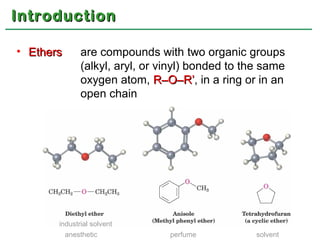
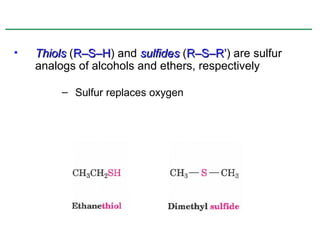
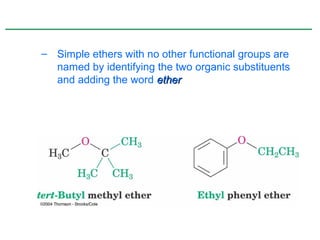
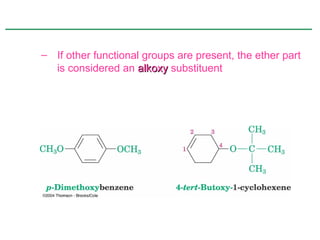
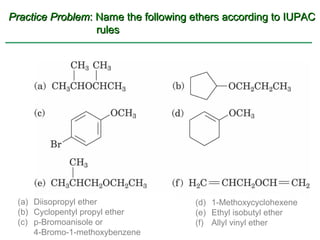
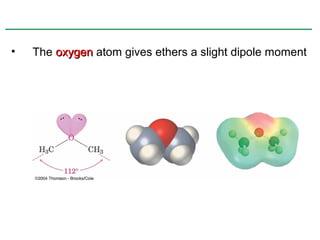
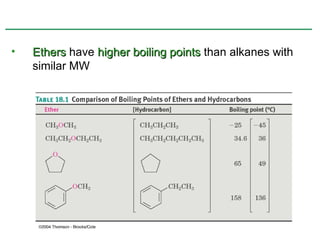
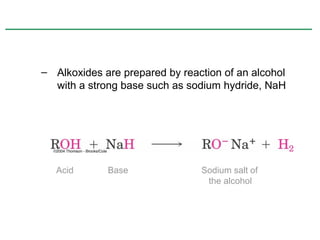
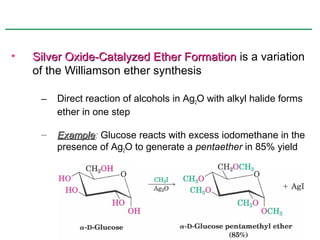
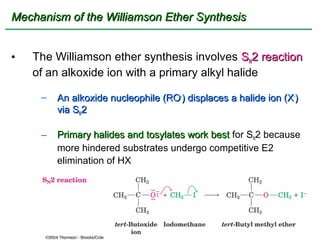
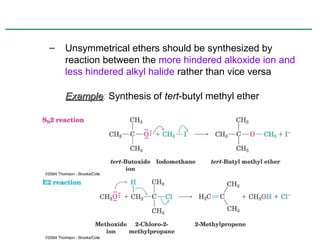
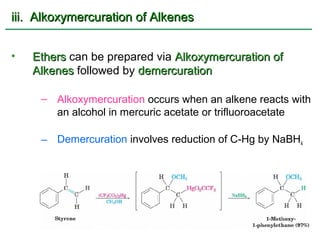
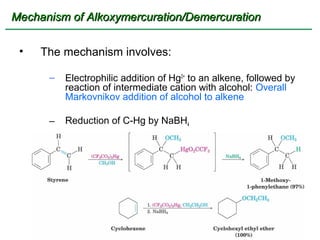
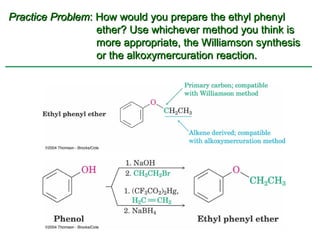
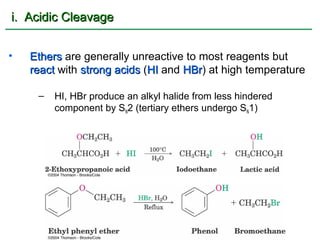
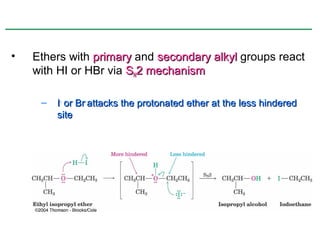
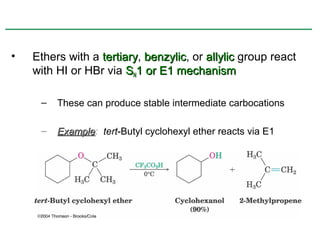
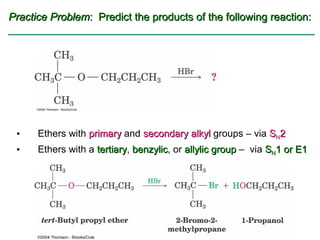
