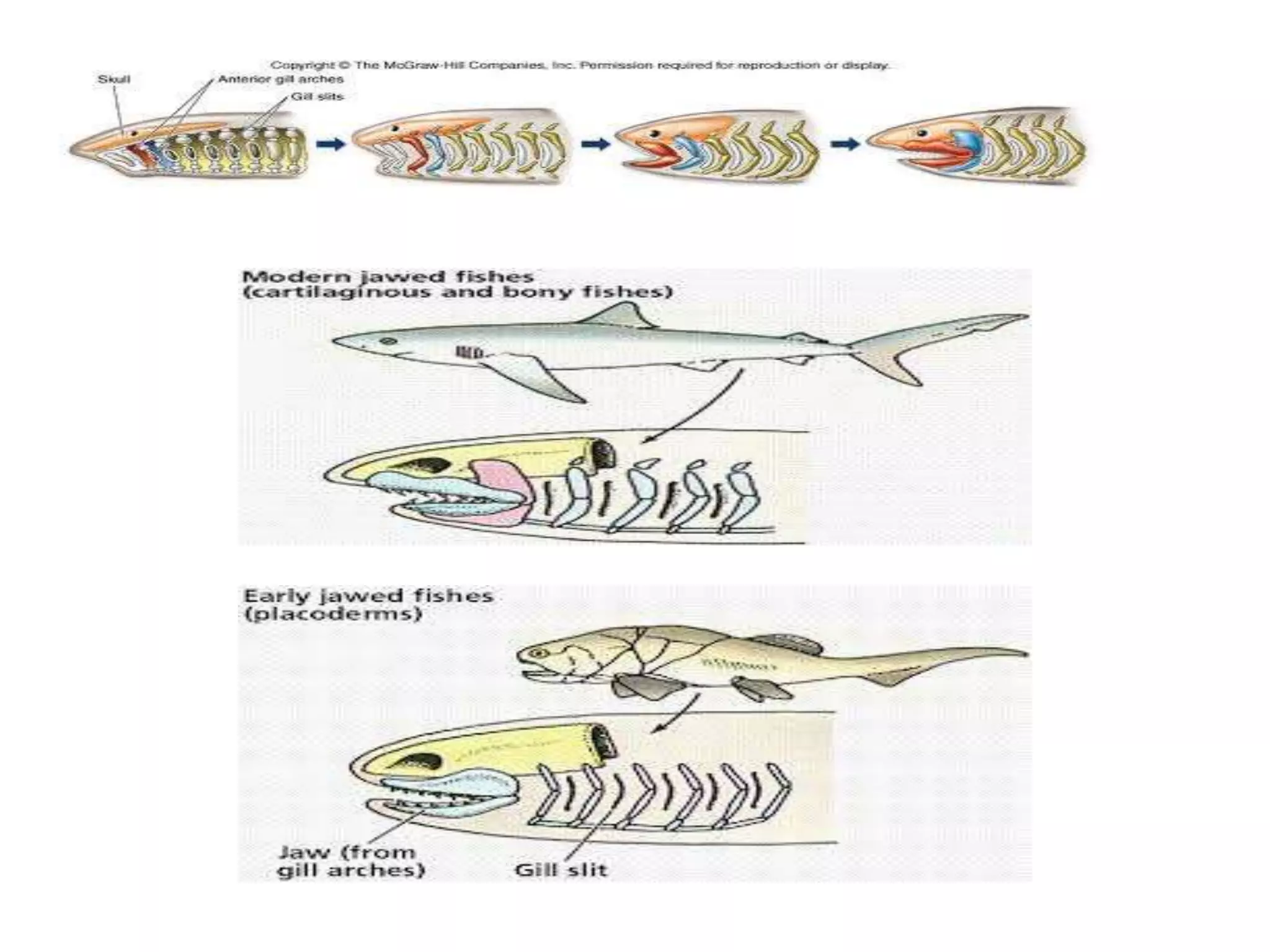
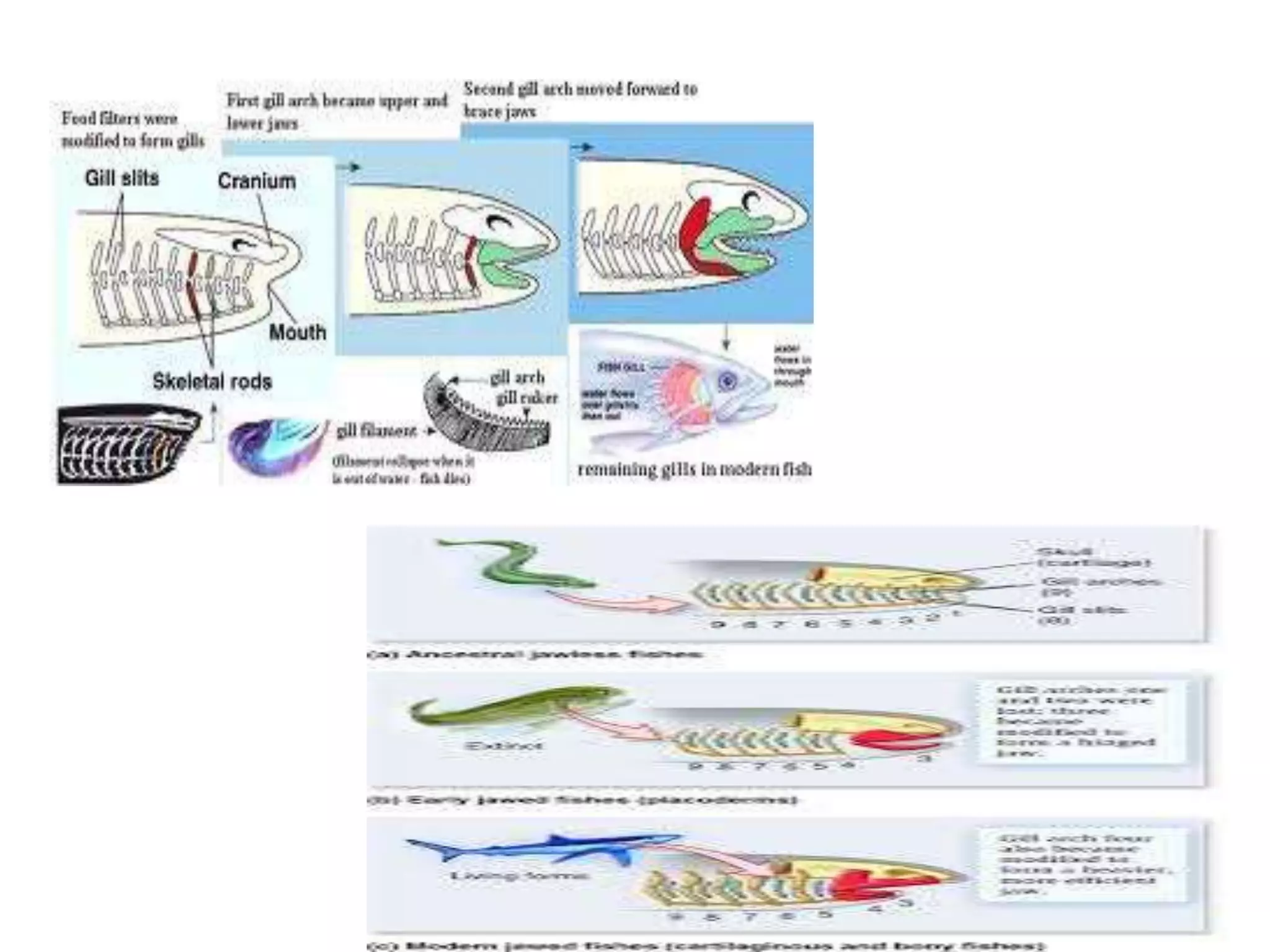
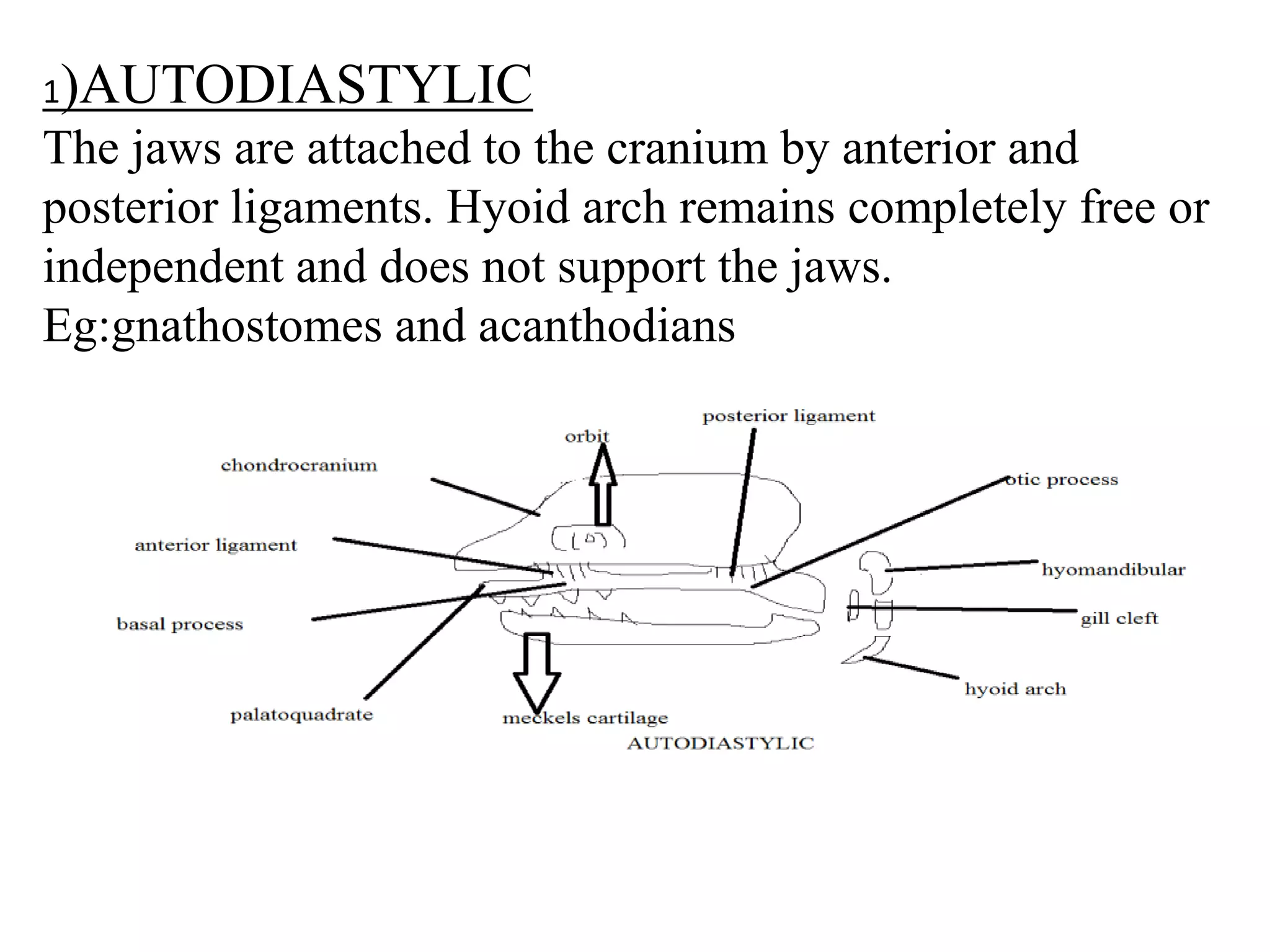
