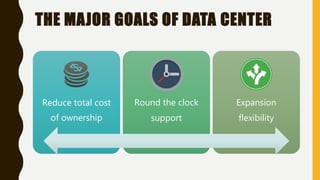
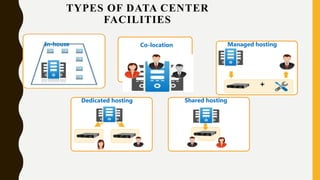
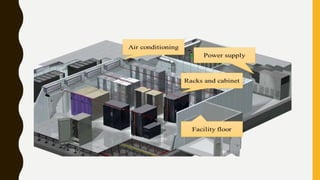
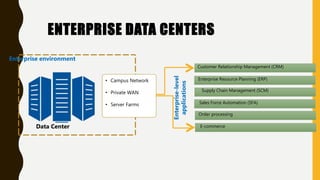
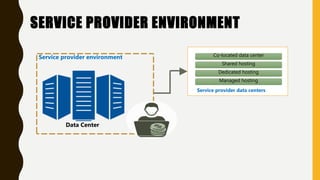
A data center contains large numbers of servers and networking equipment that support business operations. It provides reliable computing resources, redundant power and networking, and high security. Data centers are classified into tiers based on their redundancy and fault tolerance, with tier 4 being the most fault tolerant. The major goals of data centers are to reduce costs, provide 24/7 support, and allow for expansion flexibility. Data centers require environmental controls, reliable power supplies, fire protection systems, and physical security measures to protect the servers and data. Data centers can be in-house, co-location facilities, or managed by service providers to support a variety of hosting needs for enterprises.