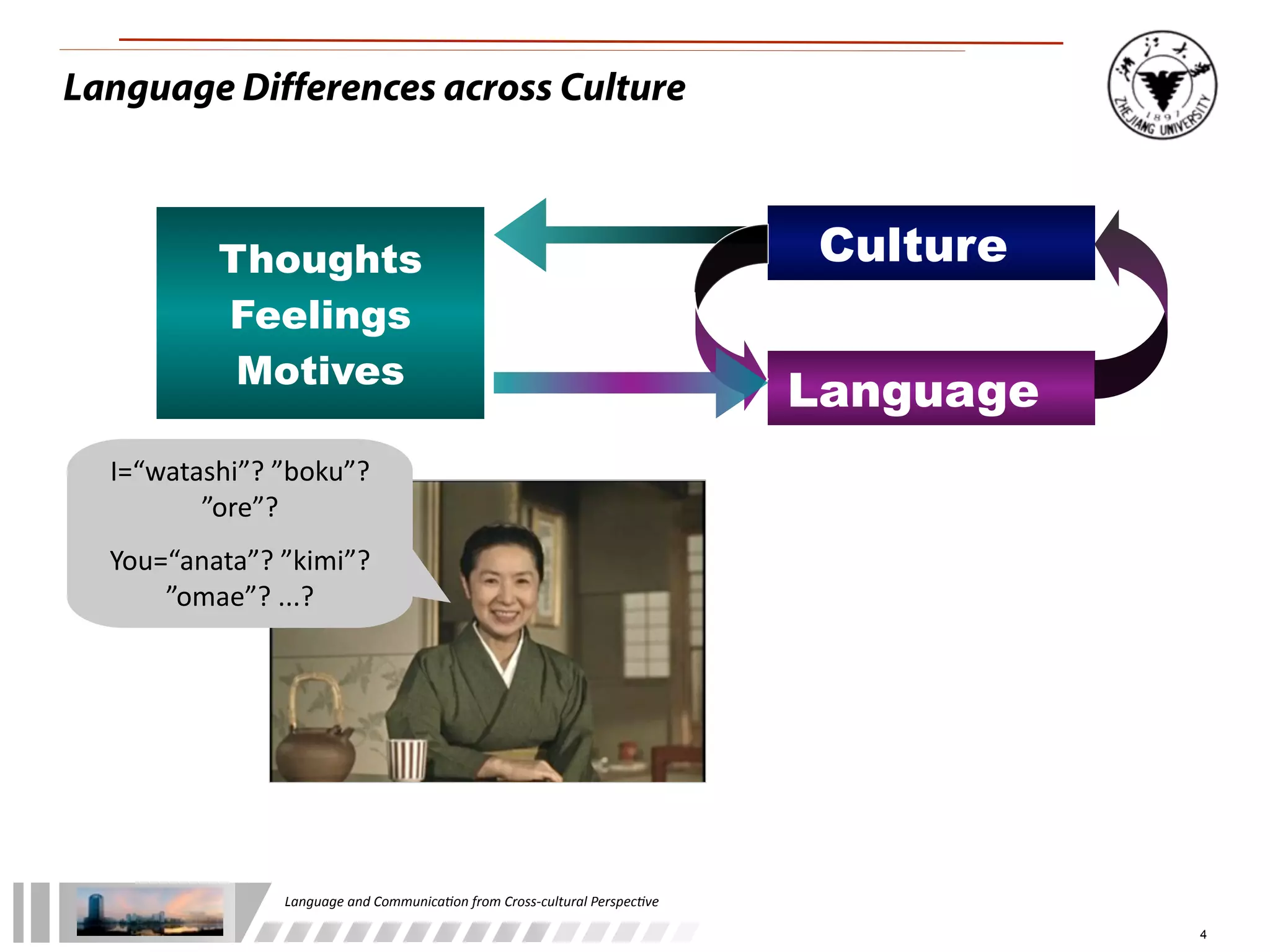
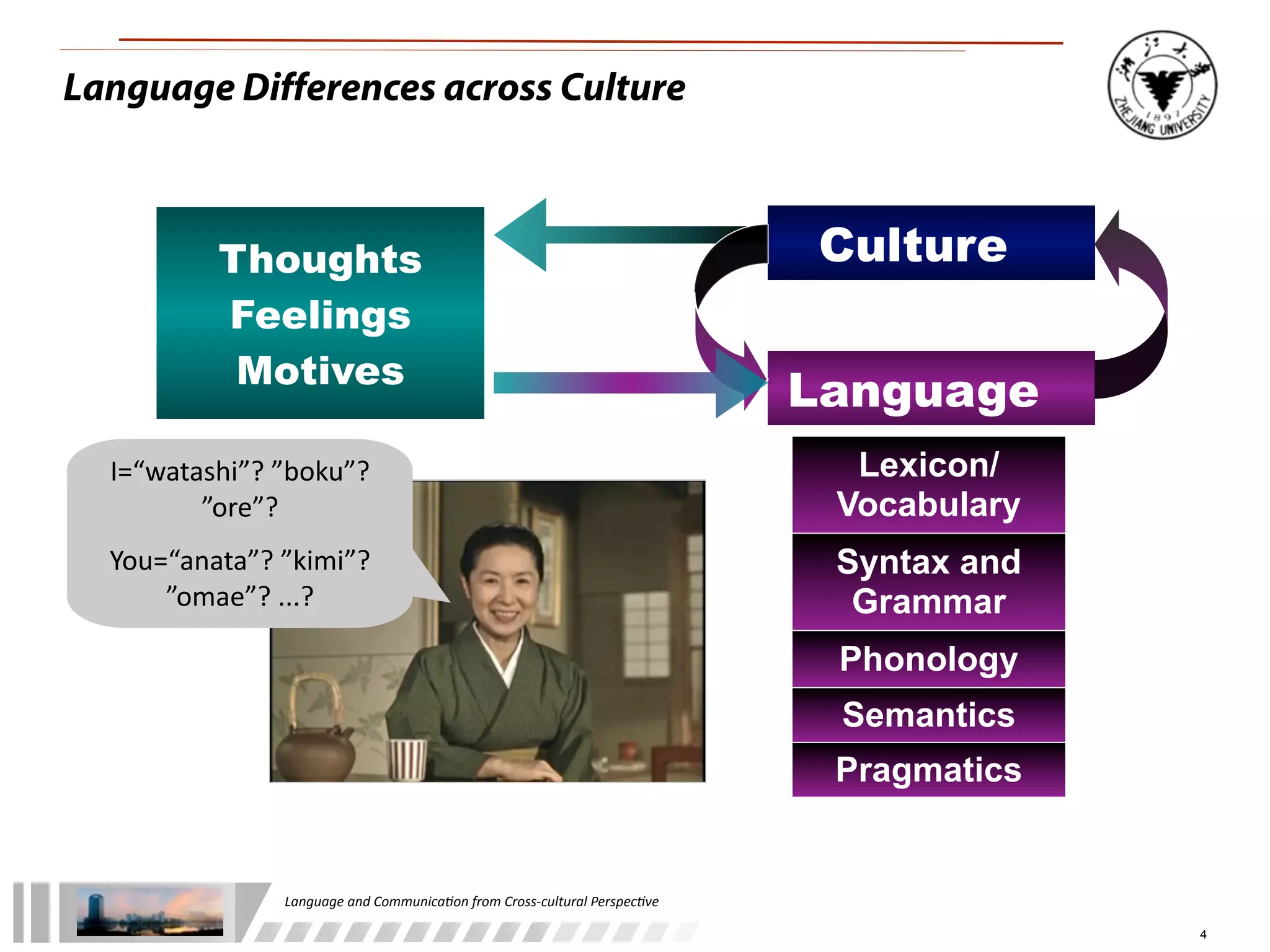
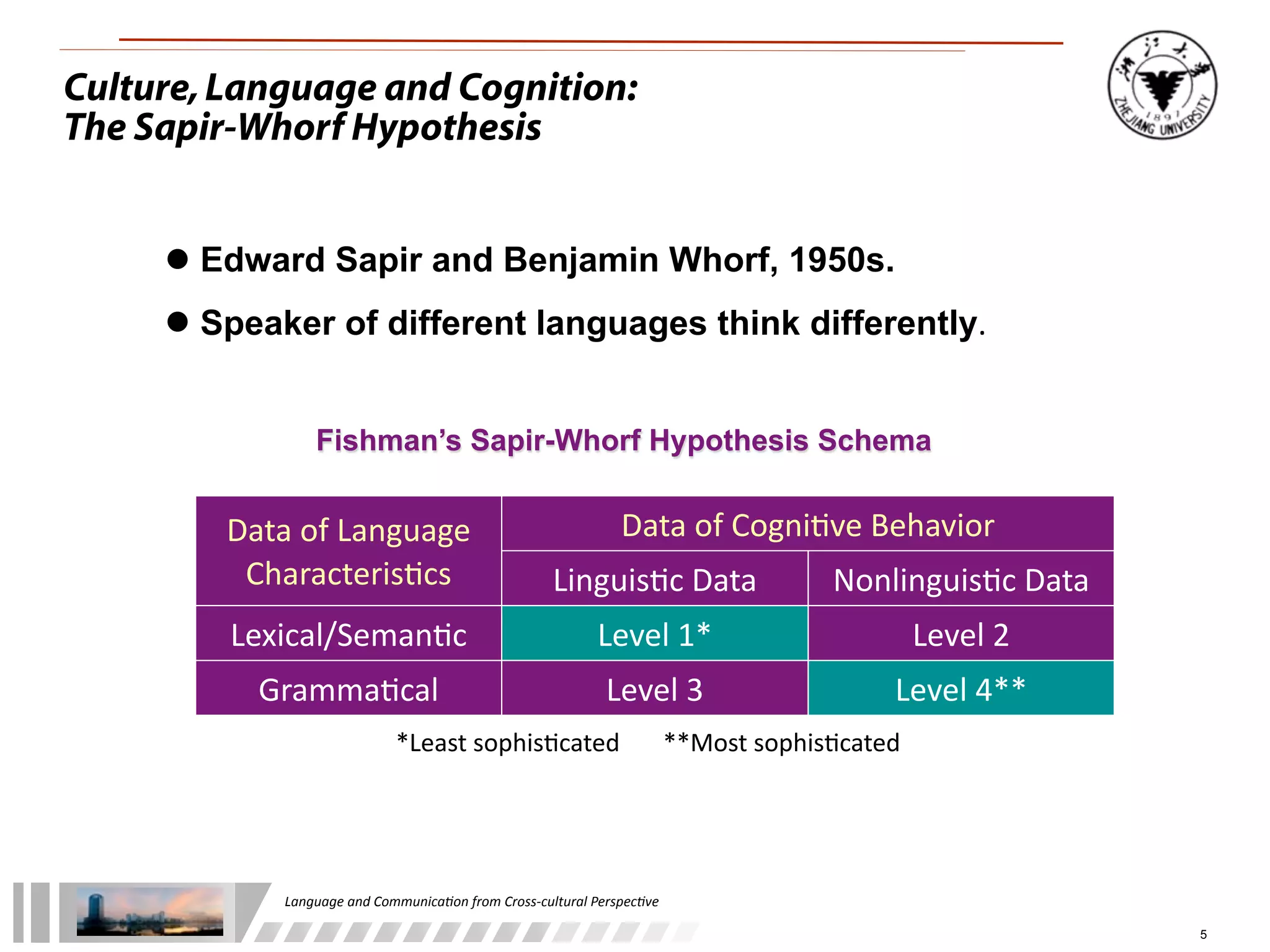
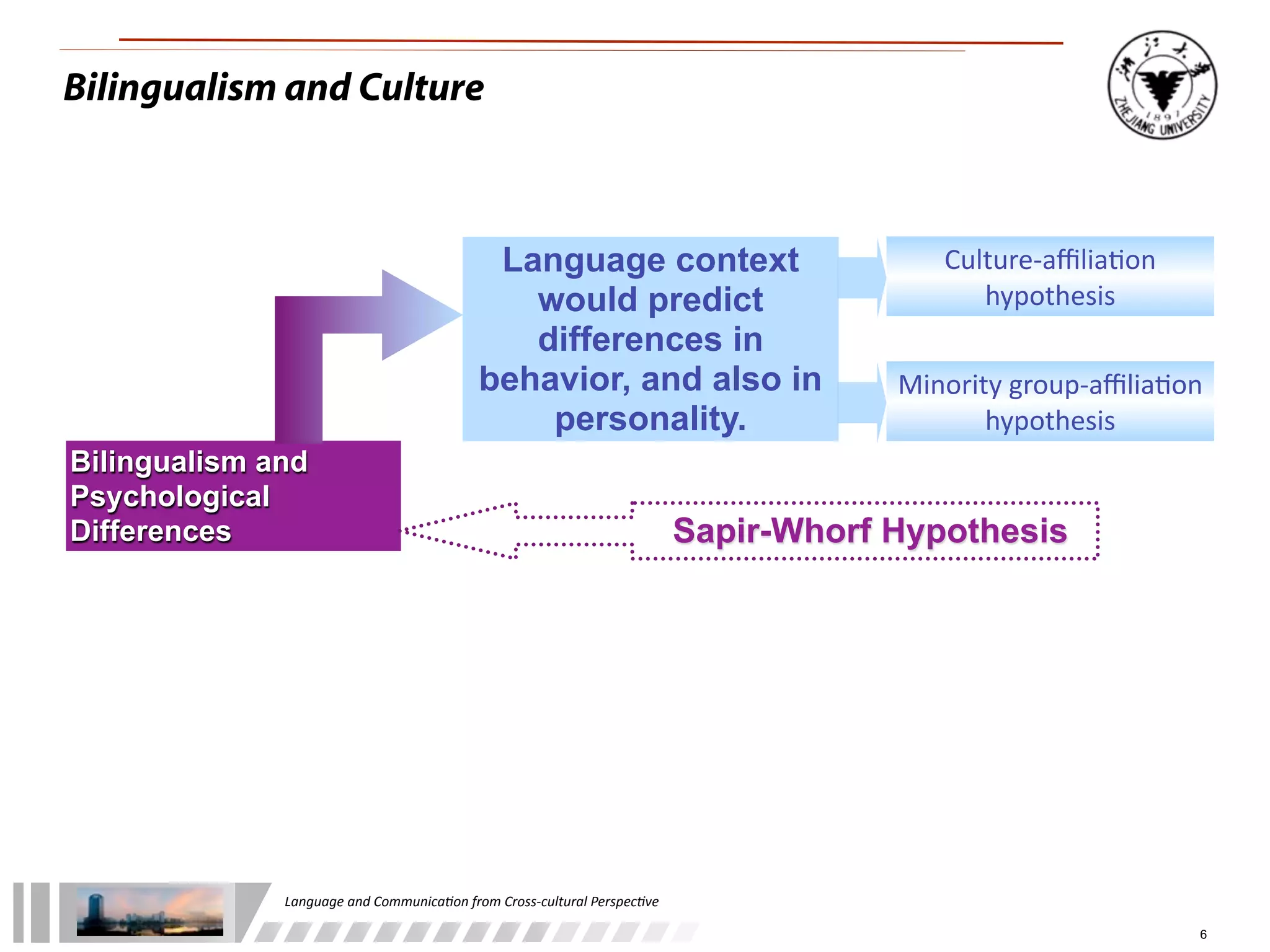
