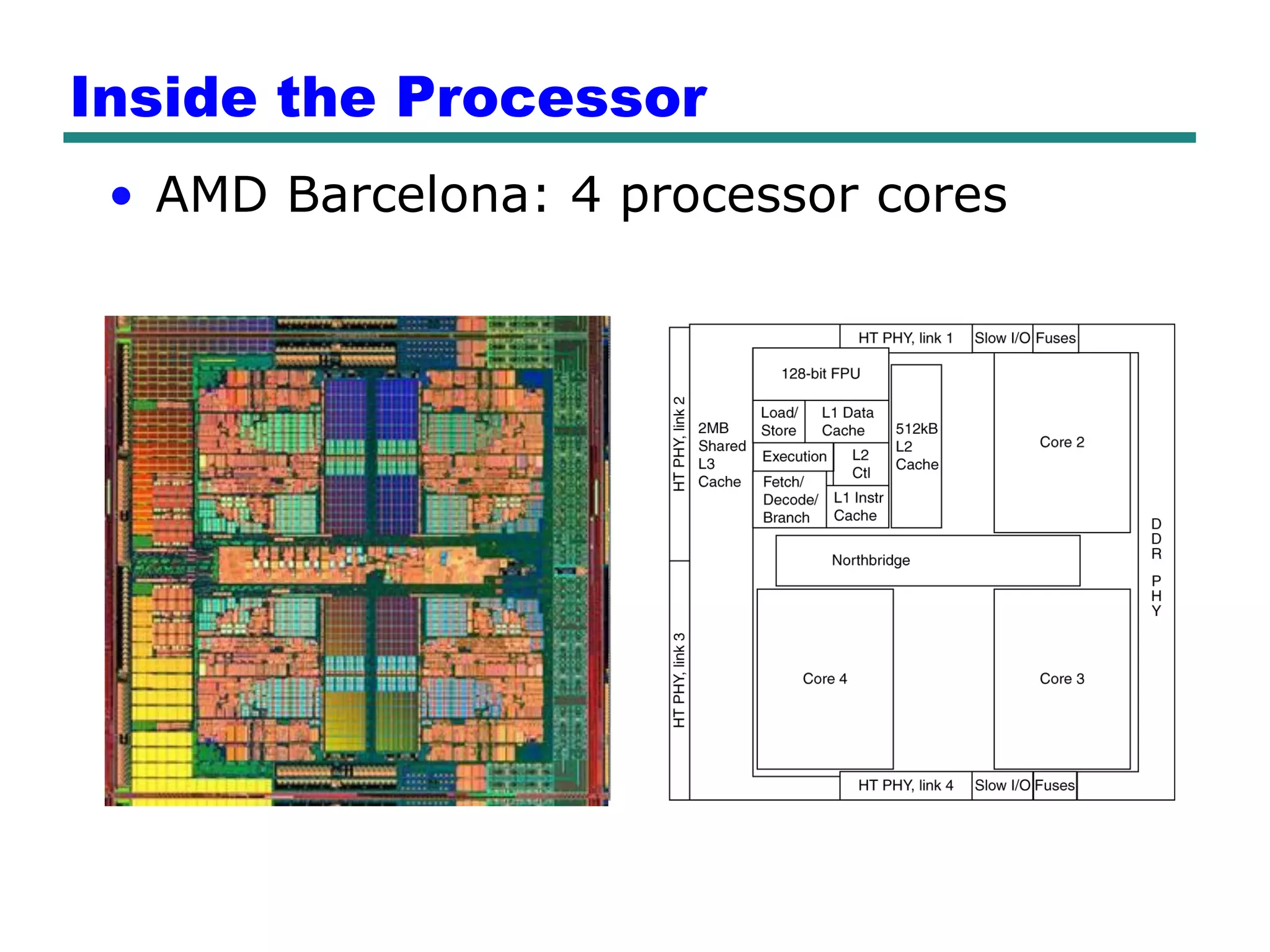
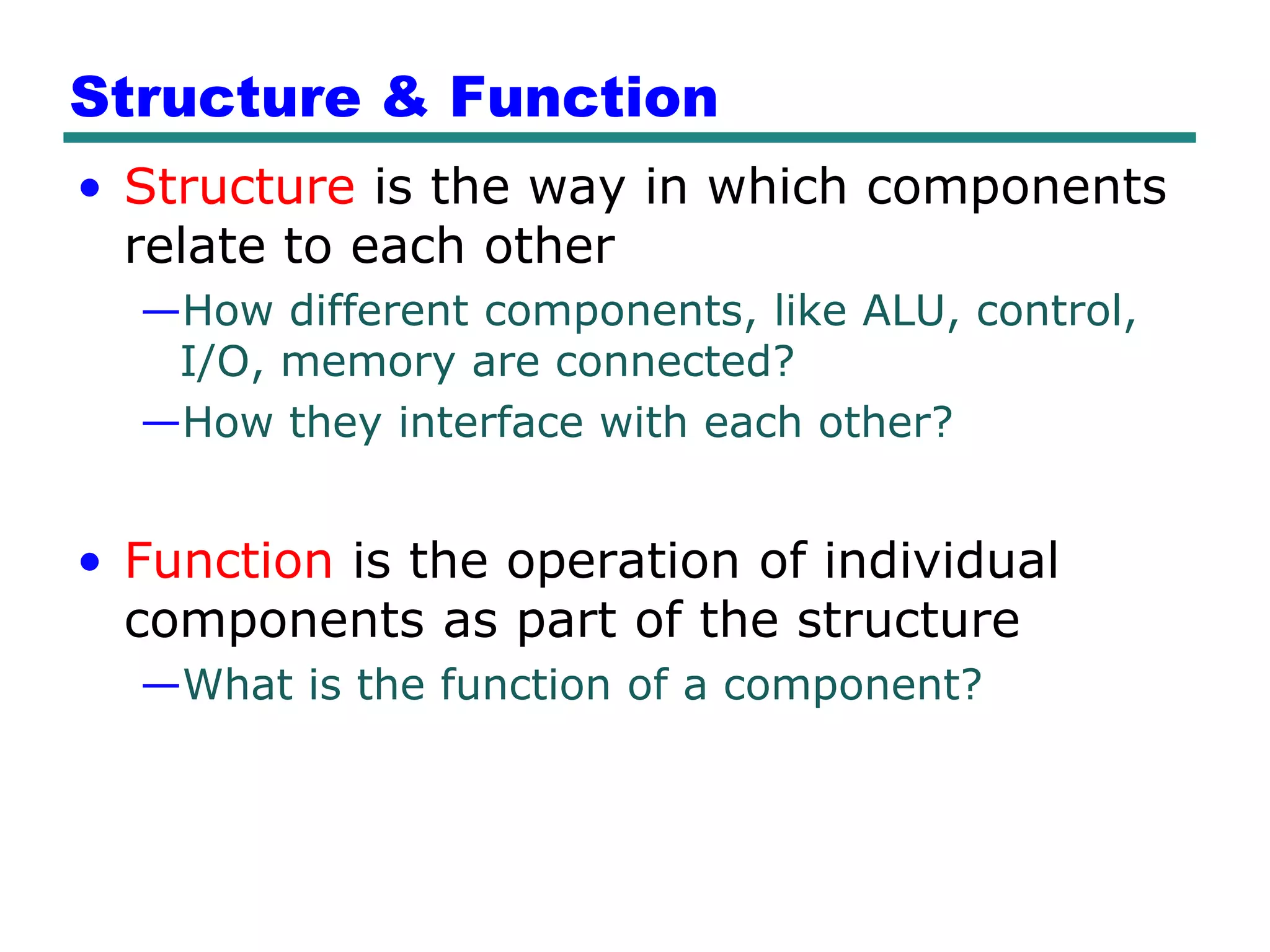
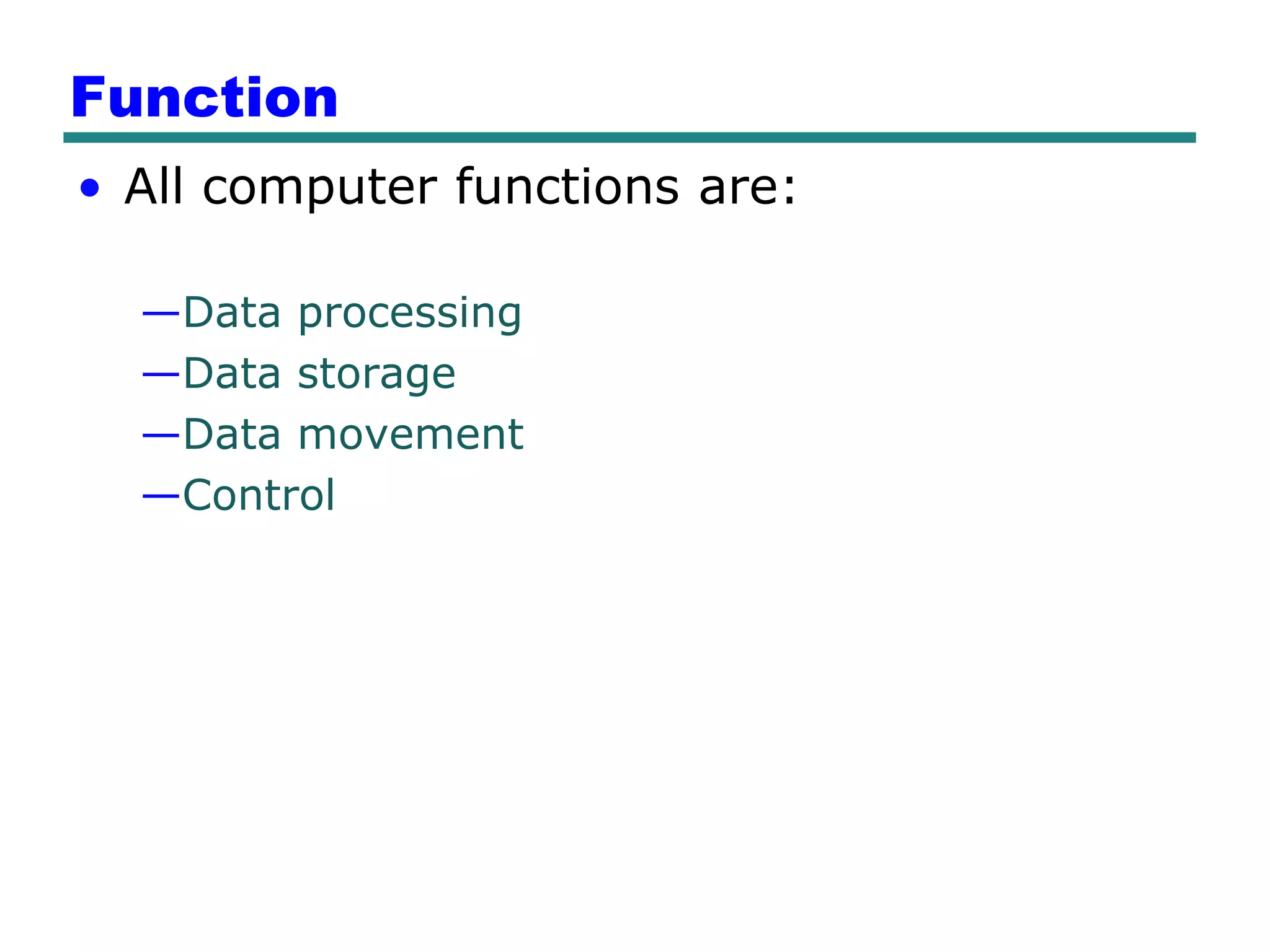
