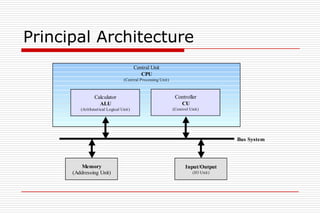
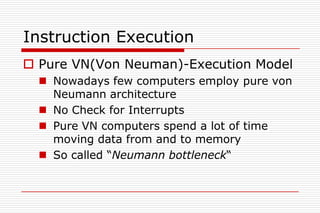
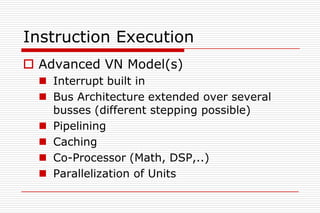
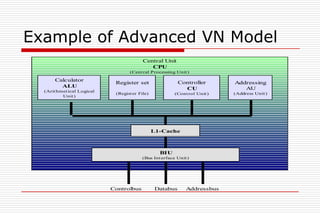
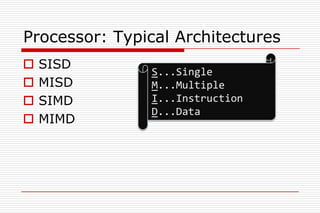
This document discusses processor architectures and their history. It begins with an overview of the history of computing from early switches to modern microprocessors. It then describes the principal Von Neumann architecture and variations like RISD, CISC, and VLIW. It also covers parallel architectures like SIMD, SISD, MISD, and MIMD. The document provides examples of different processor types and looks at potential future architectures like DNA and quantum computing.