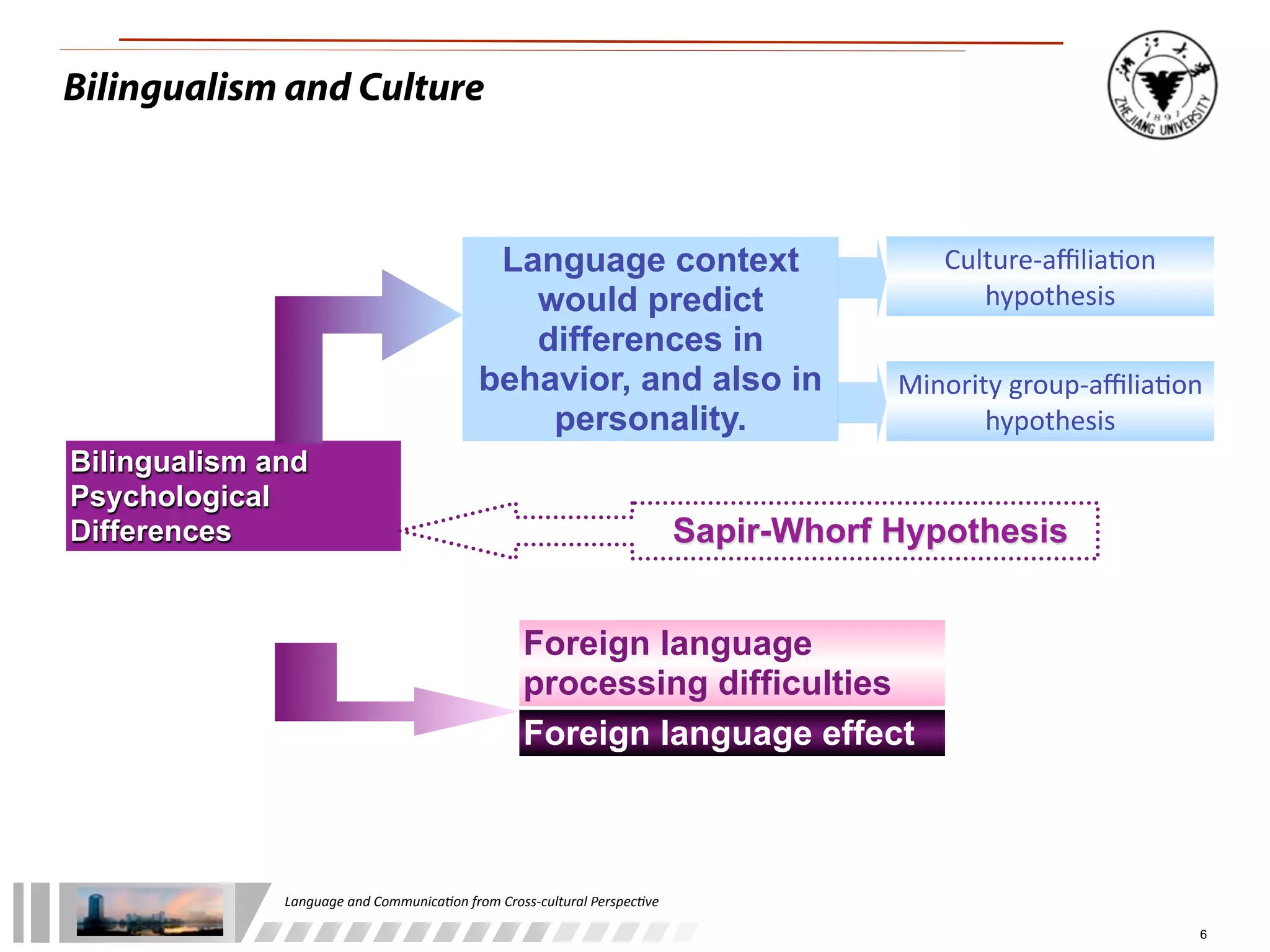
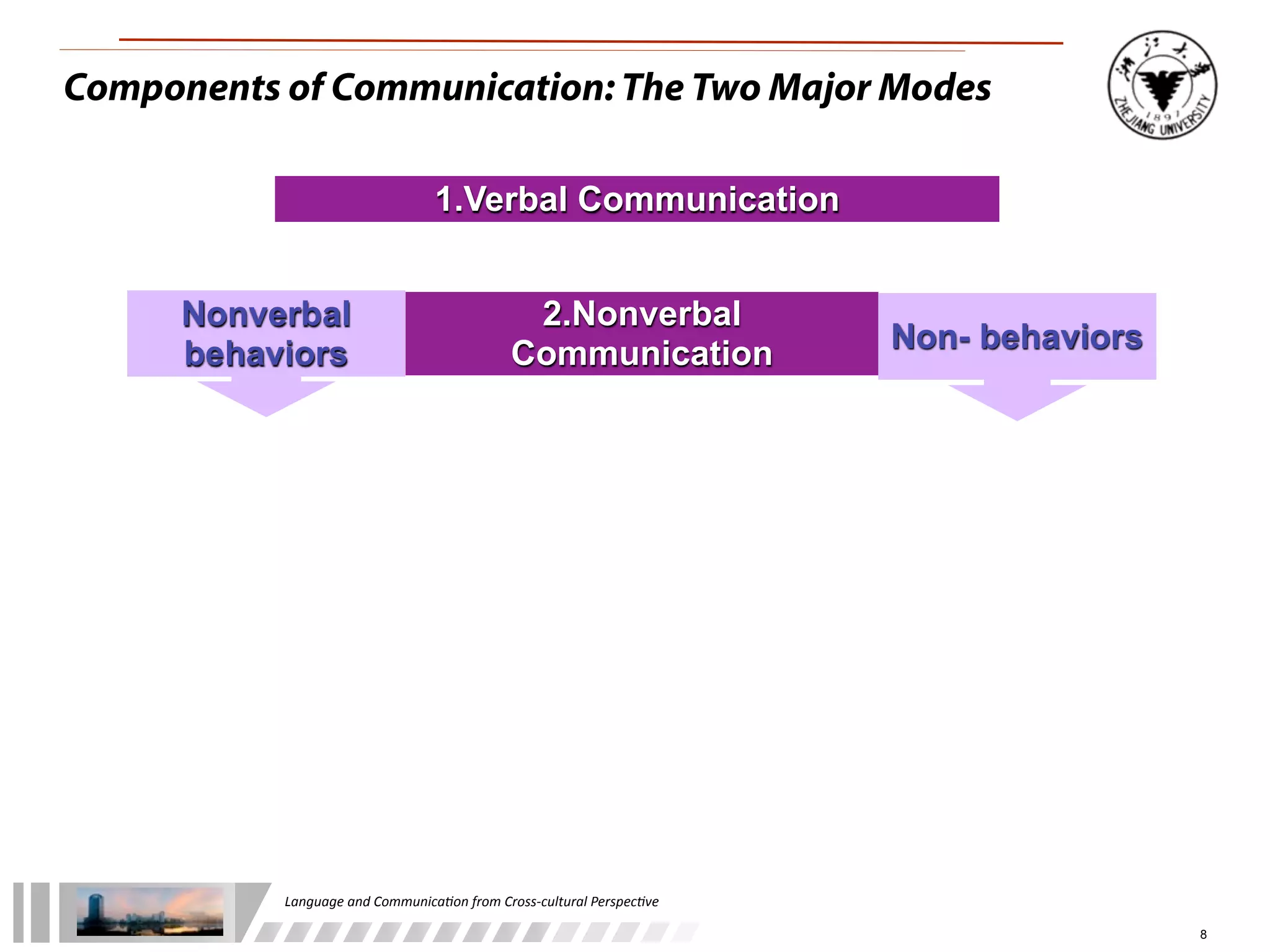
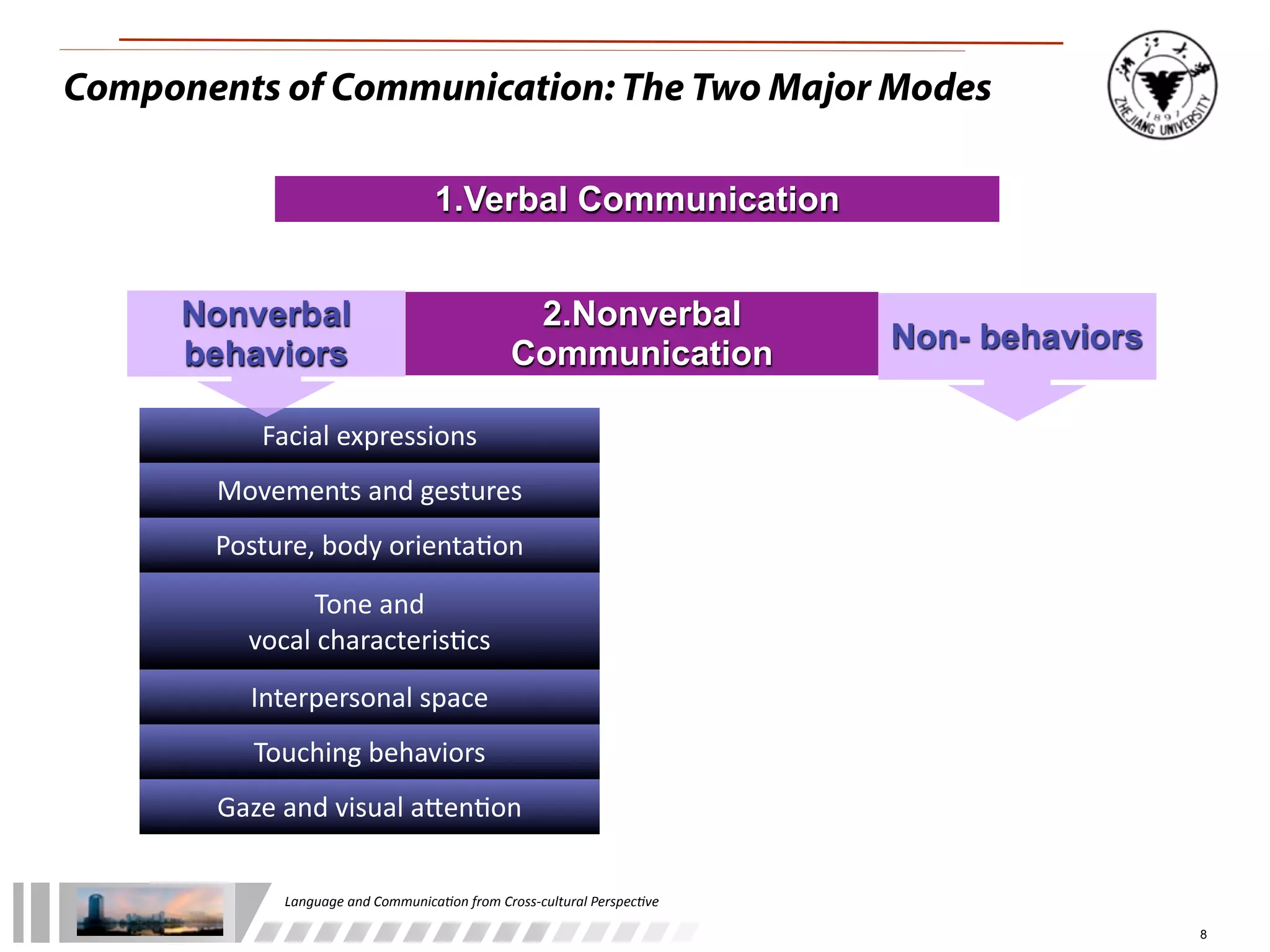
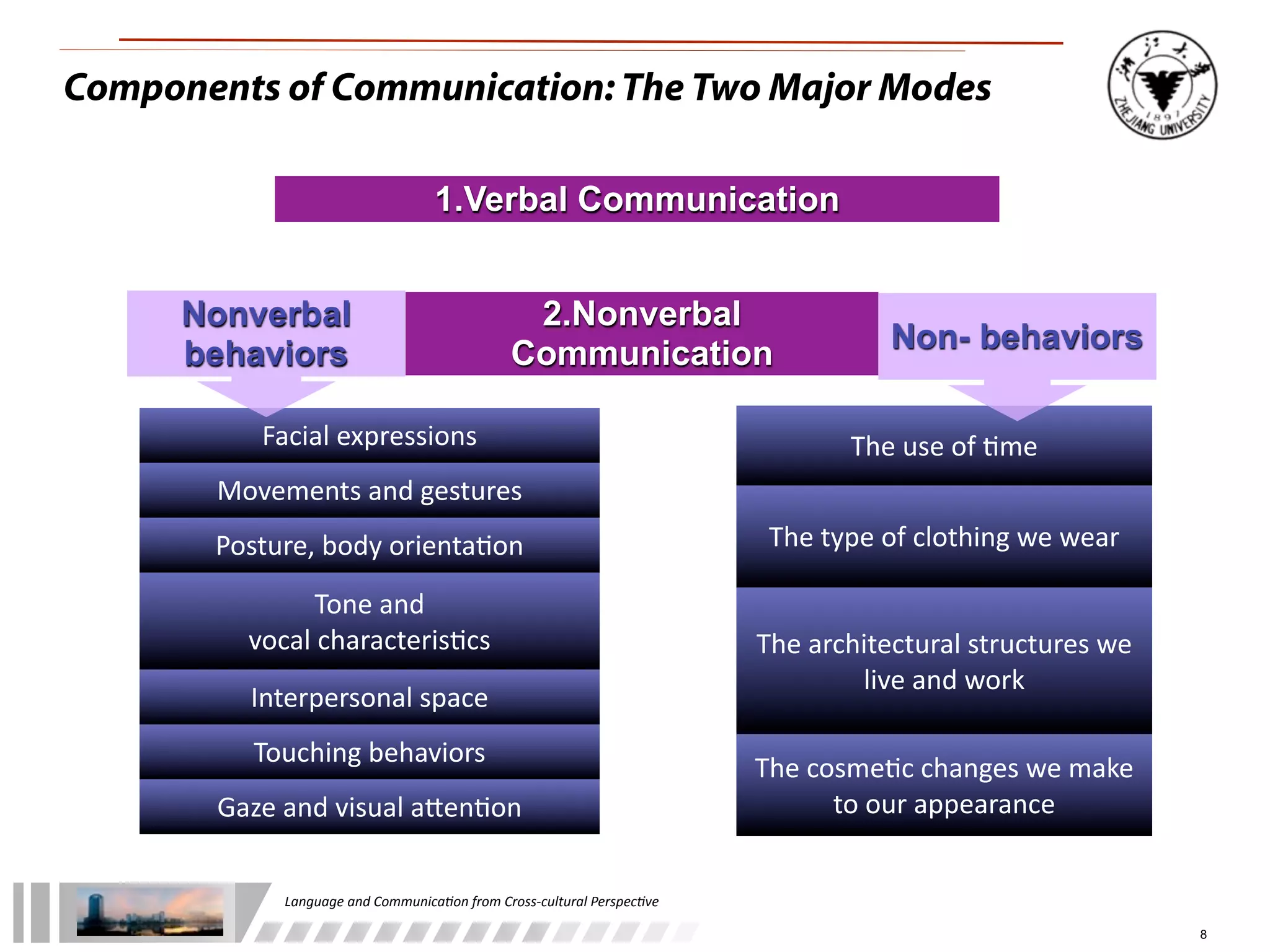
