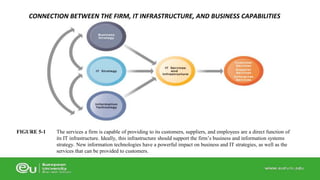
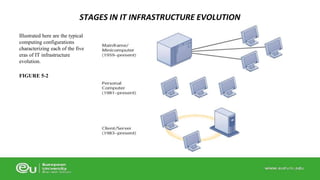
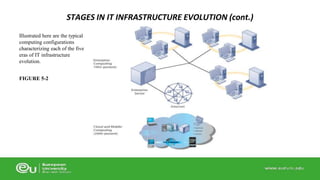
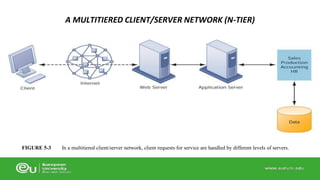
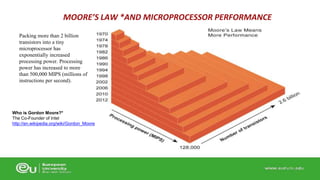
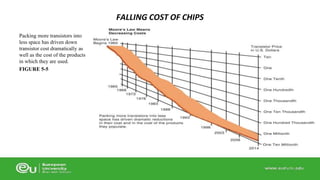
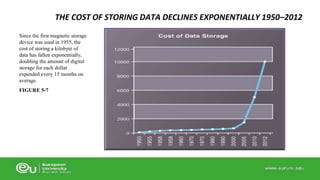
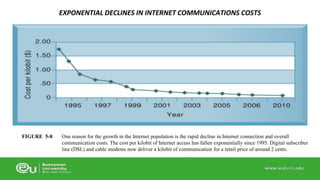
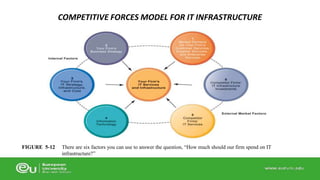
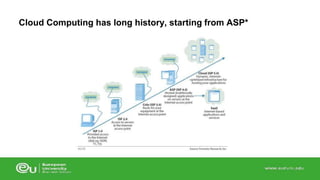
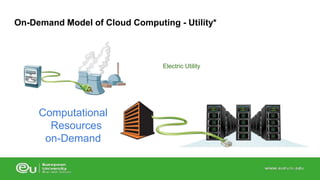
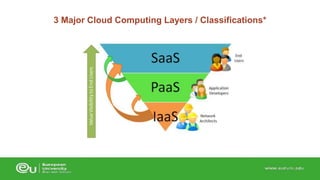
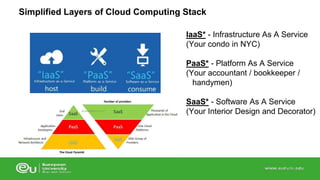
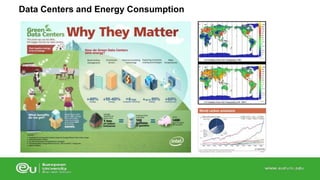
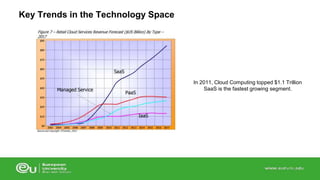
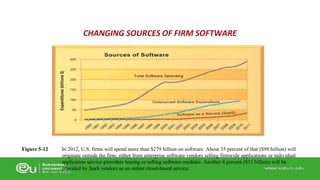
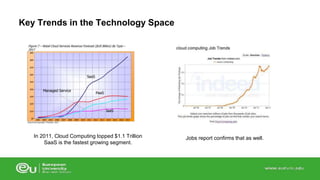
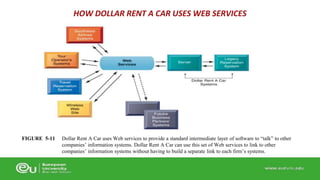
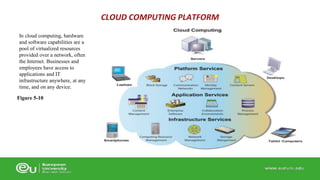
This document discusses IT infrastructure and cloud computing. It begins by defining IT infrastructure as the set of physical devices and software required to operate an enterprise, including computing platforms, telecommunications services, data management services, and application software. It then discusses the evolution of IT infrastructure from mainframes to personal computers to client/server systems to today's enterprise computing and cloud/mobile era. The document also covers technology drivers like Moore's Law, factors to consider when determining an IT budget, and provides an overview of cloud computing including its origins and value proposition.