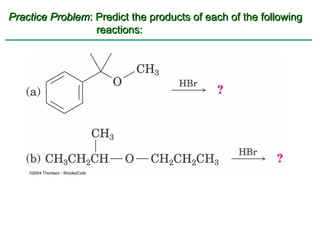
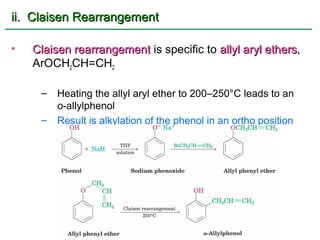
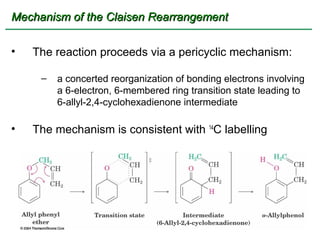
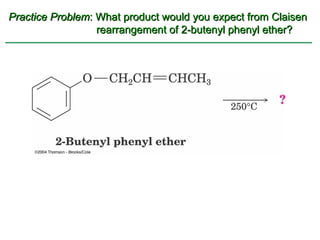
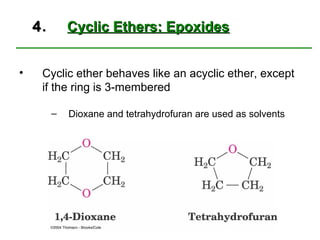
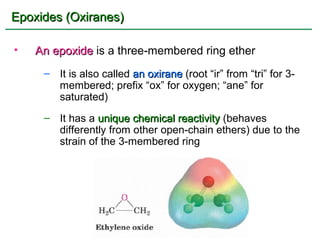
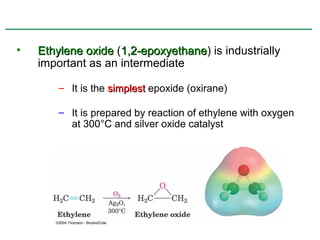
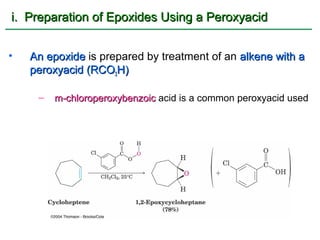
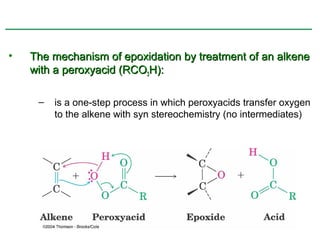
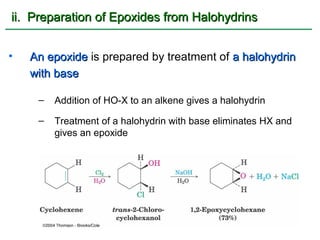
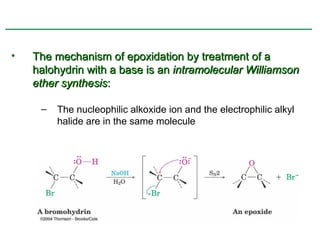
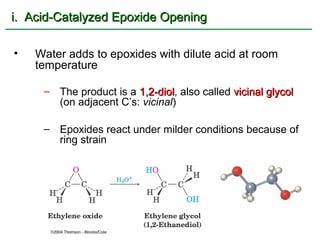
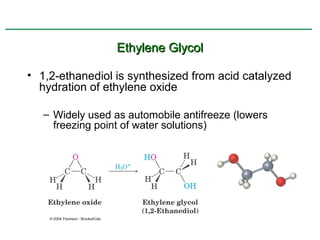
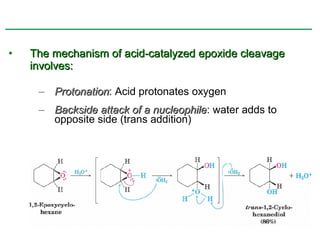
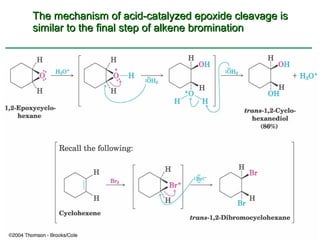
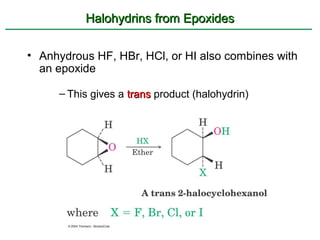
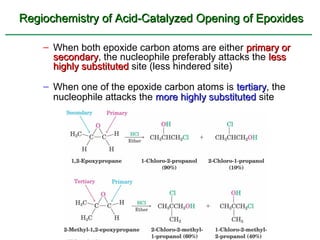
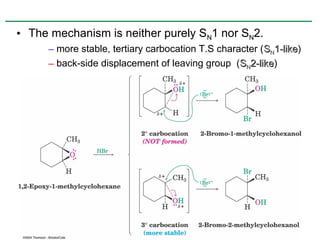