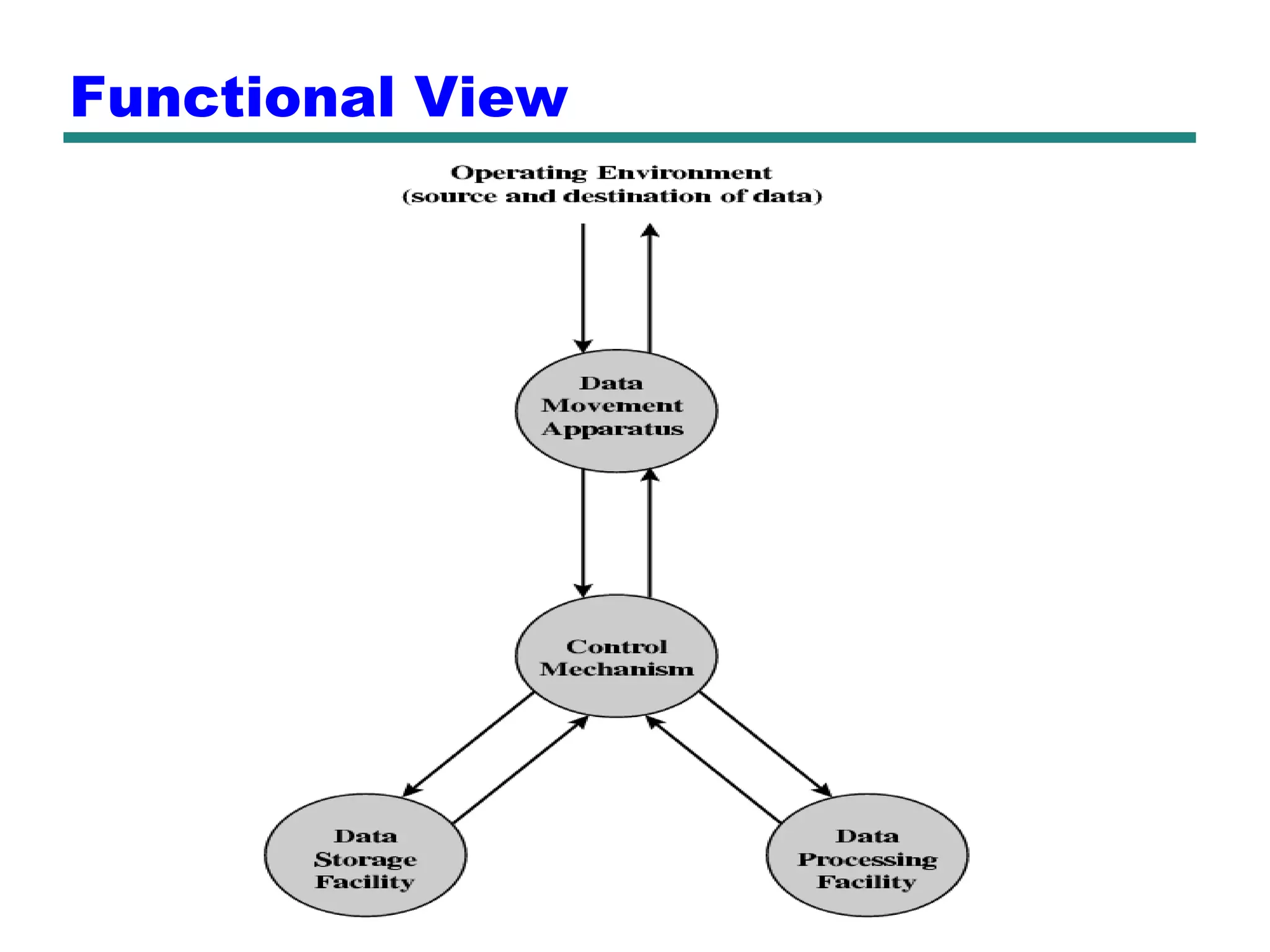
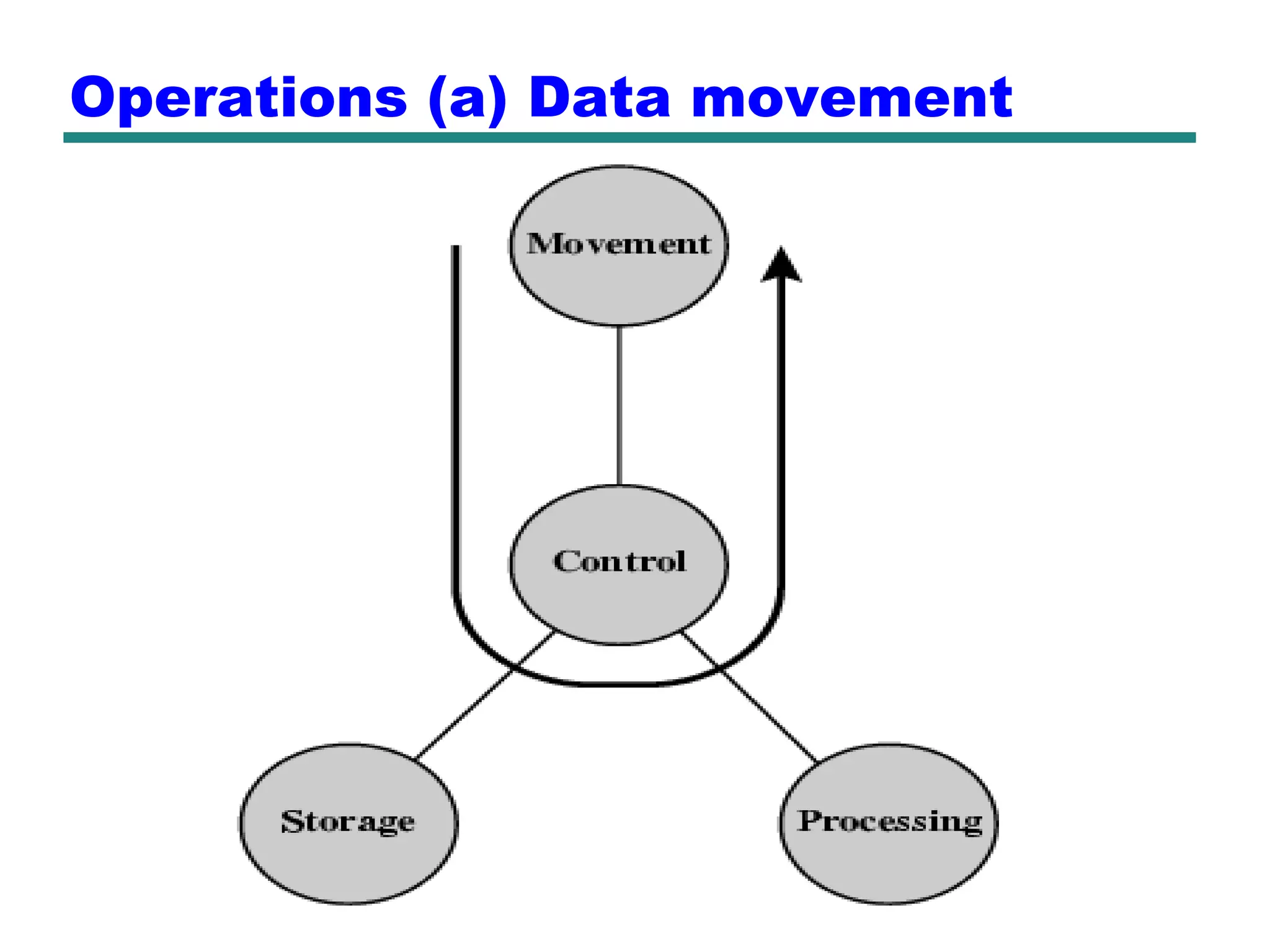
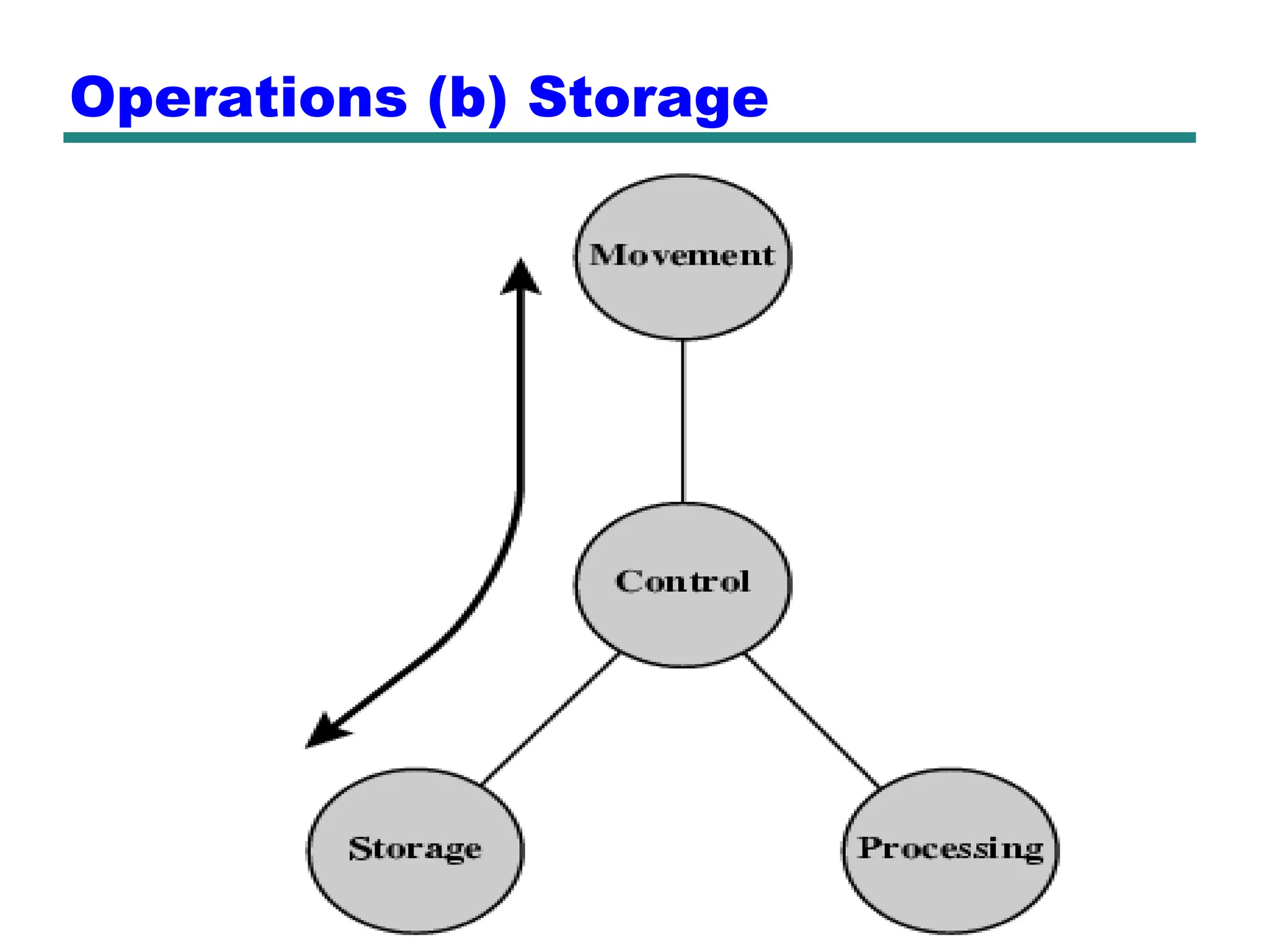
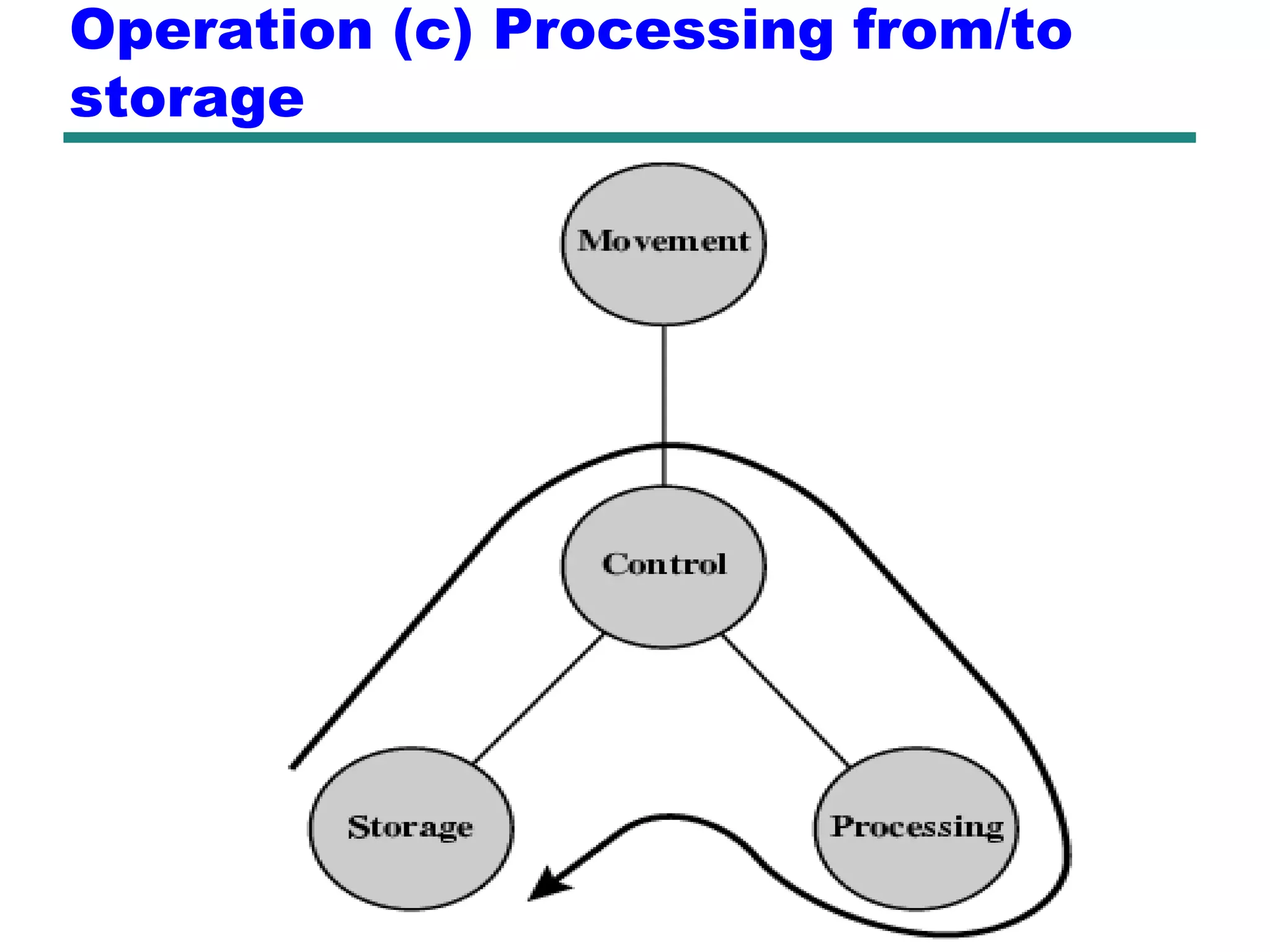
