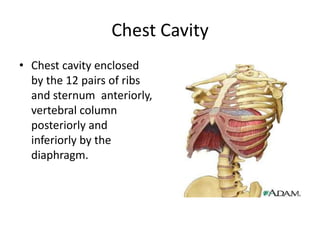
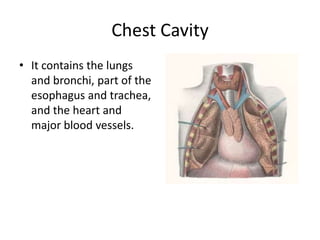
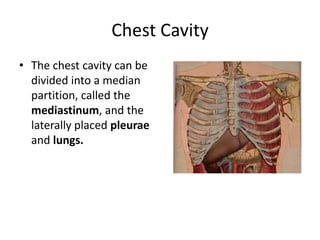
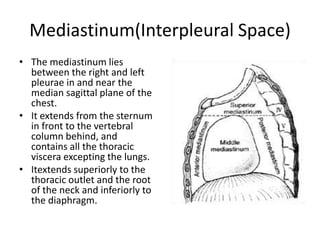
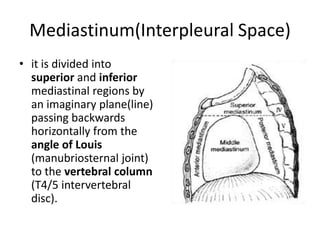
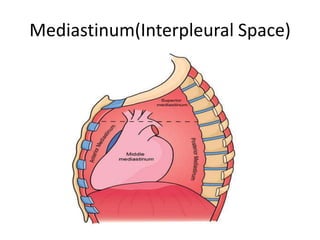
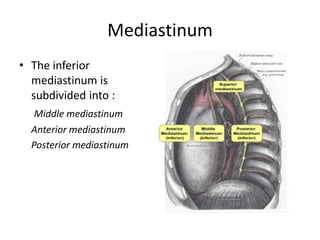
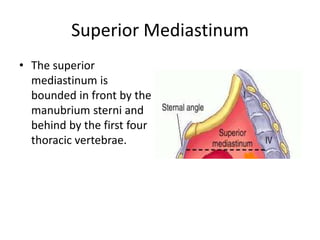
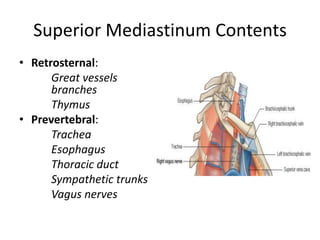
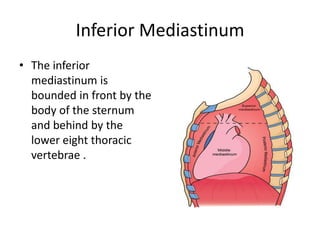
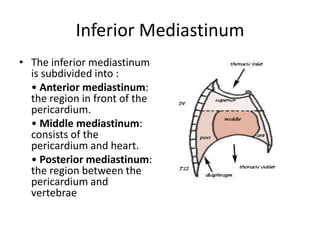
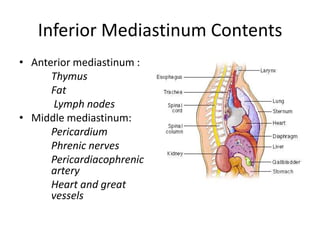
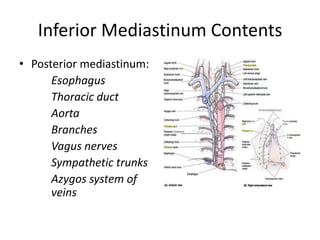
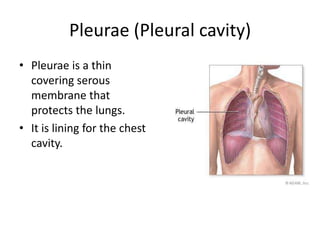
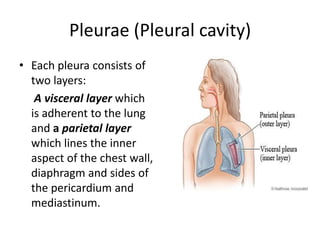
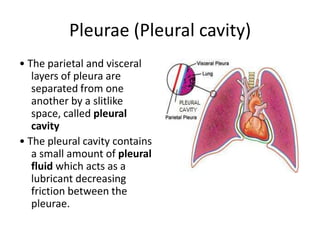
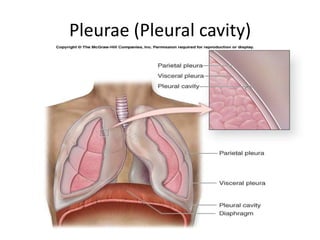
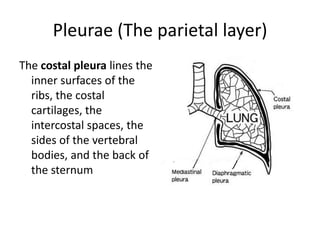
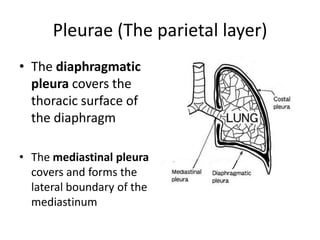
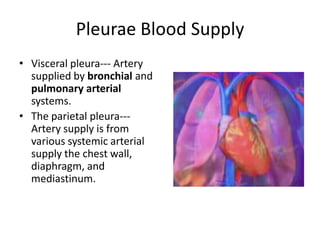