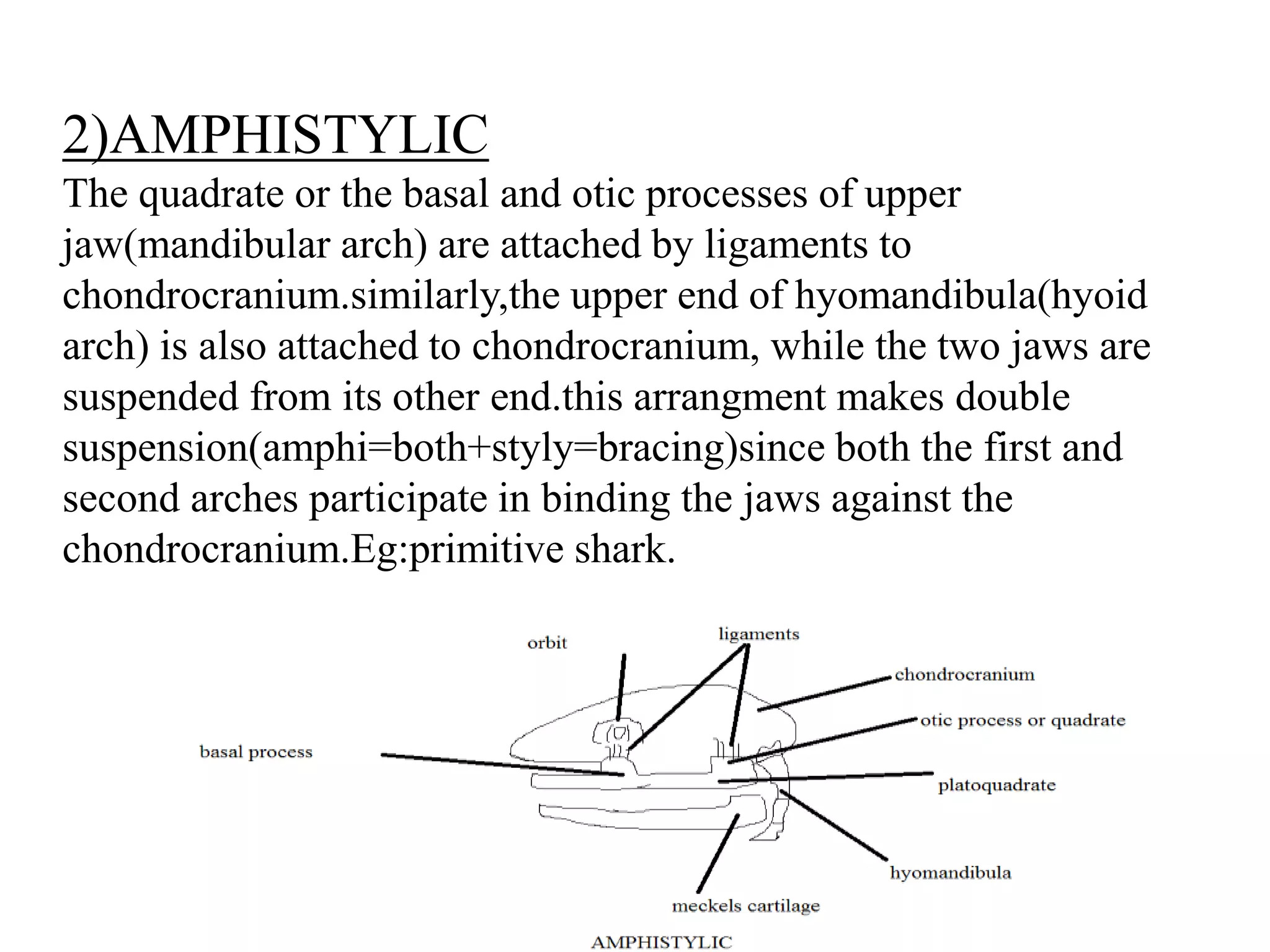
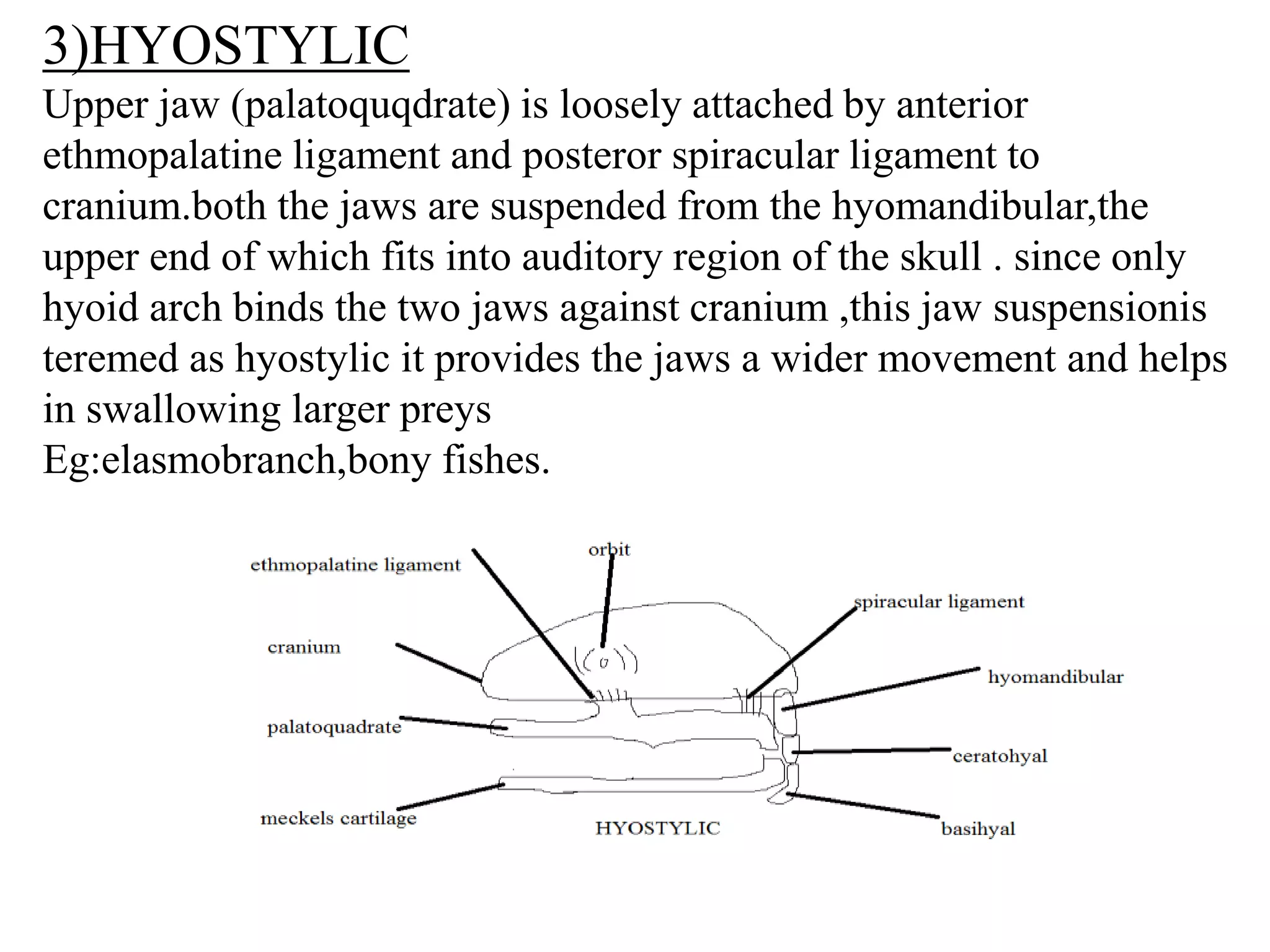
