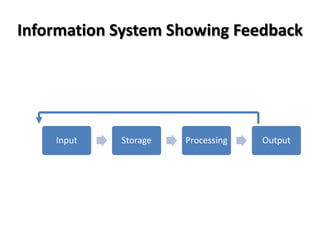
An information system has four main functions: input, storage, processing, and output. There is often a feedback loop so the system output can affect future input. An information system takes in detailed data through input, stores and processes it, and produces output information. The output can then provide feedback to users to influence future inputs into the system and analyses requested. Key elements that make up an information system include data, people, hardware, software, and telecommunications infrastructure.