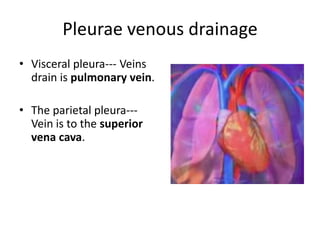
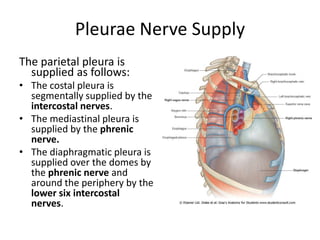
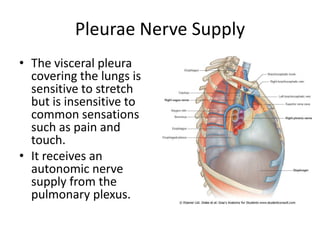
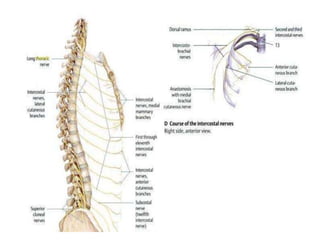
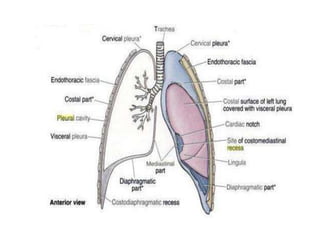
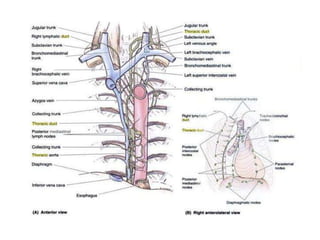
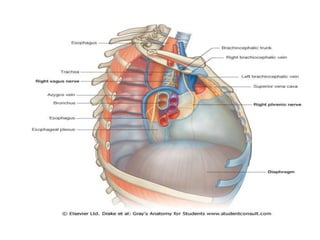
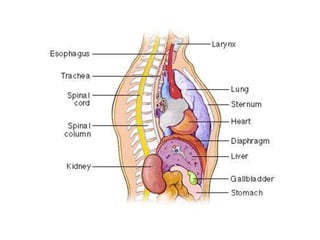
The chest cavity contains the lungs, heart, major blood vessels, and other structures. It is bounded by the ribs, sternum, vertebral column, and diaphragm. The chest cavity is further divided into the pleural cavities and mediastinum. The mediastinum is the median partition between the lungs and contains the esophagus, trachea, thymus, and major blood vessels. Each lung is surrounded by a pleural membrane made of visceral and parietal layers that create a pleural cavity containing fluid.