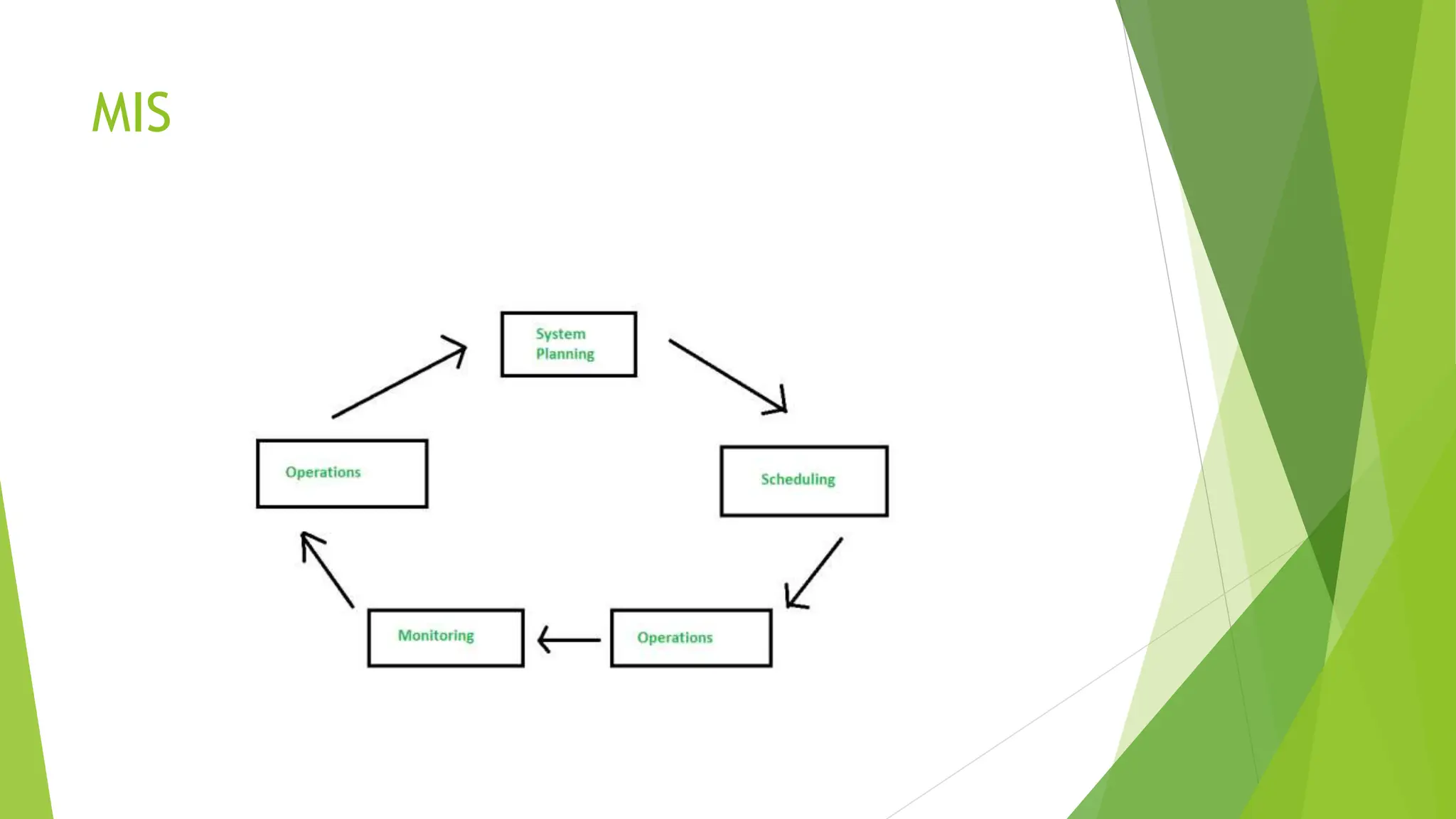
This document provides an overview of management information systems (MIS). It begins with an introduction to information systems in business and their typical components, including hardware, software, data, and telecommunications. It then discusses the fundamentals of information systems and defines the major types of information systems, including transaction processing systems, office automation systems, knowledge work systems, management information systems, decision support systems, and executive support systems. The document also distinguishes MIS from data processing and outlines some key characteristics of MIS.