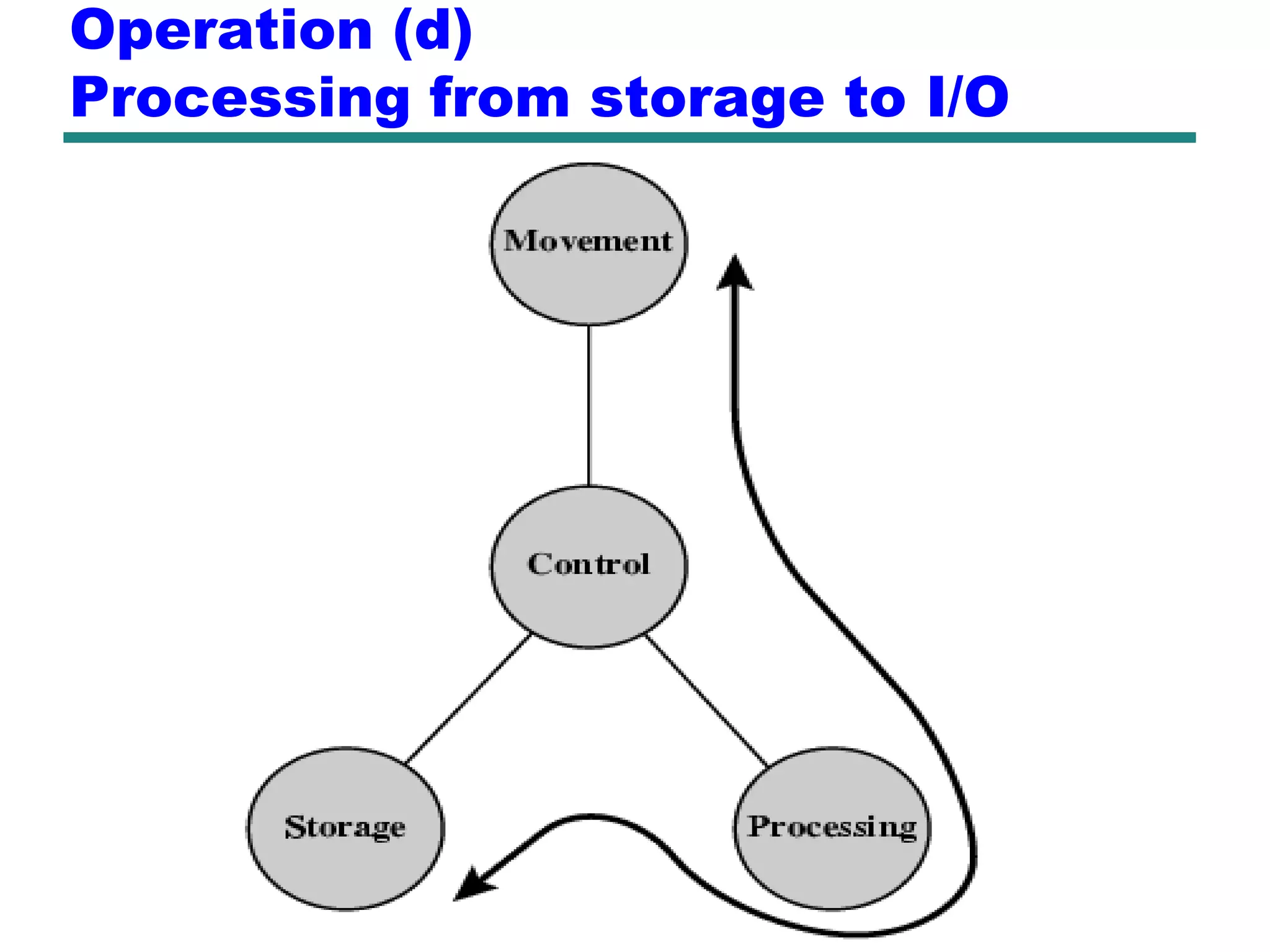
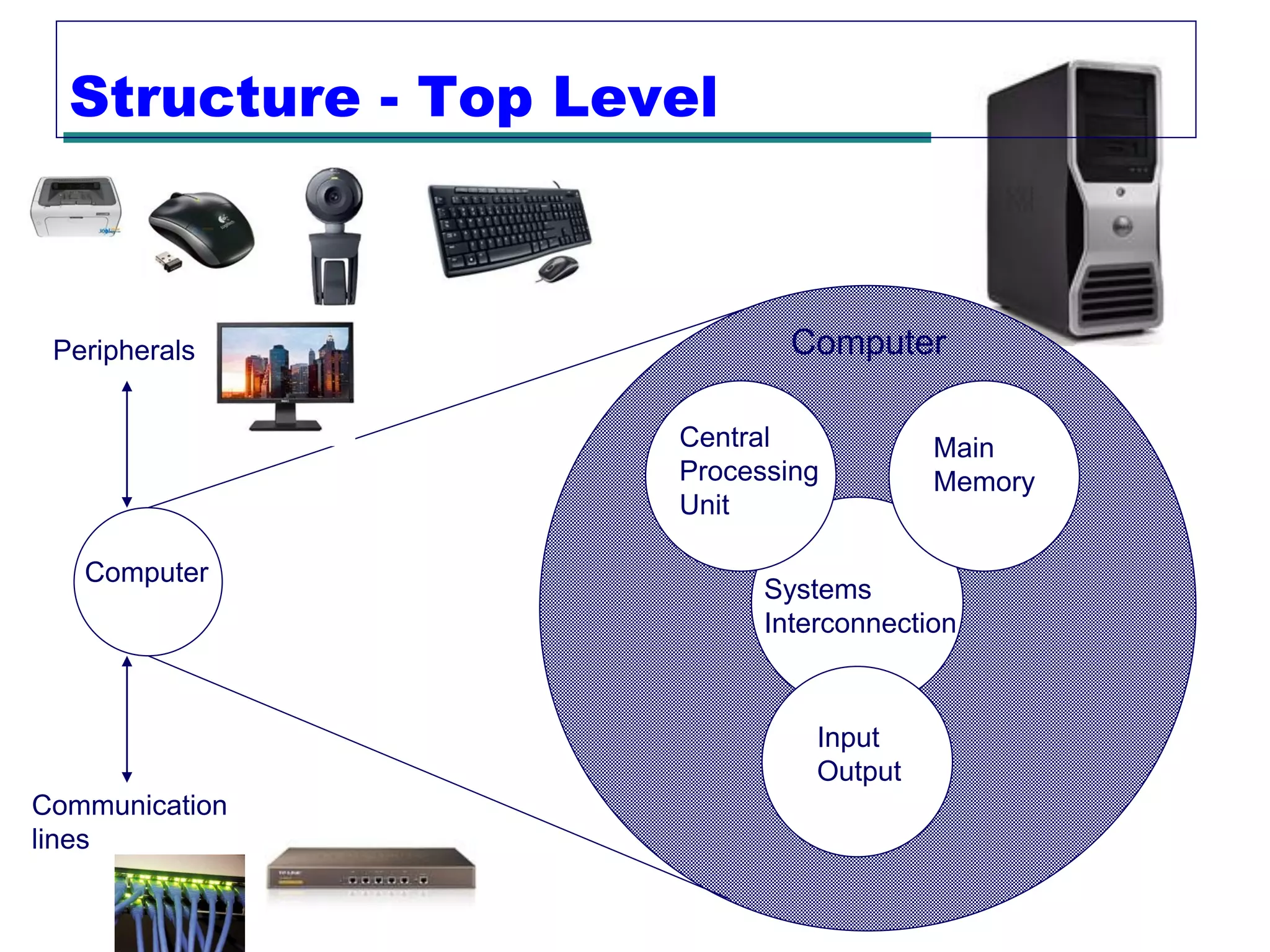
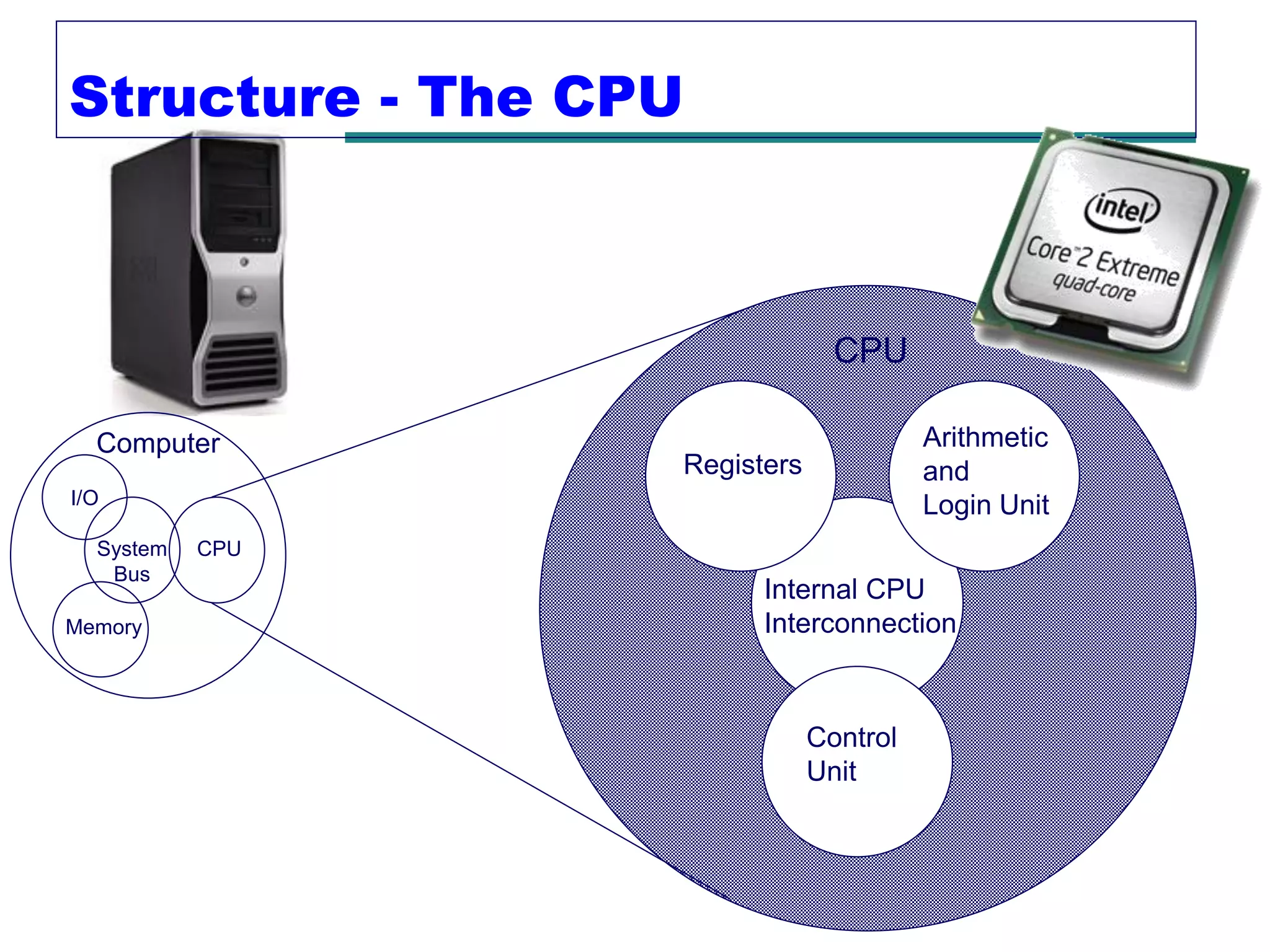
