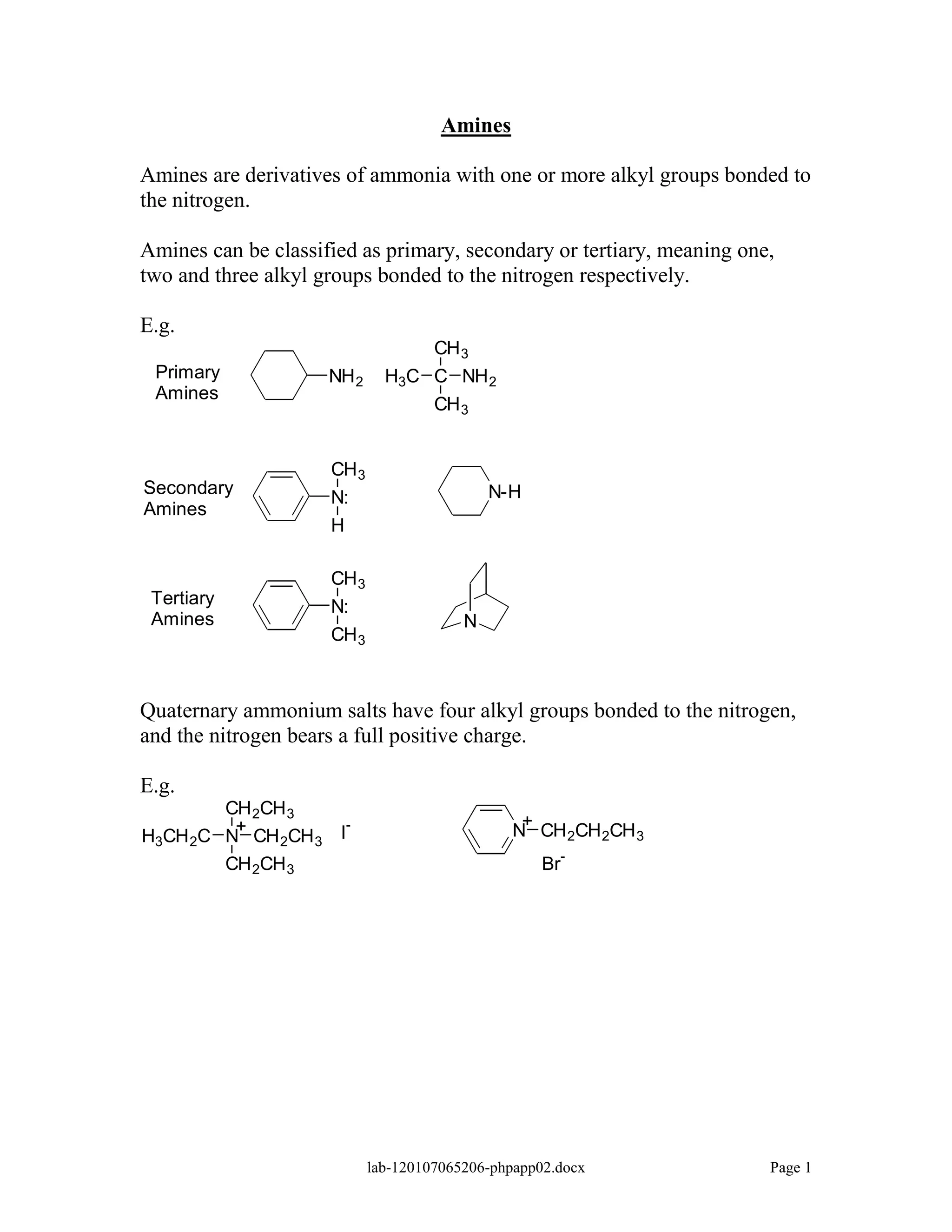
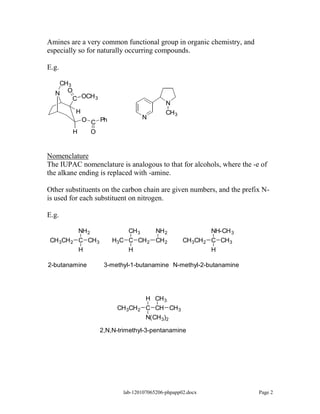
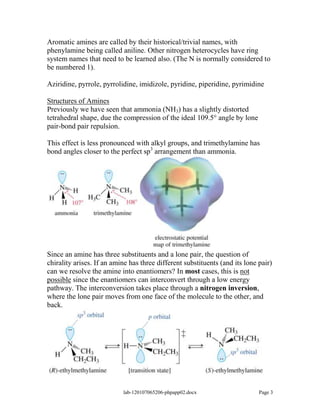
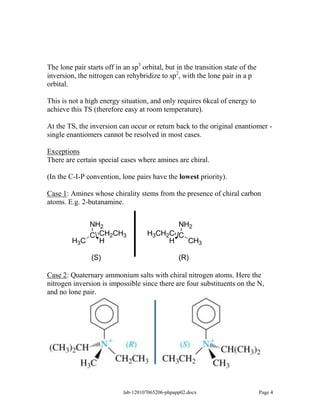
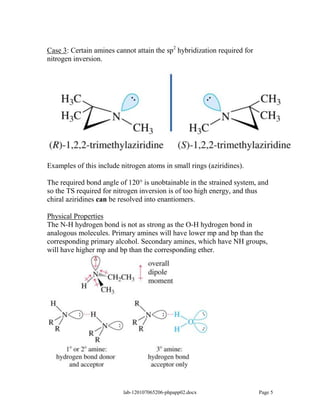
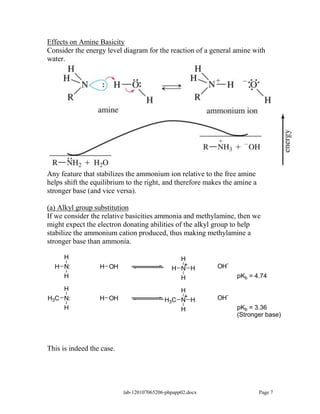
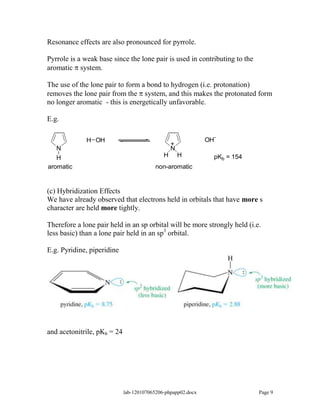
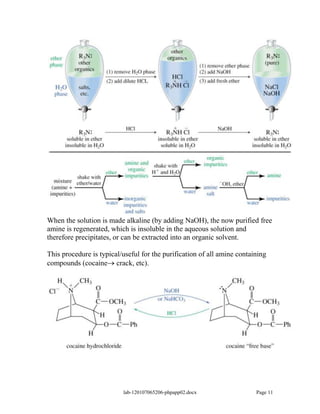
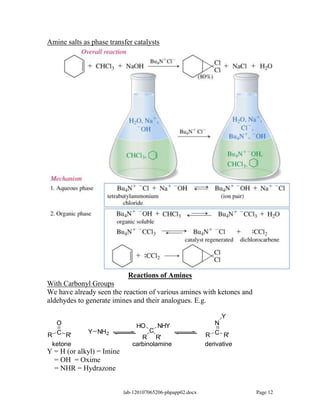
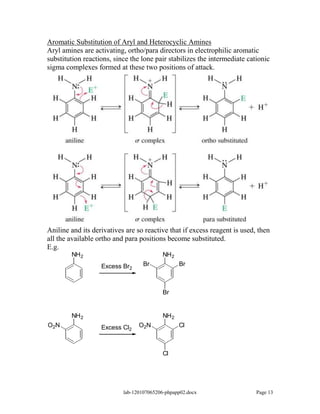
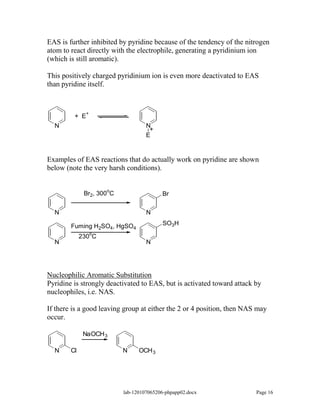
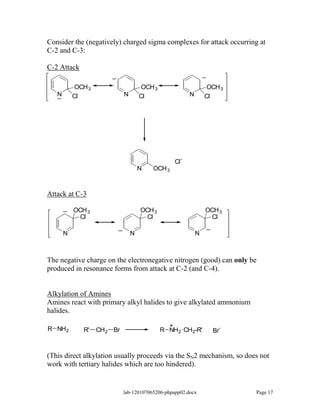