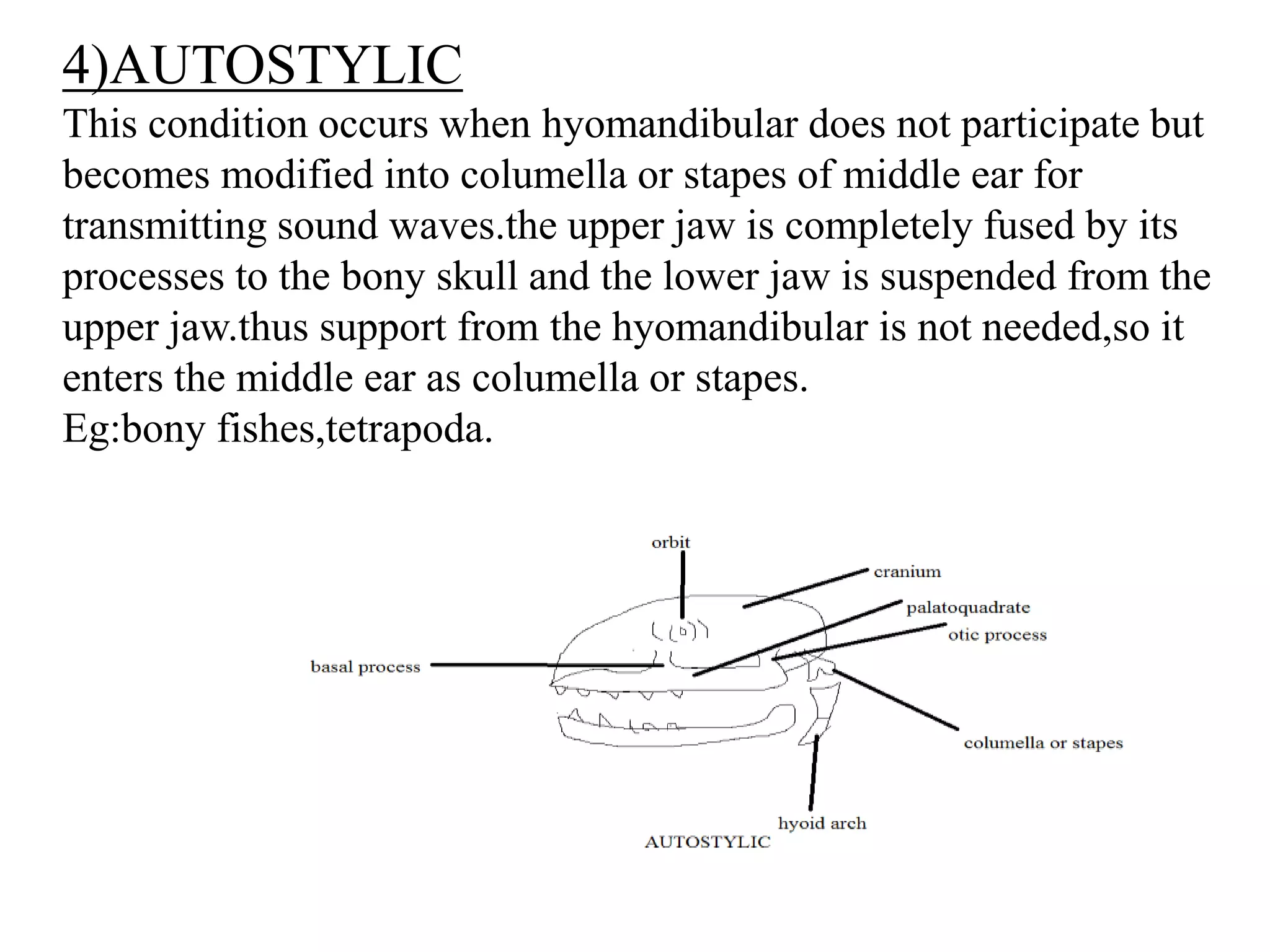
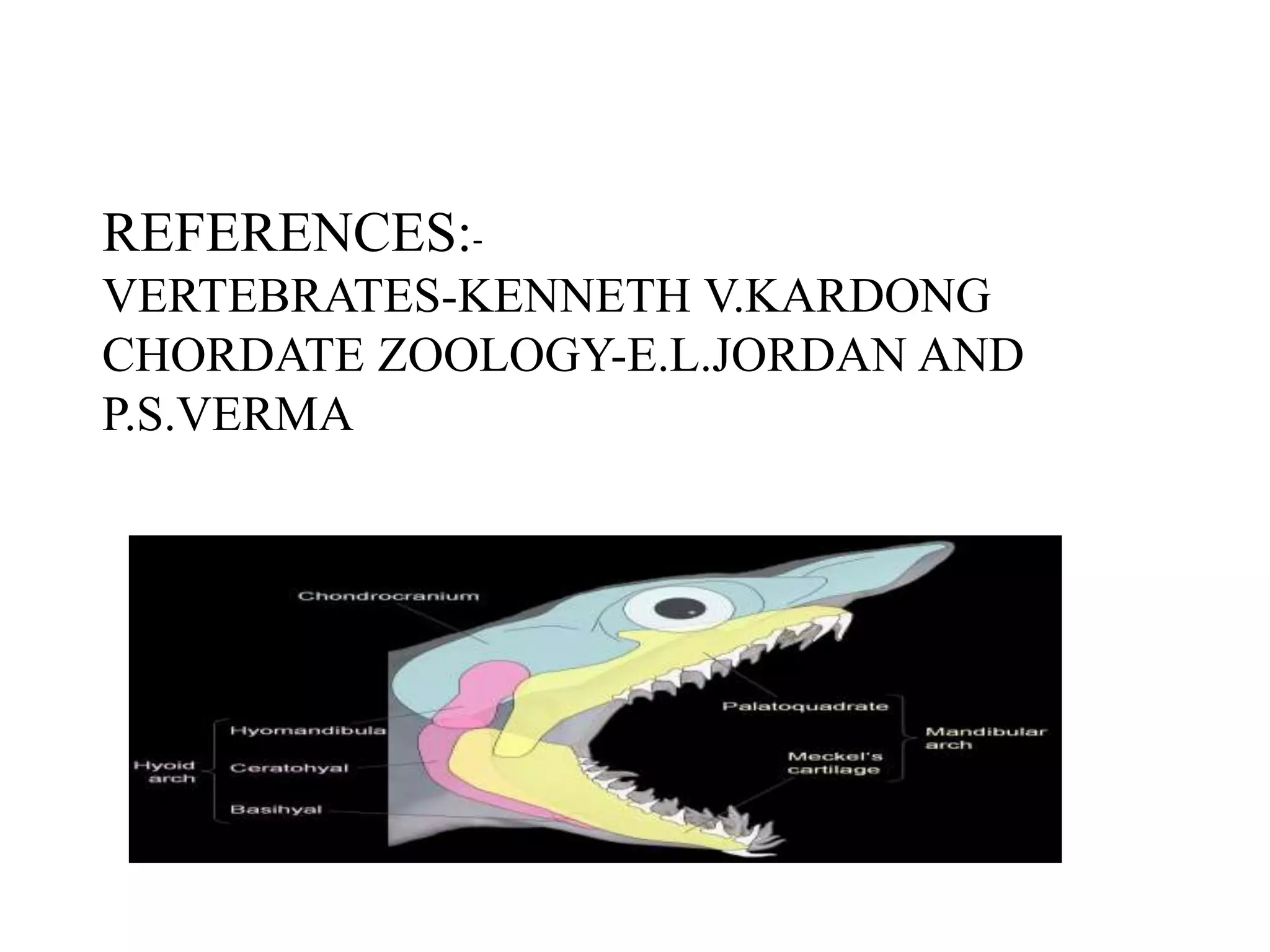
This document presents a comparative account of jaw suspension in vertebrates, detailing various attachment methods of jaws to the skull across different species. It outlines five main types of jaw suspension: autodiastylic, amphistylic, hyostylic, autostylic, and craniostylic, along with their characteristics and examples. The evolution of jaws is discussed, emphasizing the transition in feeding methods and the significance of jaw structure for predation in vertebrates.