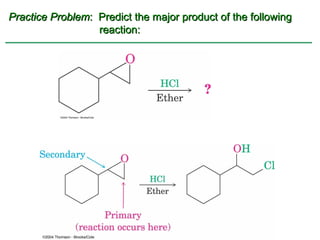
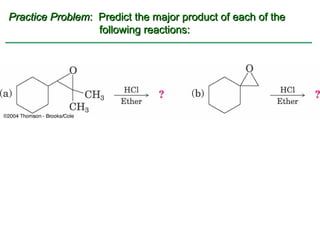
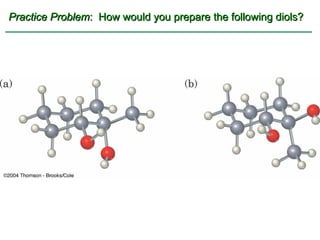
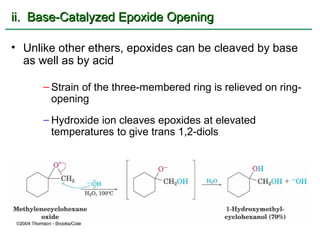
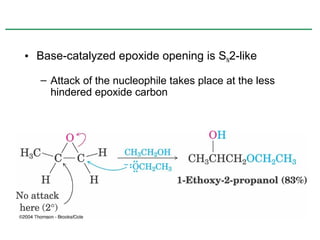
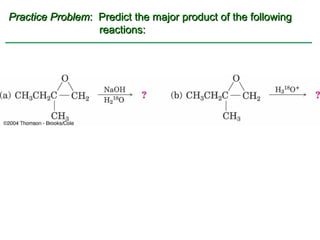
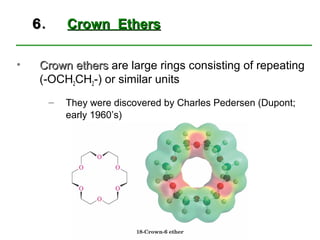
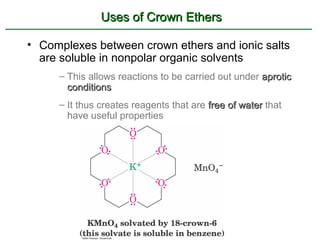
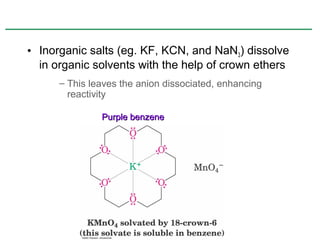
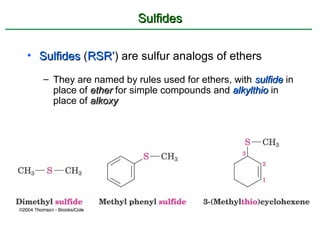
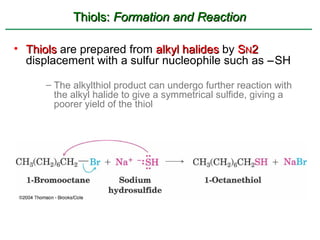
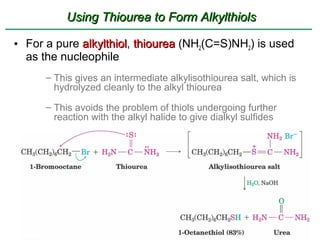
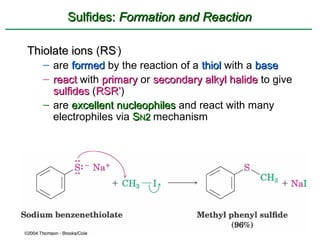
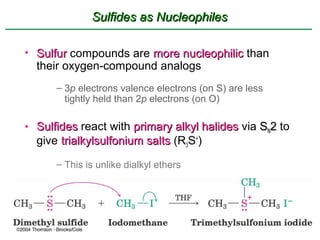
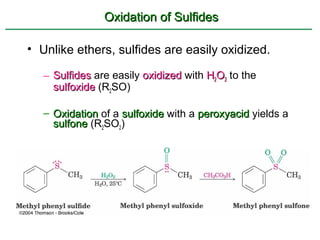
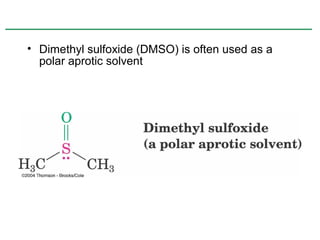
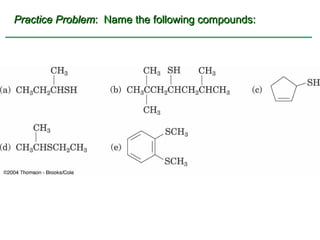
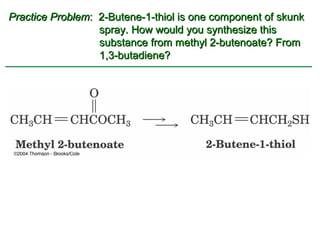