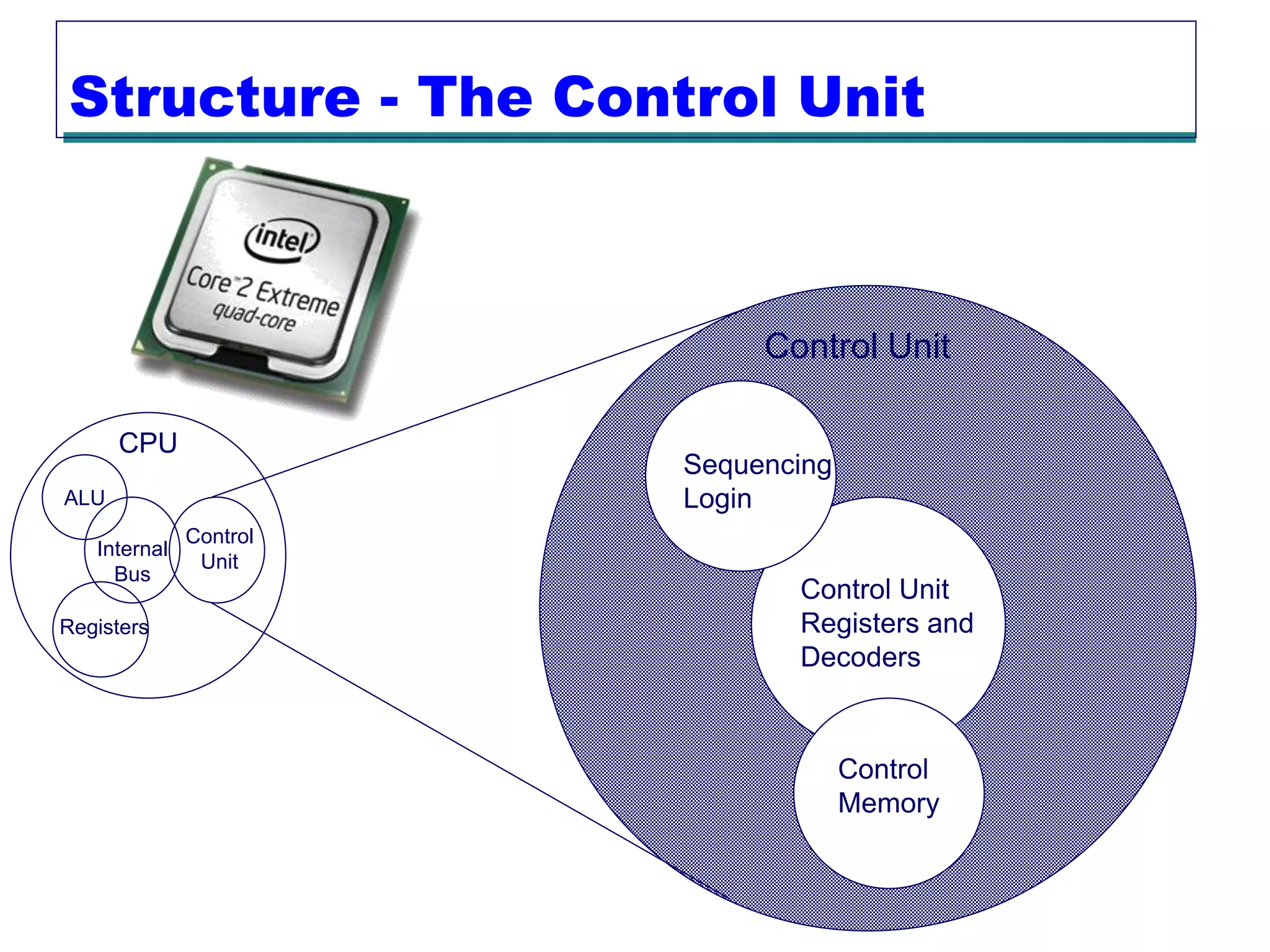
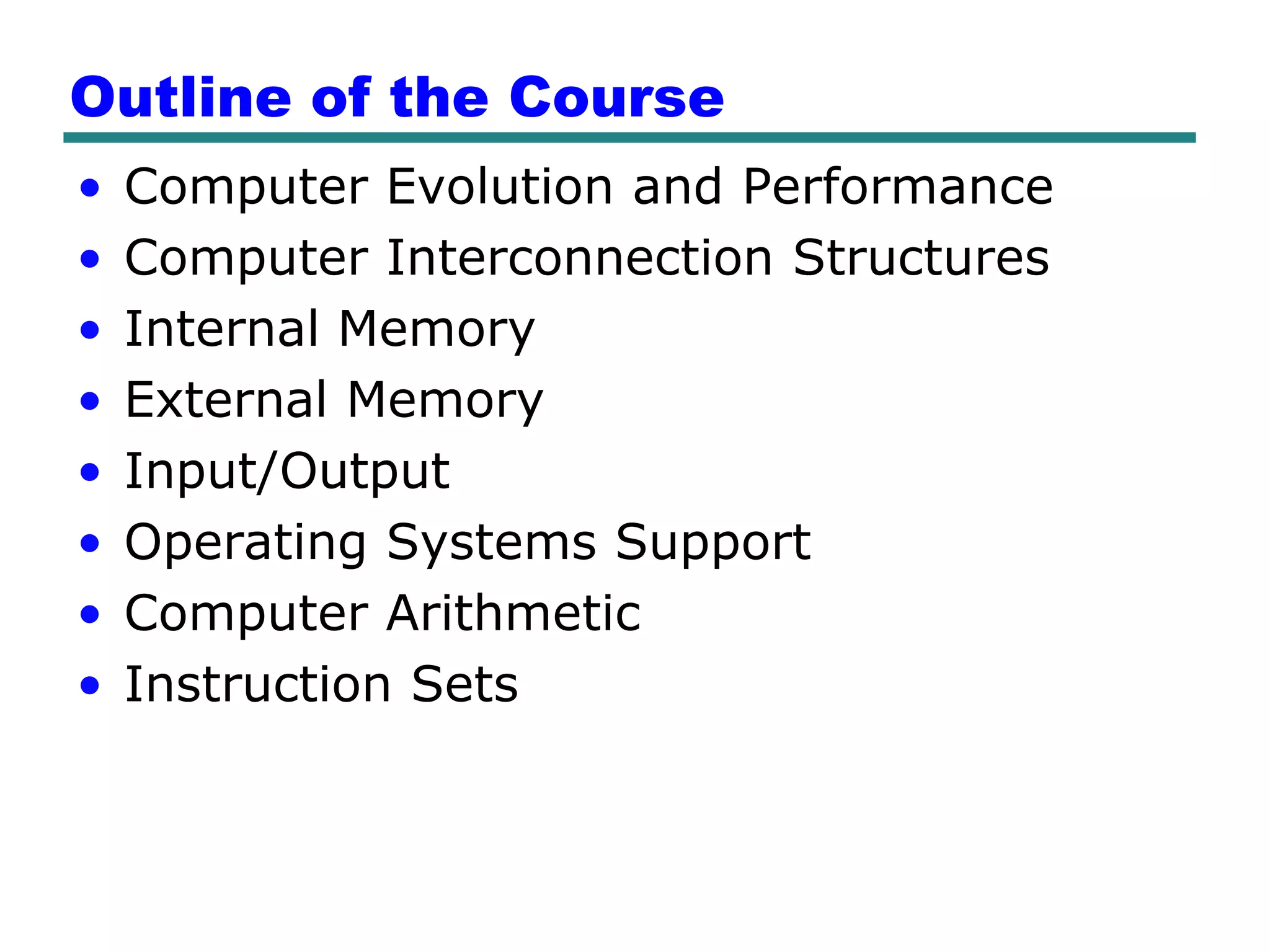
This document provides an introduction and overview of computer organization and architecture. It discusses that a computer is not intelligent on its own, but requires human programming. It describes the different levels of program code from high-level languages to machine code. It also summarizes the levels below a program including system software, compilers, operating systems, and hardware. The document outlines the course which will cover topics like CPU structure, instruction sets, memory, I/O, and parallel processing. The goal is to understand how hardware and software work together and how to write more efficient programs.