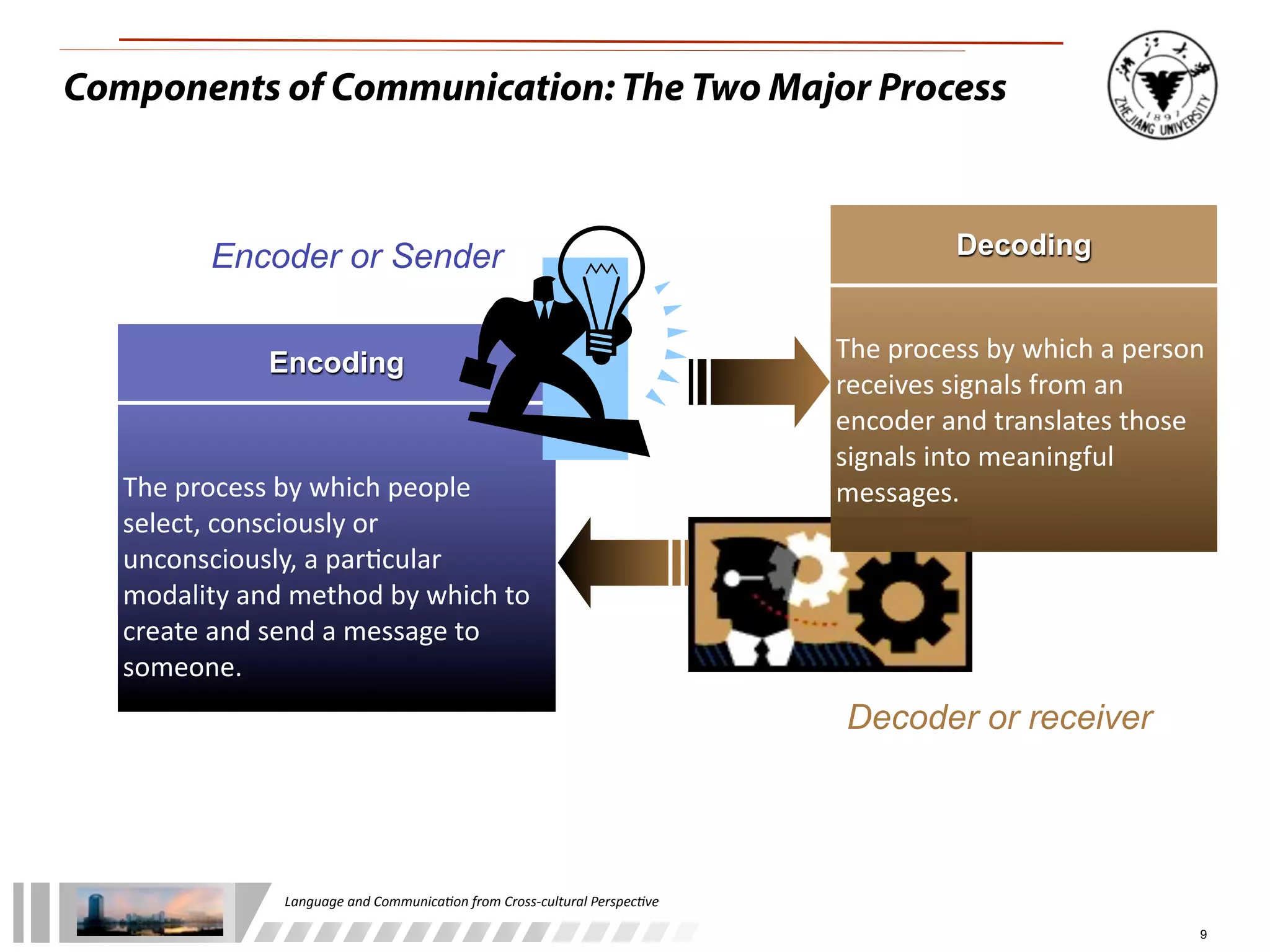
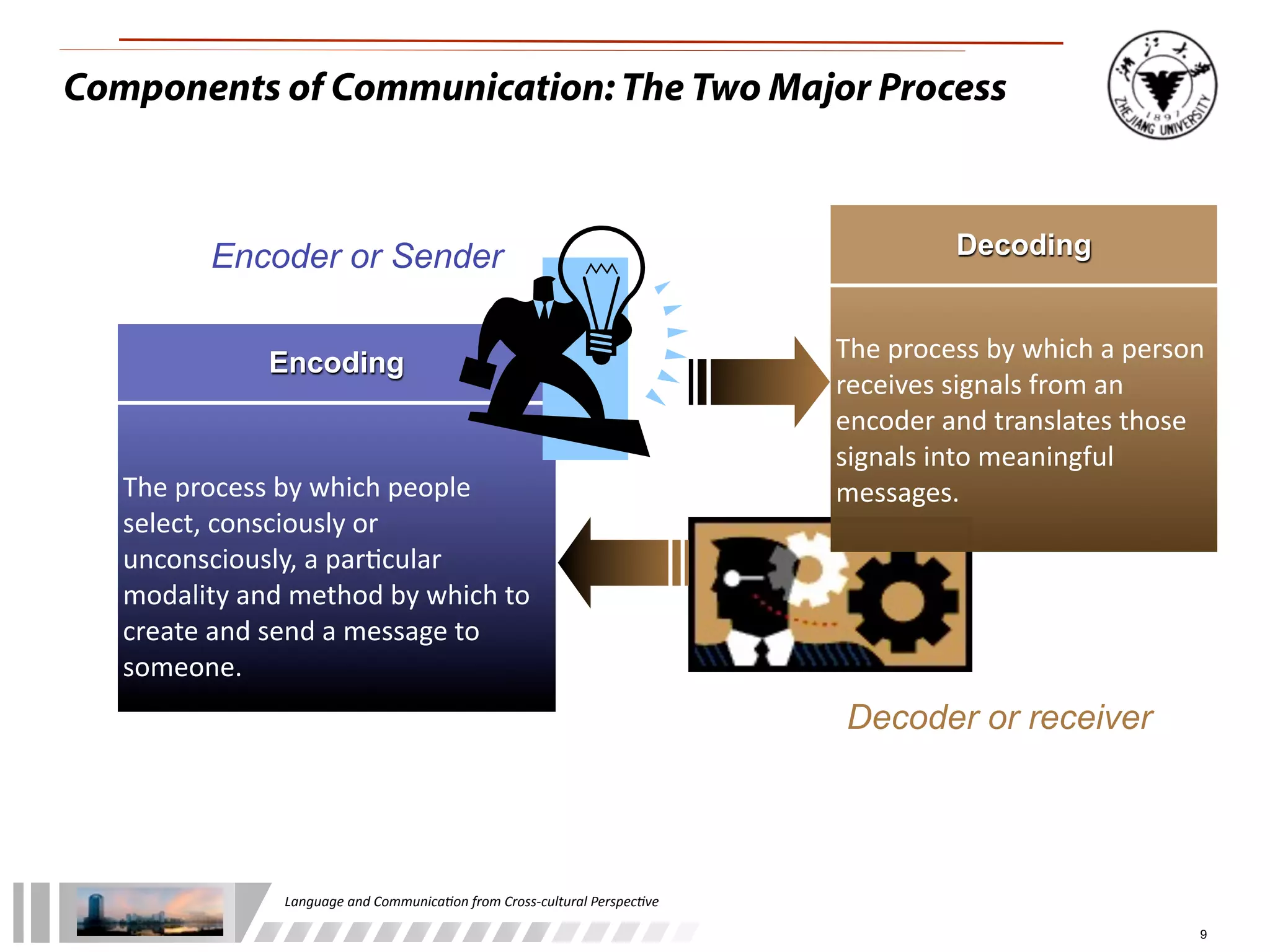
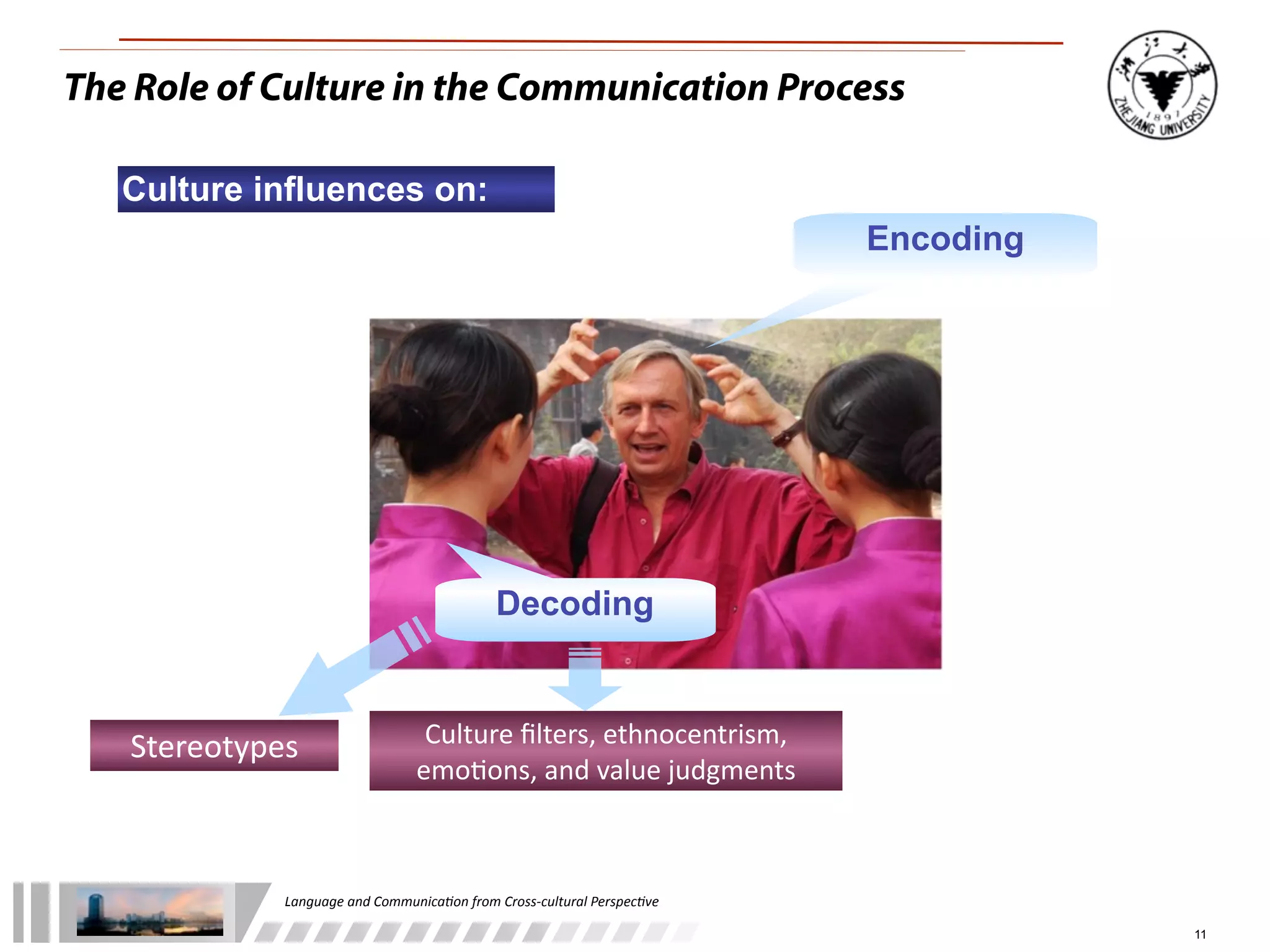
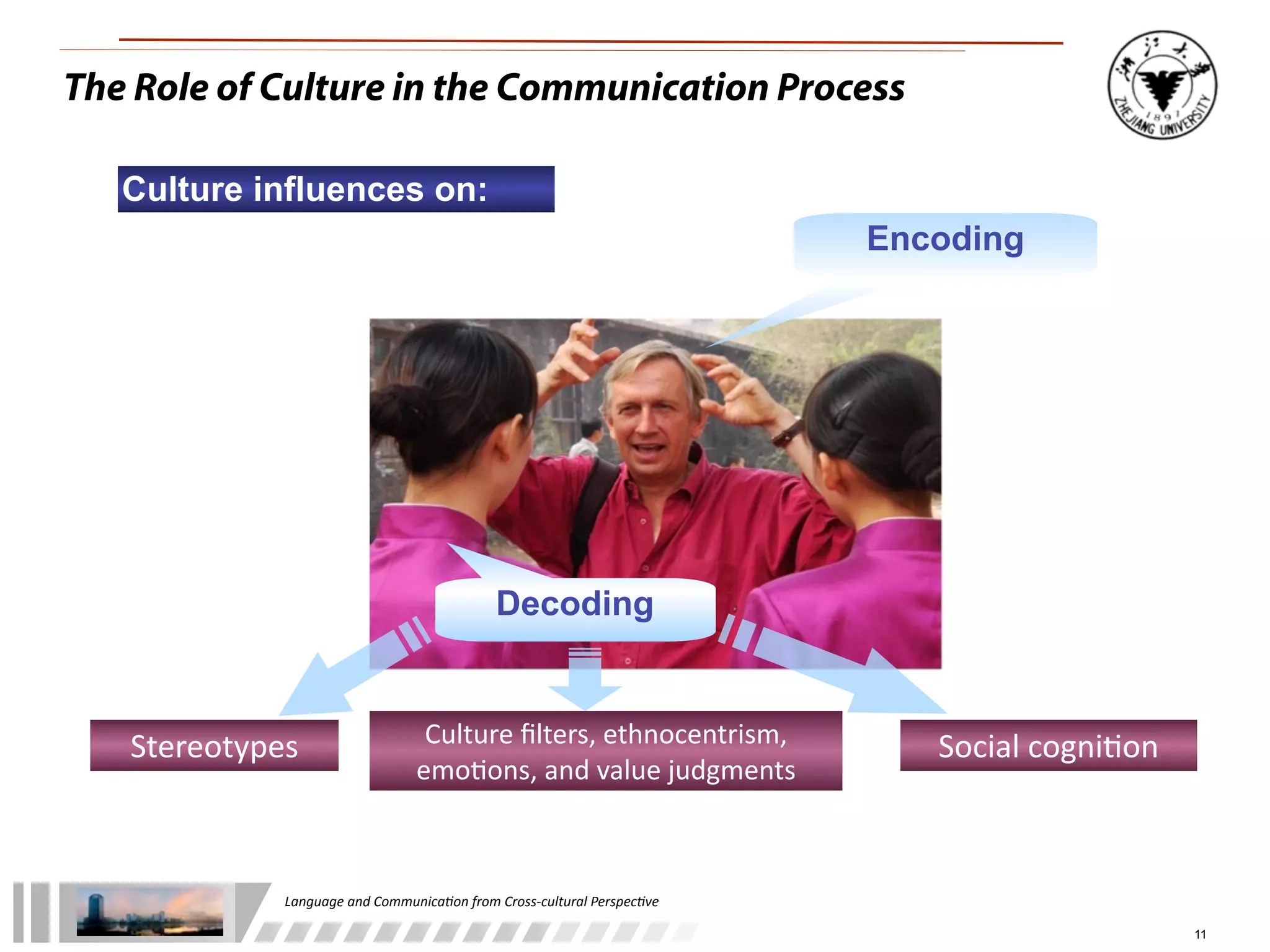