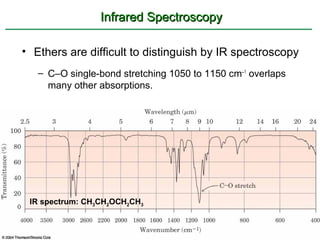
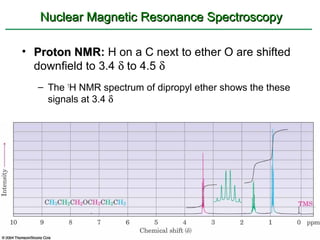
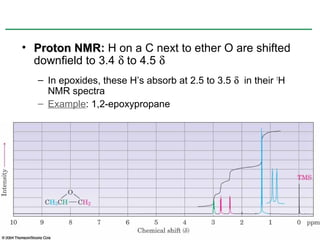
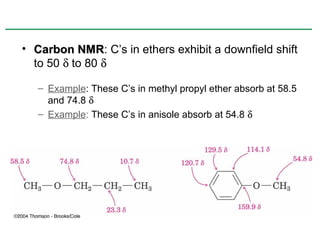
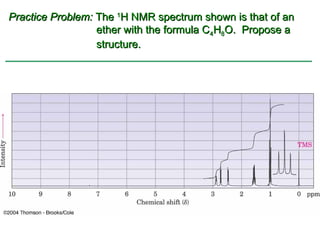
Ethers are compounds with two organic groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. They can be synthesized by acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols, Williamson ether synthesis, or alkoxymercuration of alkenes. Ethers undergo acidic cleavage reactions and Claisen rearrangement. Cyclic ethers such as epoxides undergo ring-opening reactions with acid or base to form diols. Crown ethers complex alkali metal cations and are useful for solubilizing inorganic salts in organic solvents.