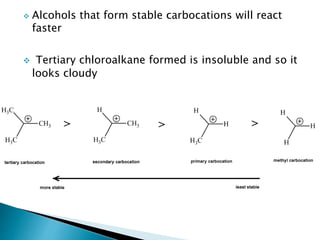
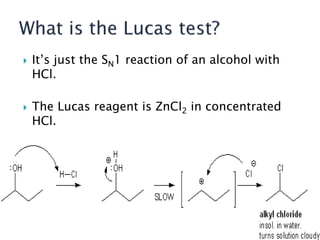
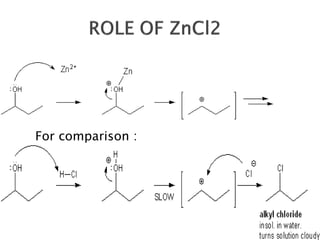
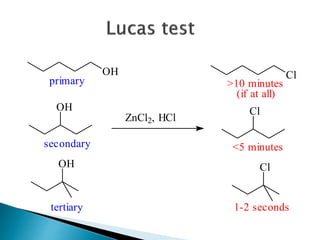
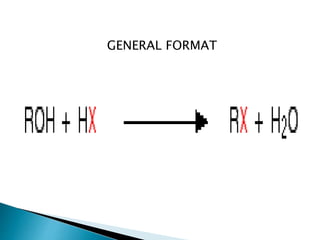
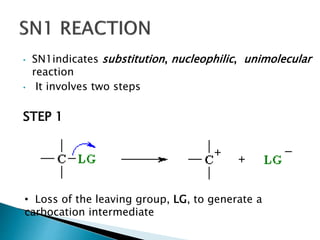
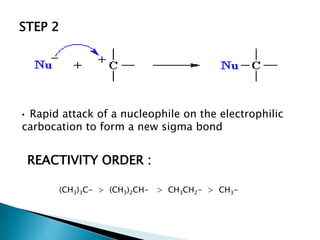
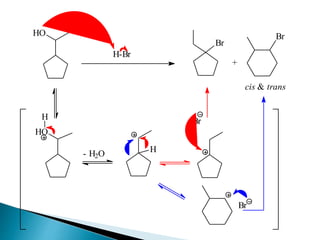
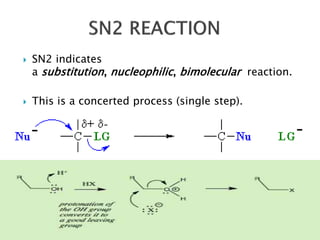
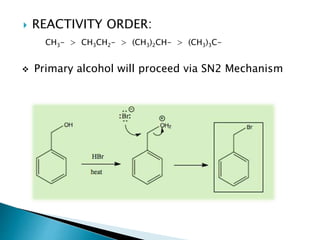
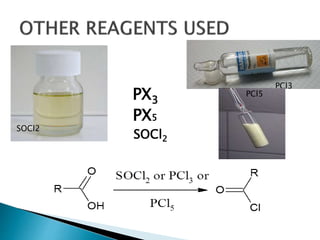
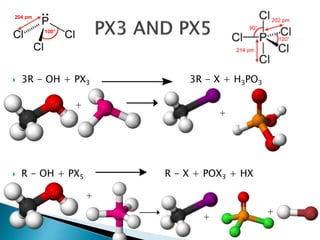
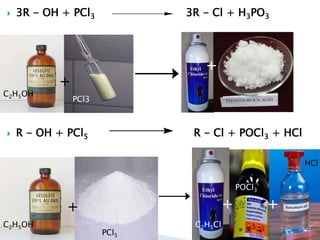
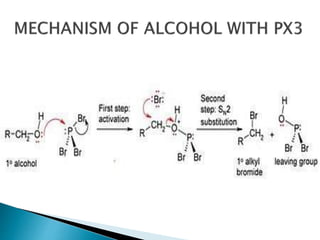
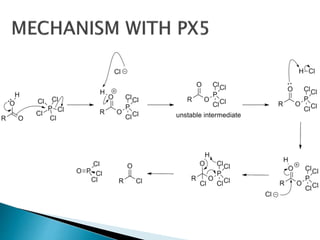
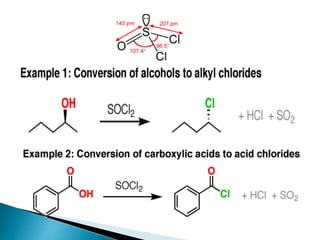
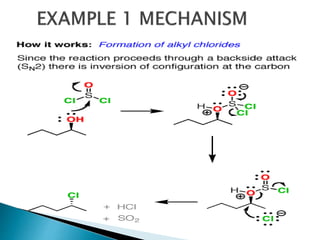
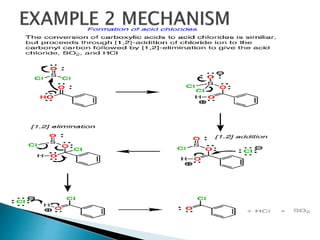
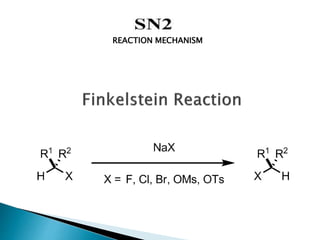
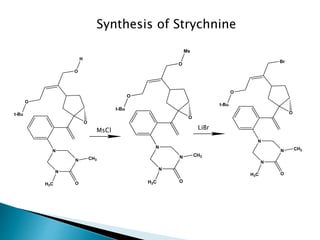
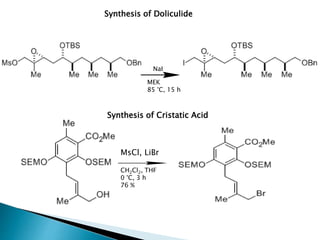
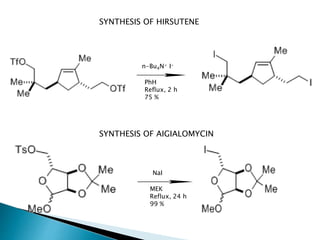
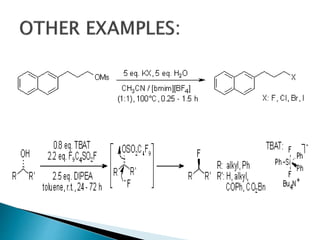
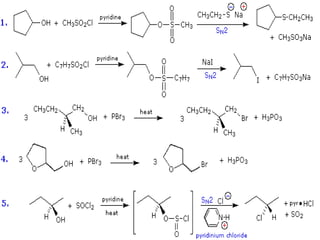
The document discusses SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms of alcohols. Tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions with hydrogen halides faster than secondary or primary alcohols due to their ability to form stable carbocation intermediates. Primary alcohols favor SN2 reactions. Polar solvents can stabilize carbocations and favor the SN1 pathway. Common reagents used to convert alcohols to alkyl halides include thionyl chloride, phosphorus halides, and halogenation using sodium halides.