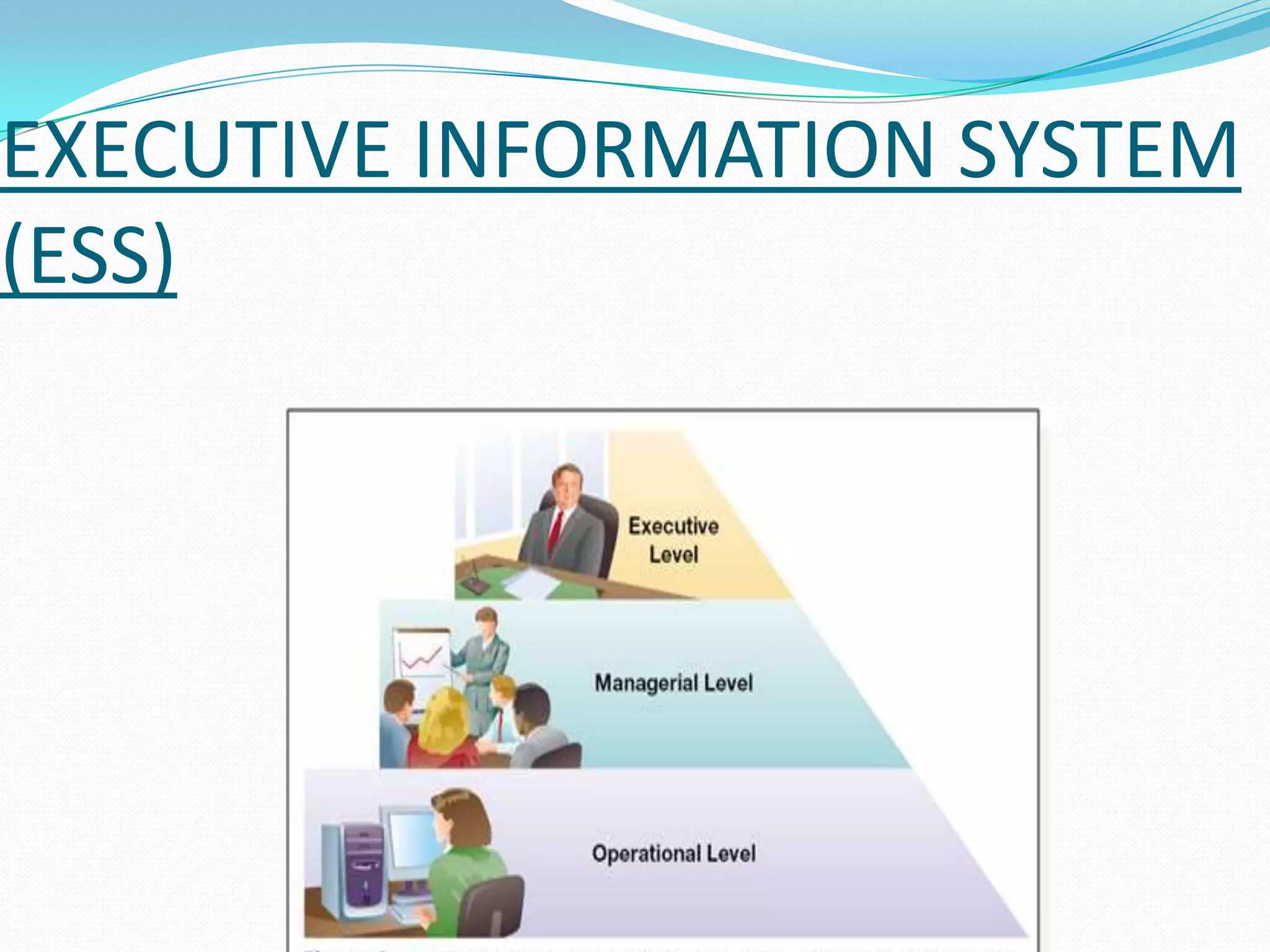
An executive information system (ESS) is a reporting tool that allows executive managers to quickly access and summarize reports from all levels and departments of an organization. It uses computer hardware, software, and user interfaces to extract summary data and solve complex problems by providing rapid access to timely internal and external information and management reports. Components of an ESS include hardware, software, a user interface, and telecommunications capabilities.