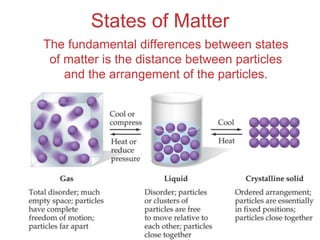
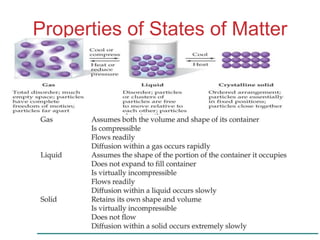
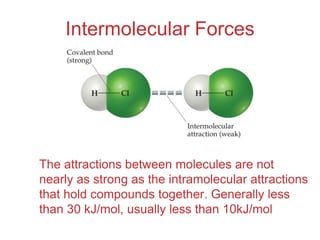
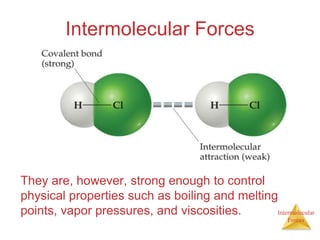
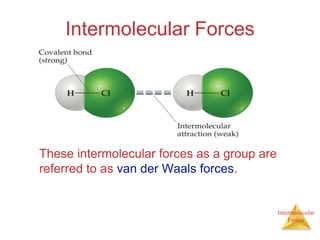
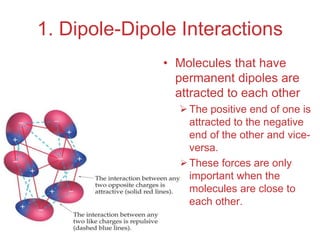
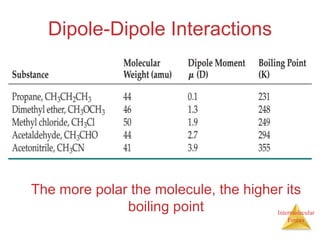
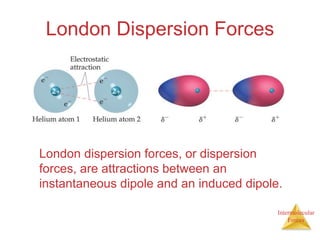
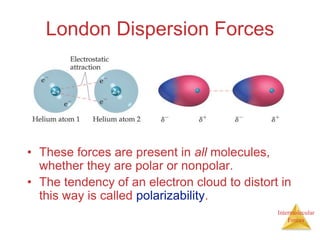
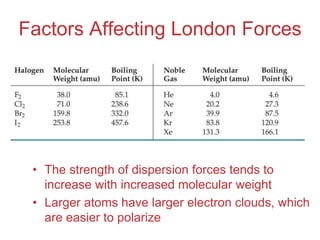
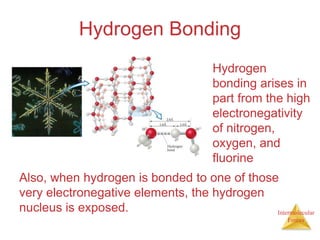
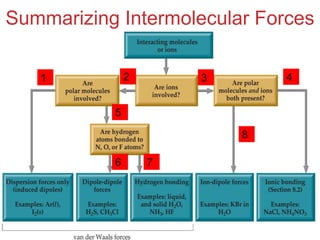
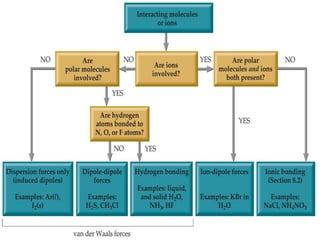
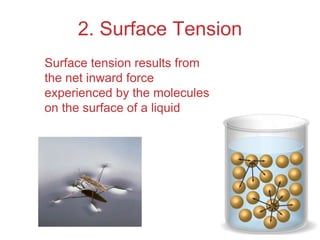
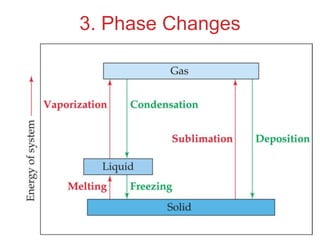
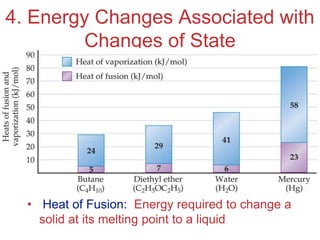
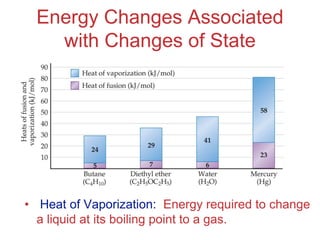
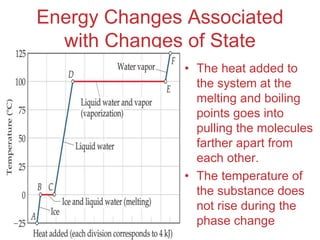
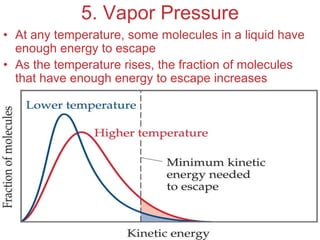
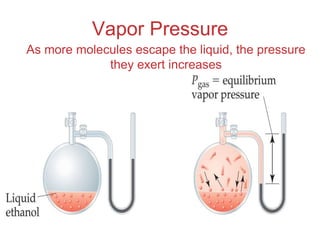
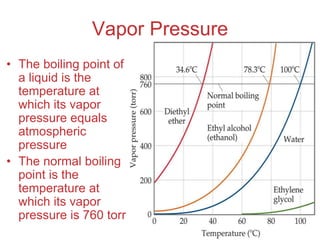
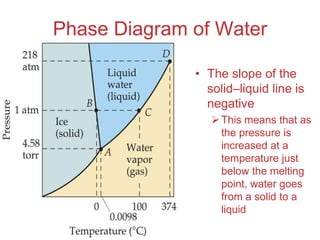