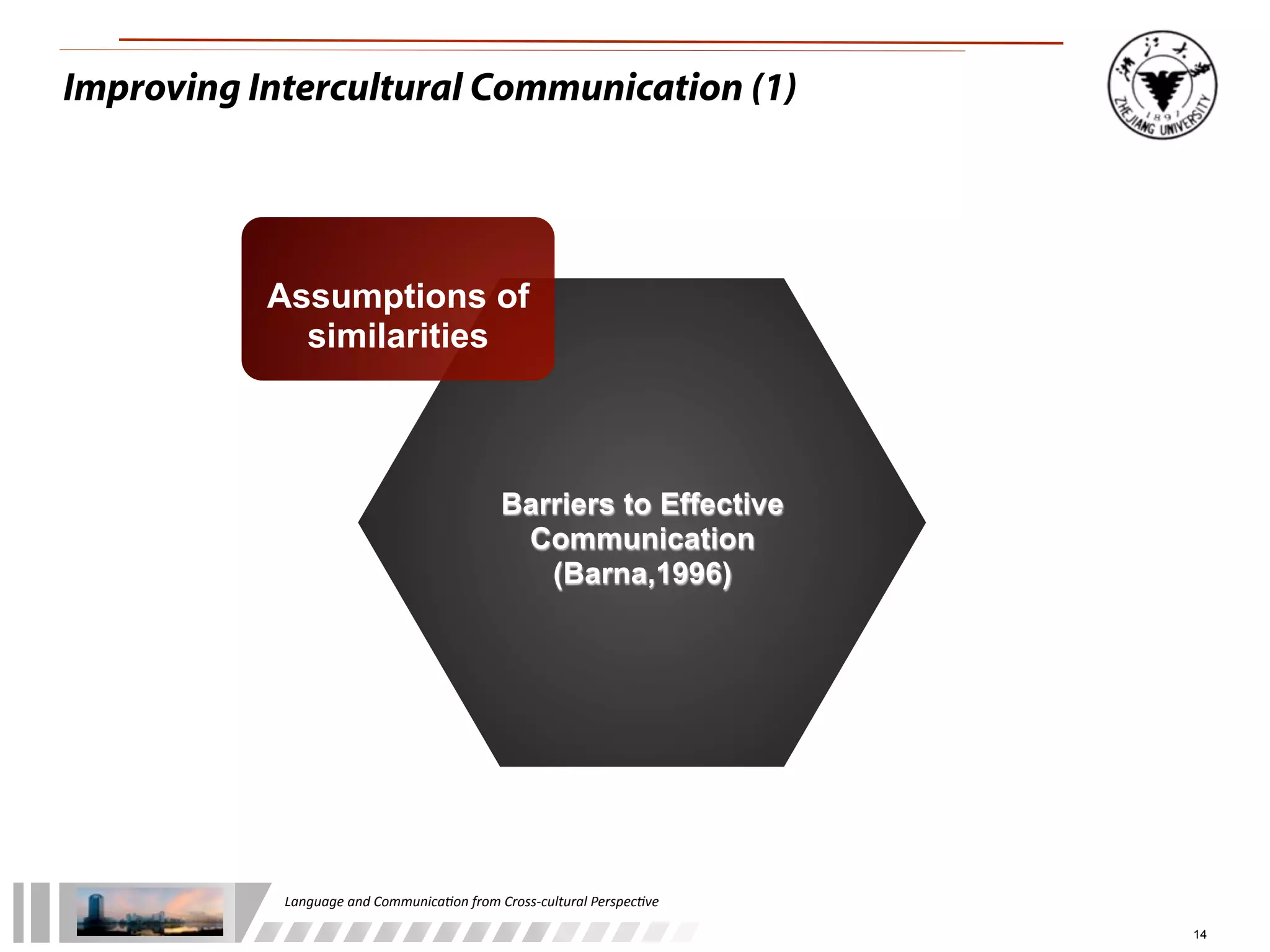
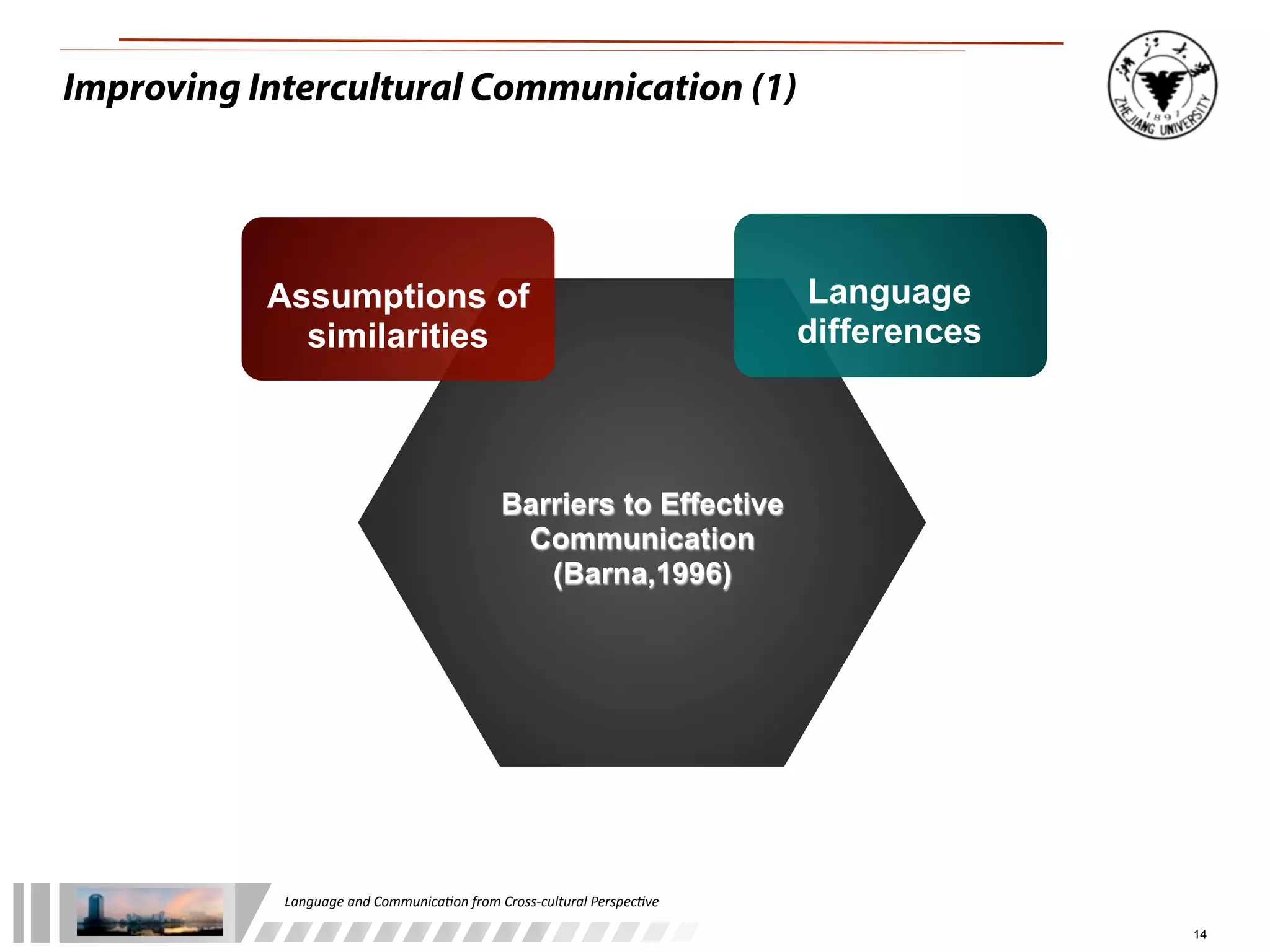
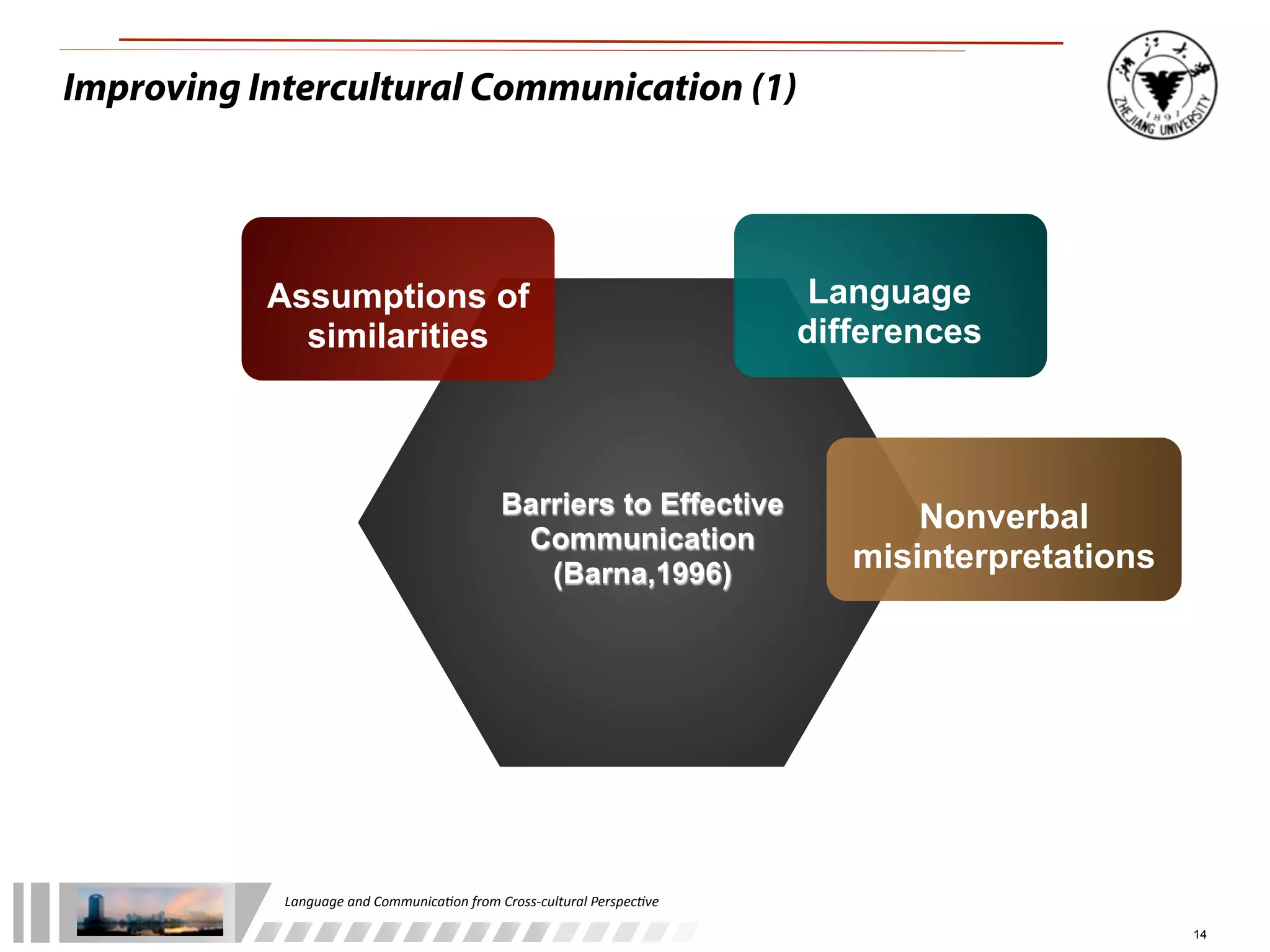
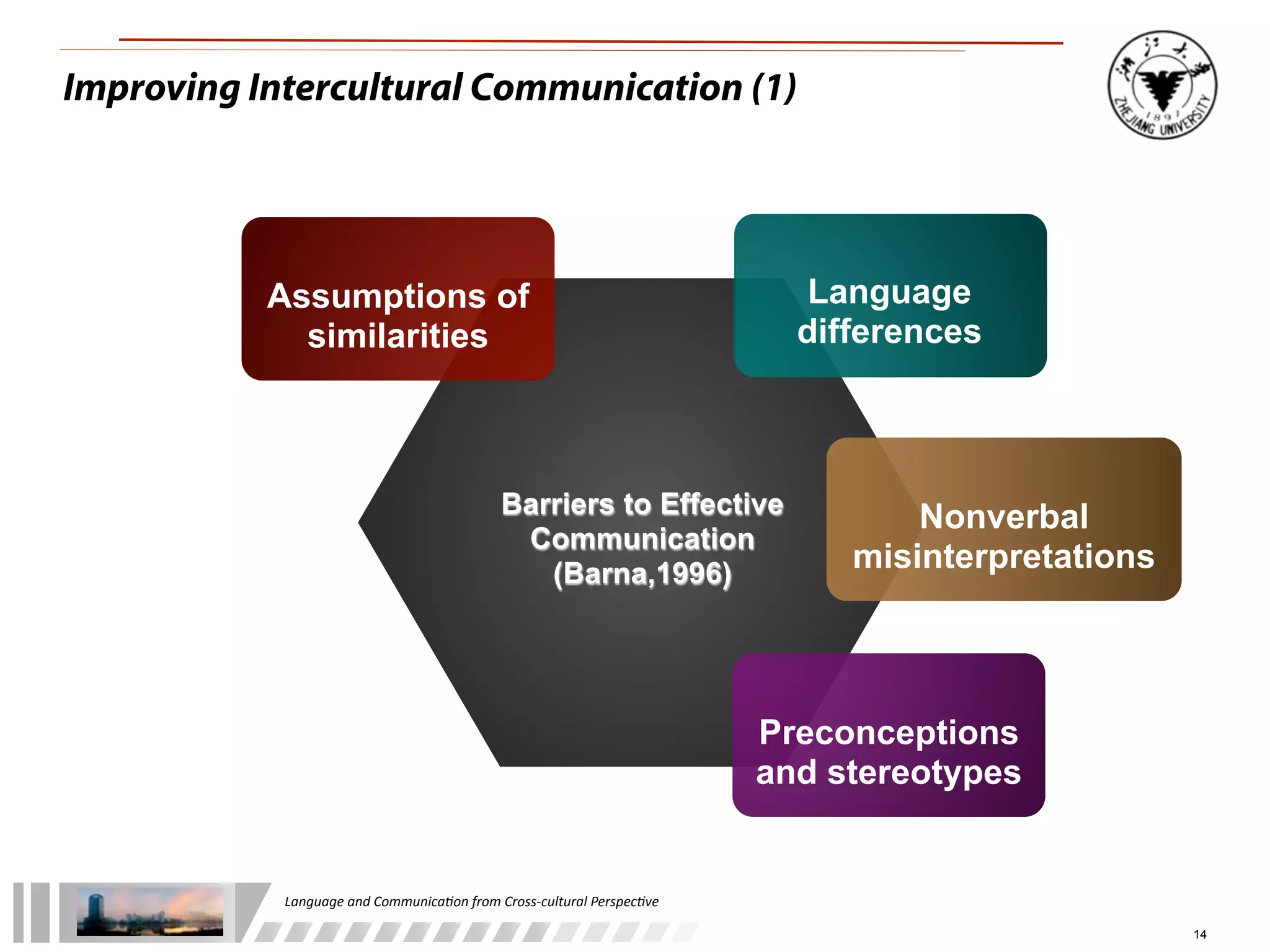
