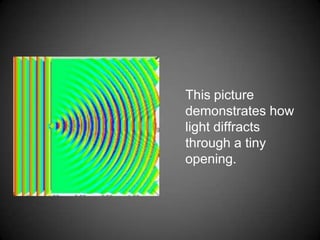
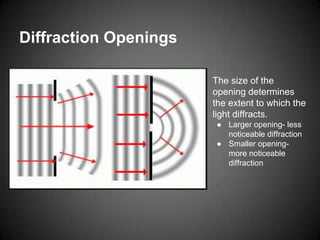
Diffraction is the bending of light around obstacles. Light diffracts through small openings more noticeably than larger openings, producing interference patterns of bright and dark fringes. A double slit experiment demonstrates diffraction through two slits, with light and dark fringes appearing from constructive and destructive interference. Diffraction gratings split light into multiple beams like how light spreads on a CD. Diffraction is used in microscopes and telescopes to resolve images by separating blurred images into distinct ones.