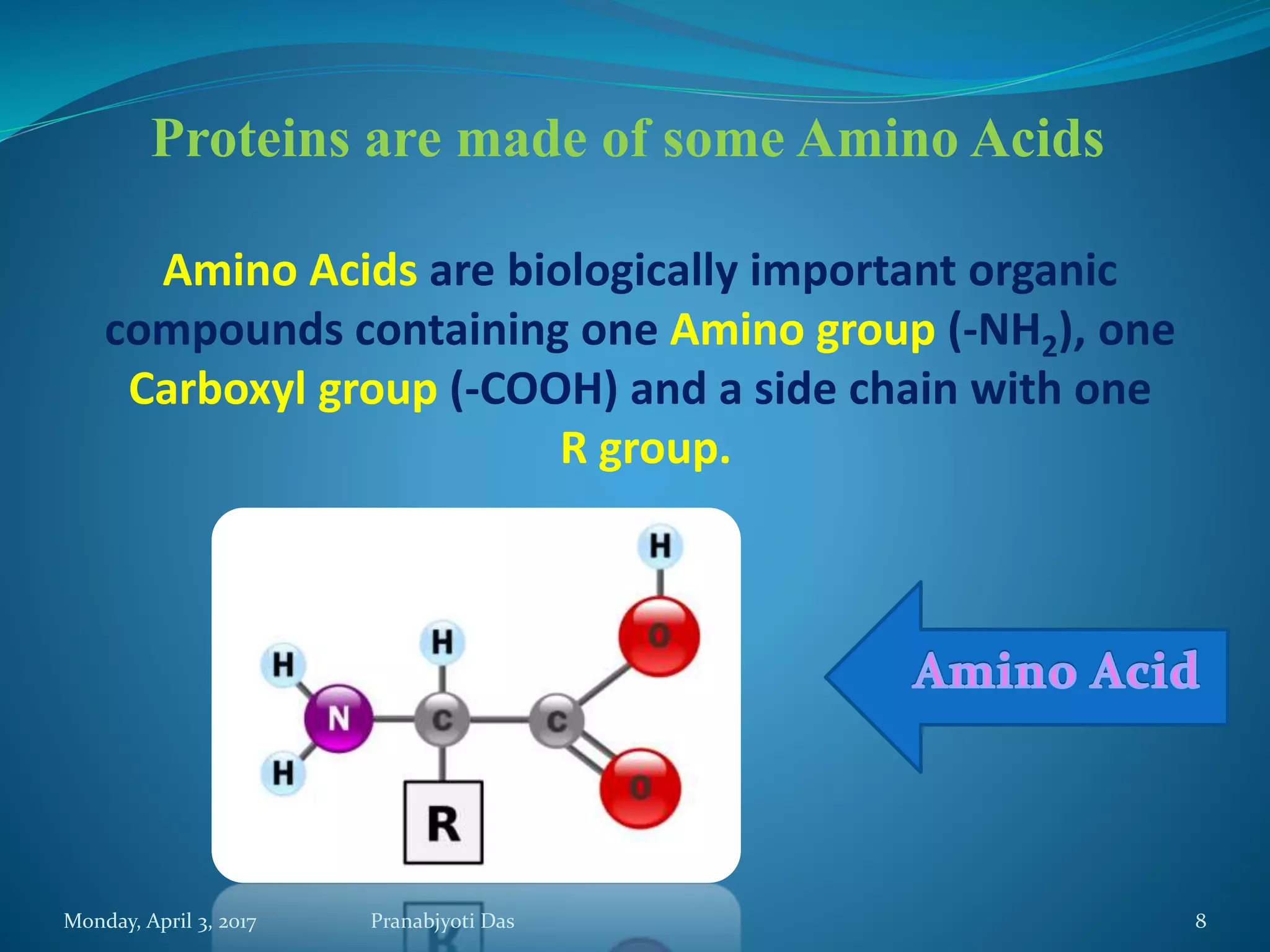
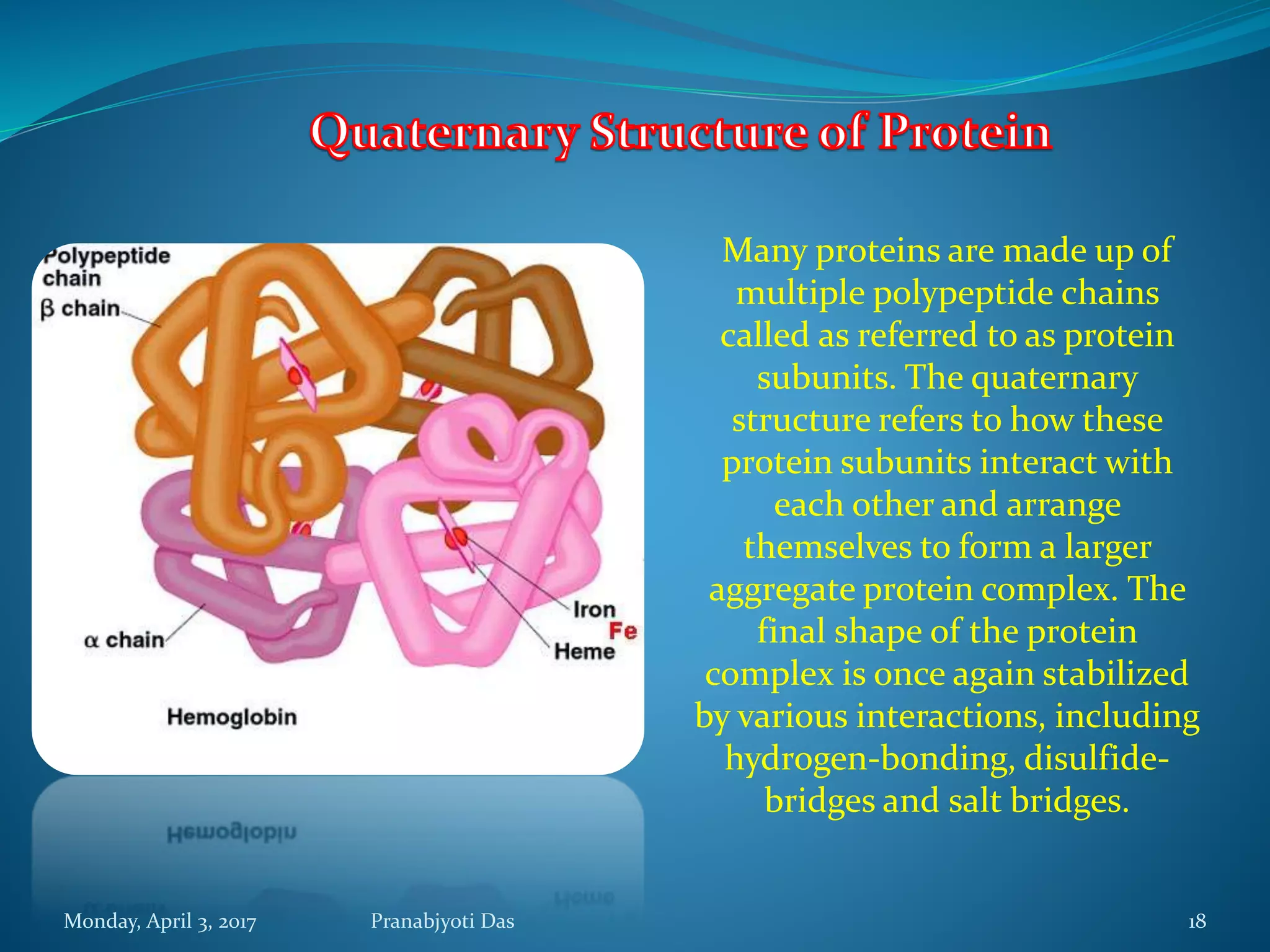
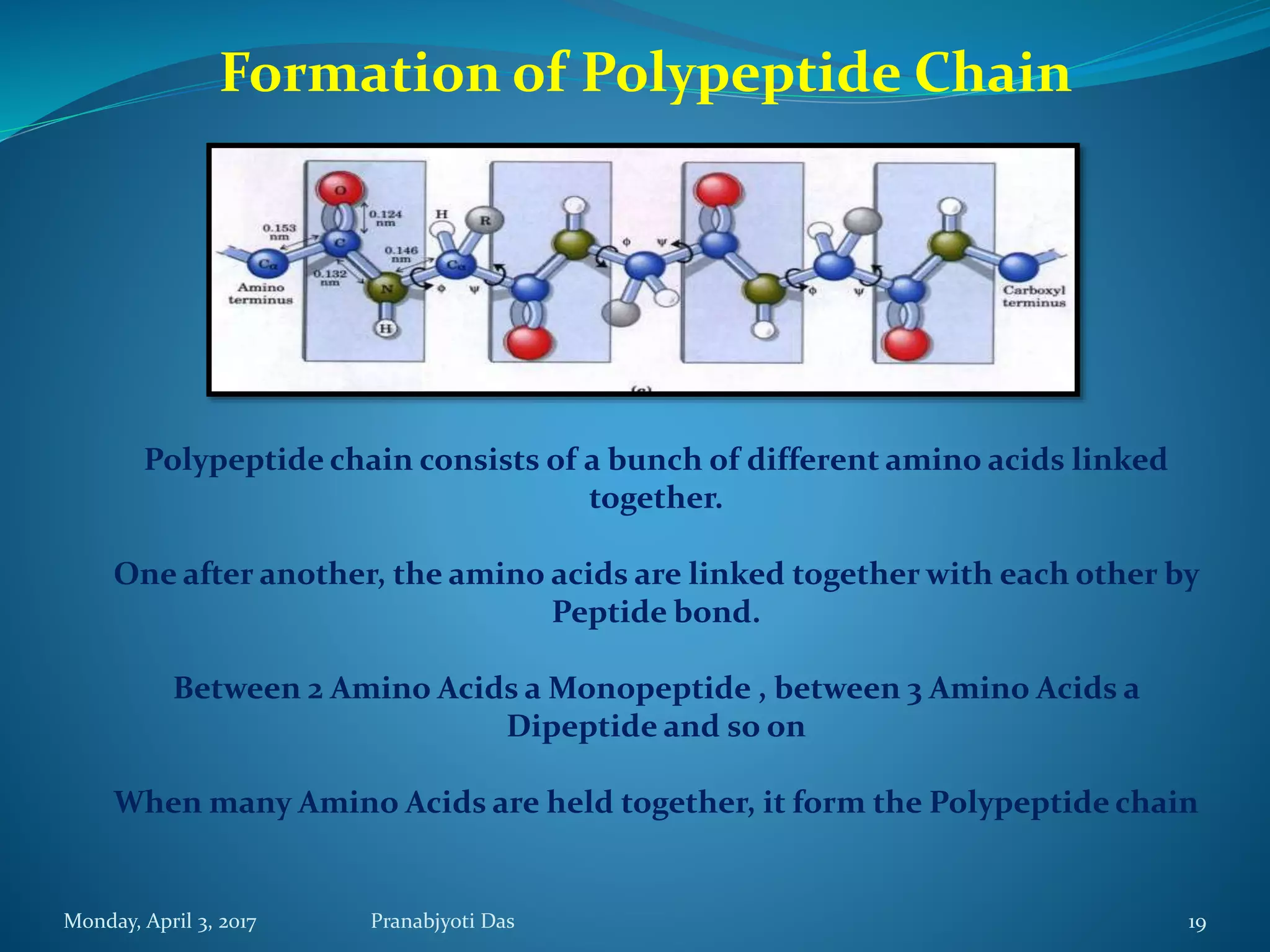
The document discusses proteins, including their structure, functions, and importance. It defines proteins as polymers of amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins. Amino acids are linked together via peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains, which then fold into complex protein structures like the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels. Proteins serve important roles in the body such as structure, storage, transport, hormones, receptors, movement, defense, and catalysis. They are essential biomolecules found in living cells.