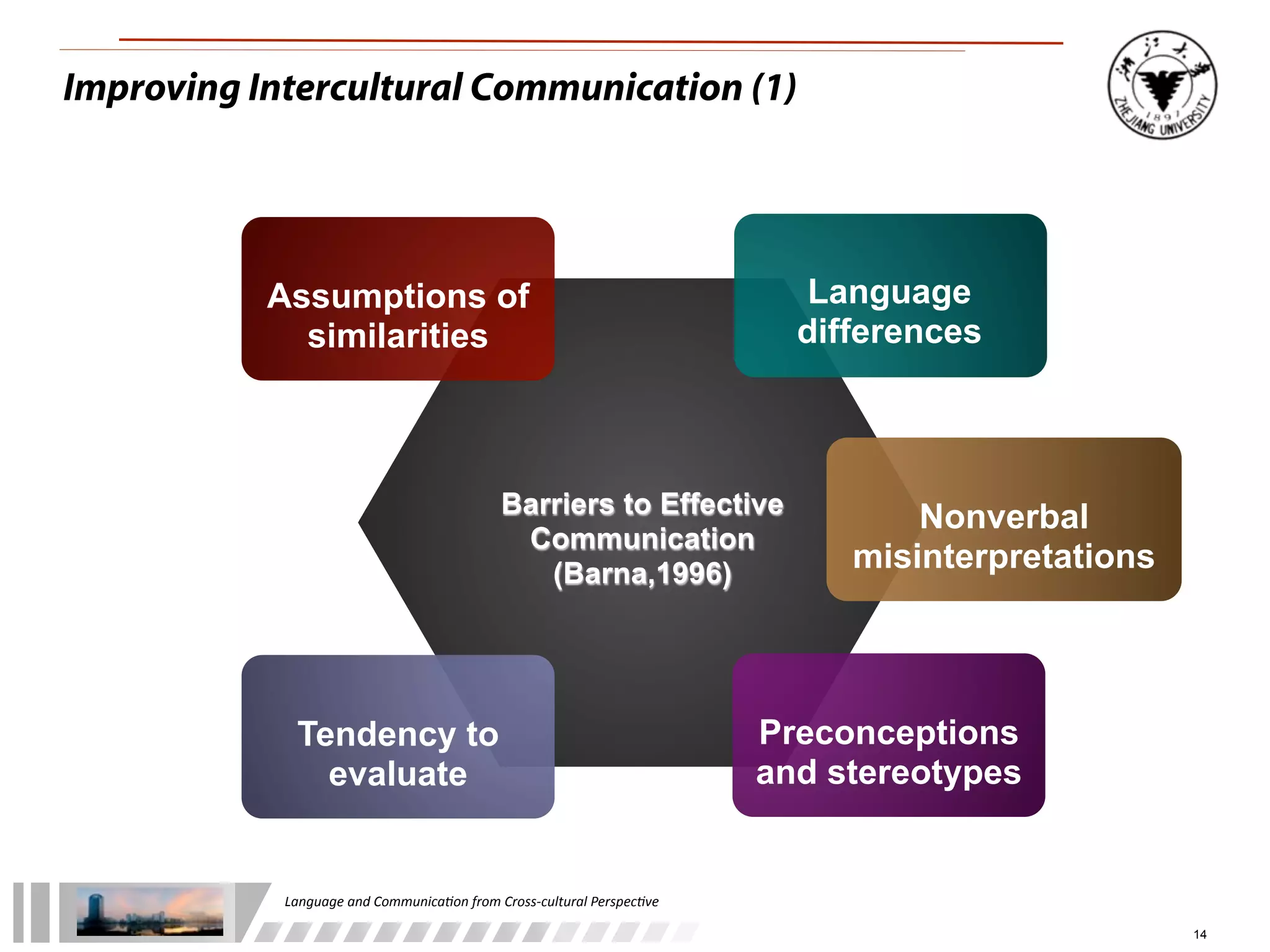
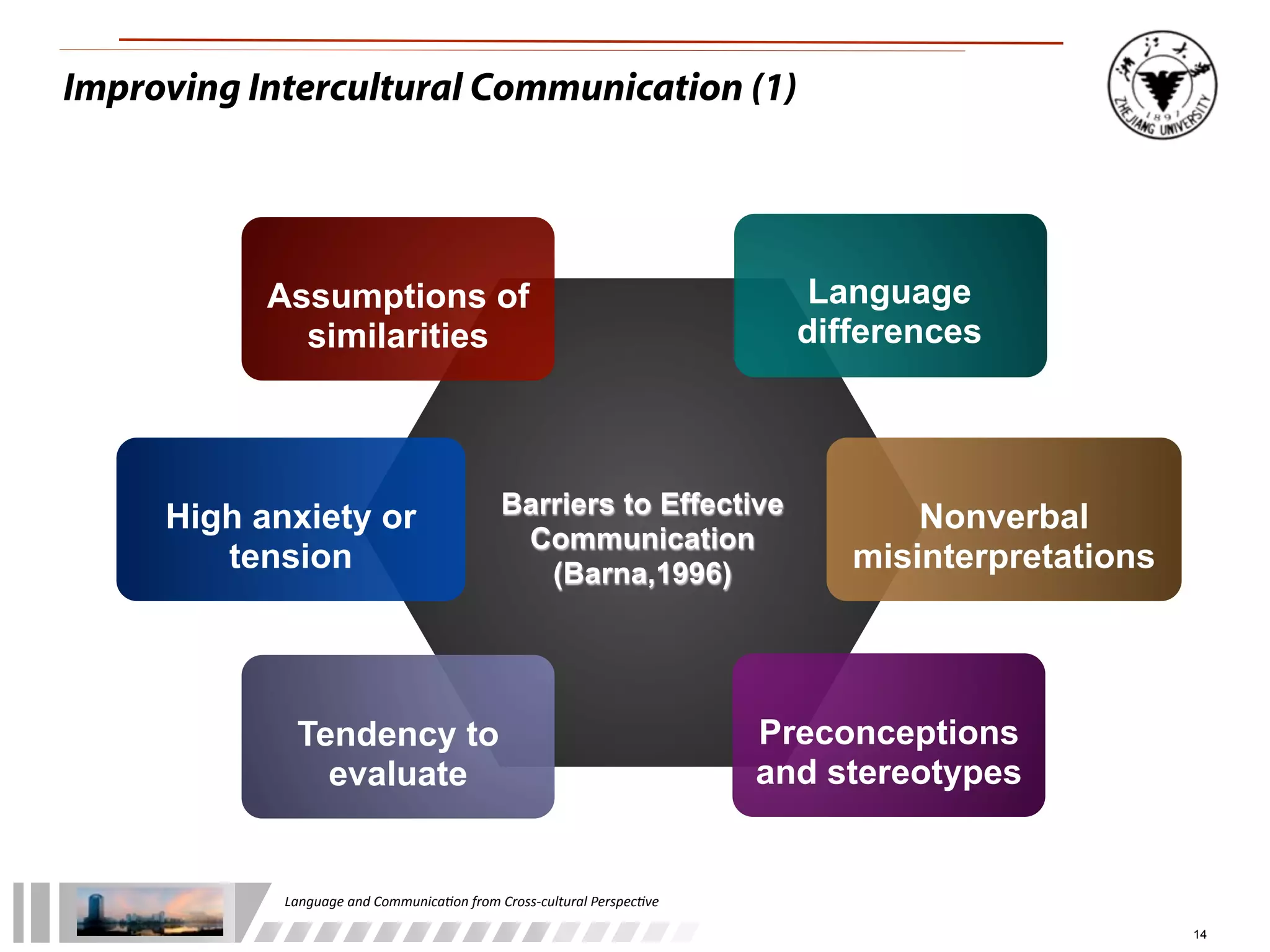
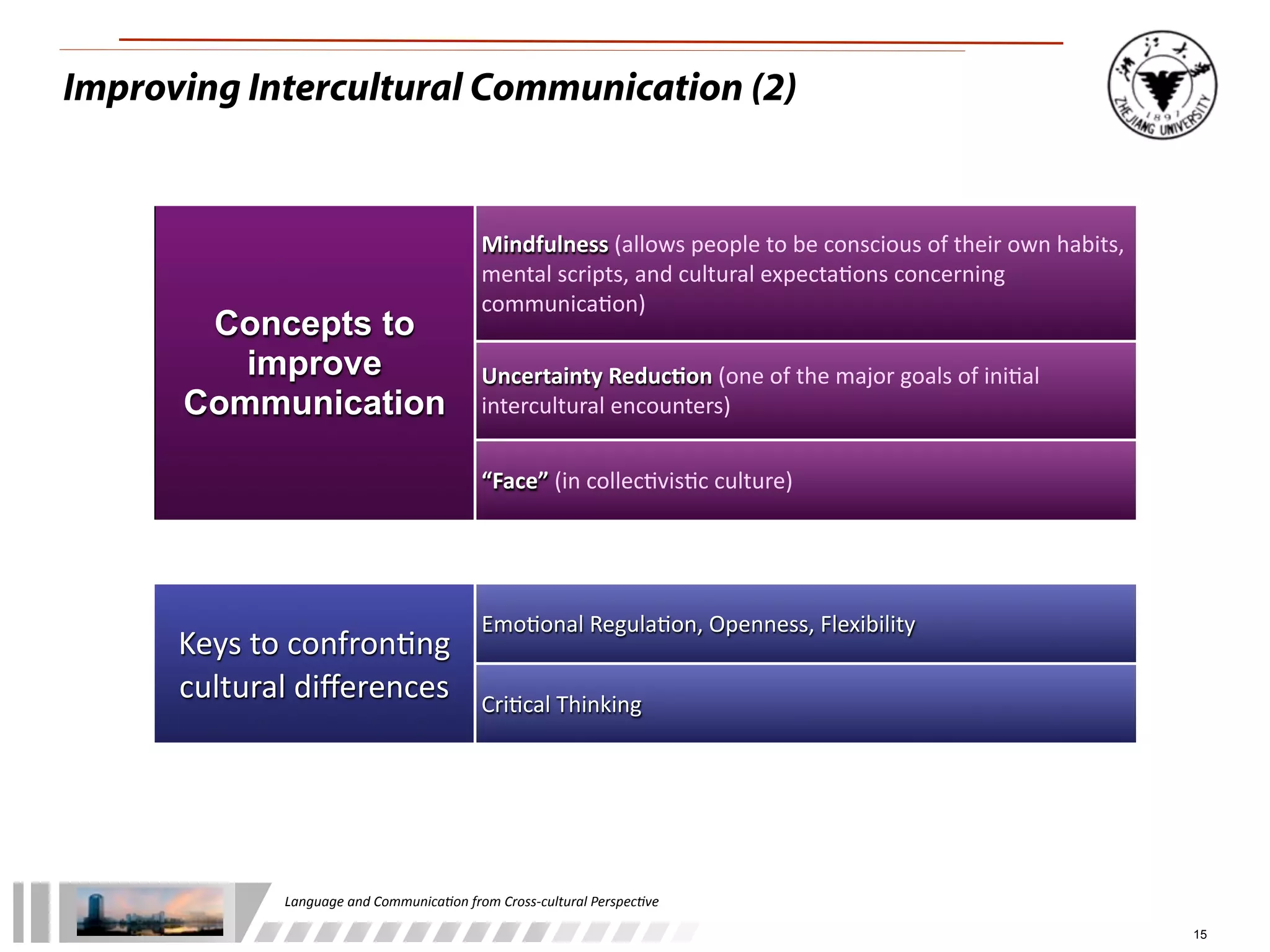
The document discusses the role of language and communication from a cross-cultural perspective, highlighting the importance of effective communication in diverse cultural contexts. It covers various aspects including the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, bilingualism, and the components of communication, such as verbal and nonverbal behaviors. Additionally, it addresses barriers to intercultural communication and provides strategies for improvement, emphasizing mindfulness and emotional regulation.