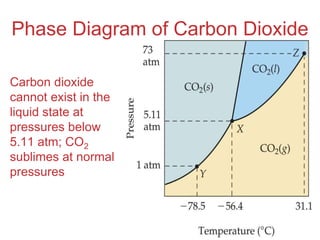
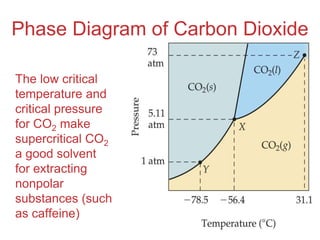
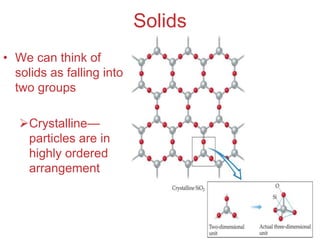
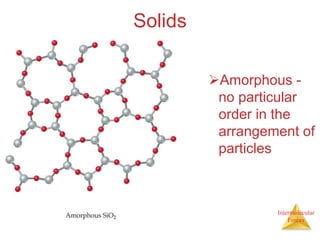
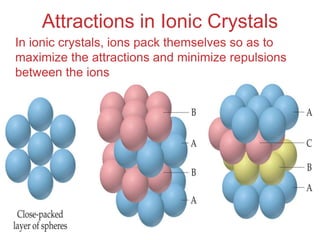
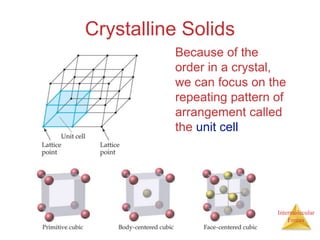
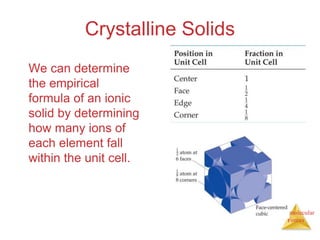
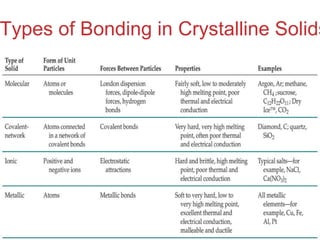
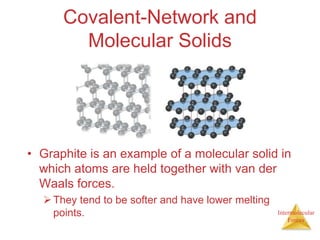
The document discusses intermolecular forces, which are the weak attractions between molecules that determine important physical properties like boiling point and viscosity. The main types of intermolecular forces are dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and London dispersion forces. These forces are responsible for controlling the phase of matter and properties of liquids and solids by influencing how close particles can pack together. Intermolecular forces determine characteristics such as the energy required for phase changes of matter.