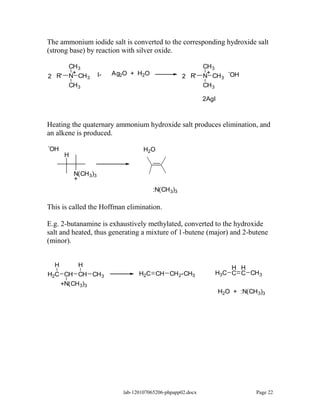
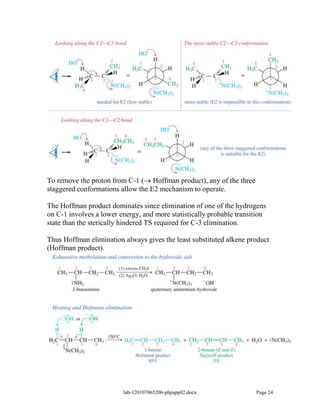
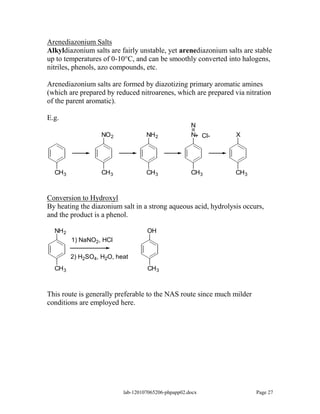
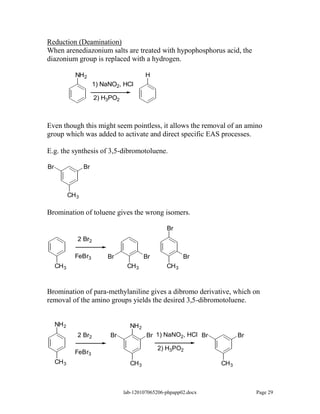
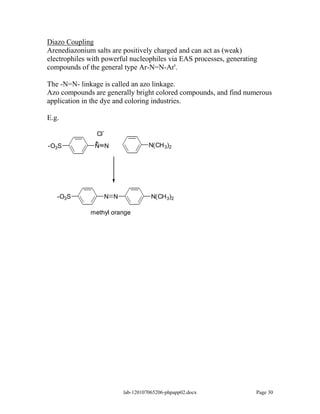
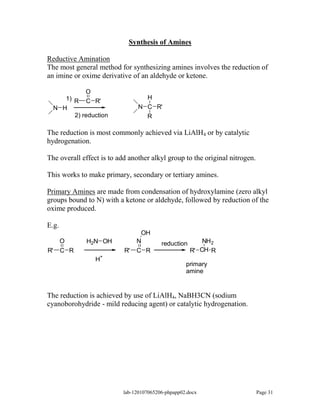
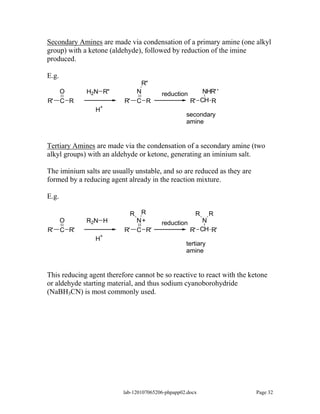
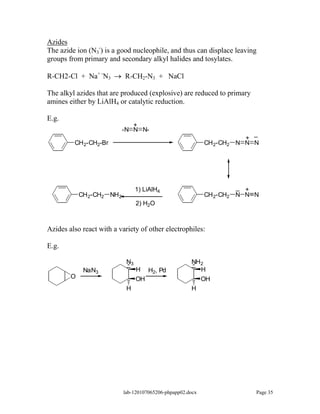
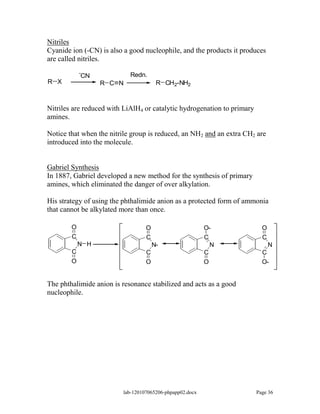
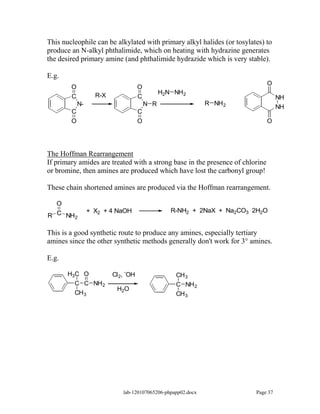
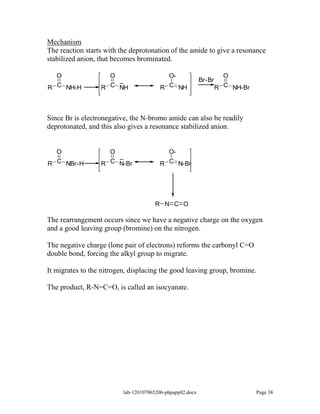
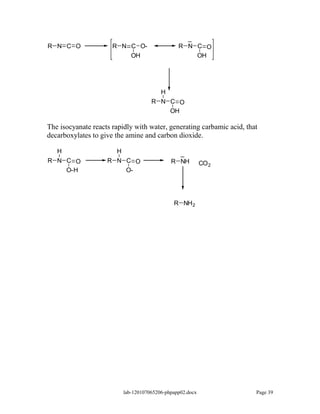
Amines are derivatives of ammonia with one or more alkyl groups bonded to the nitrogen. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on having one, two, or three alkyl groups respectively. Amines exhibit basic properties due to the lone pair on the nitrogen. The basicity depends on factors like resonance, hybridization, and substituents. Amines undergo reactions like substitution, alkylation, and reactions with carbonyl compounds to form imines. Some amines like pyridine are deactivated toward electrophilic aromatic substitution.