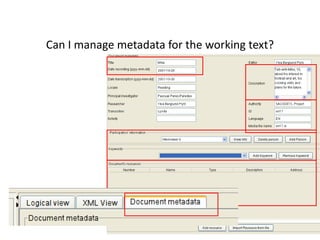
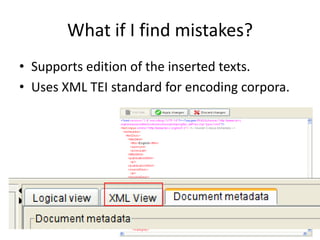
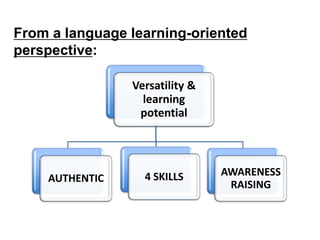
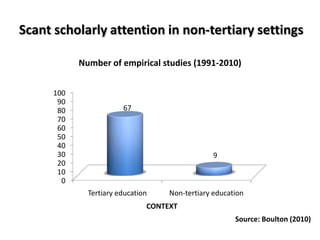
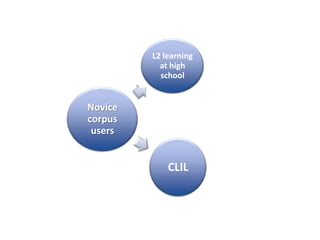
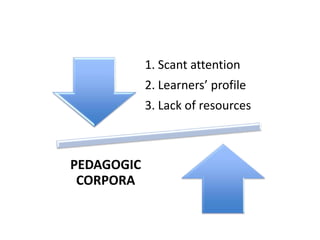
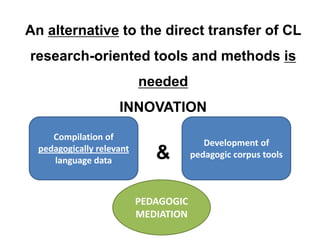
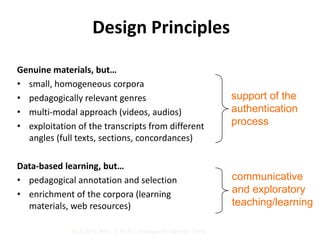
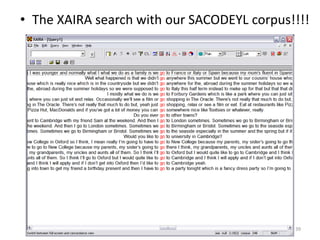
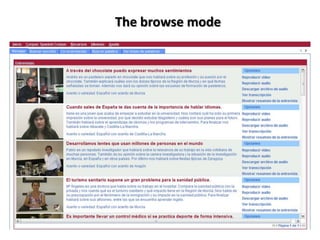
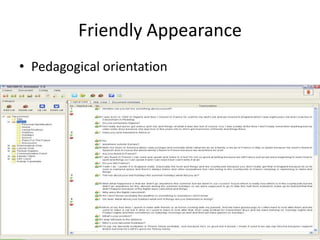
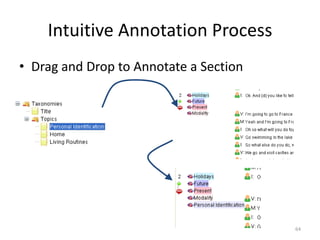
This document discusses using pedagogic corpora in English language teaching. It introduces pedagogic corpora as an alternative to directly transferring corpus linguistics research methods to the classroom. Pedagogic corpora are compiled with thematic relevance and recontextualization for authentication. The document also describes tools for annotating pedagogy in corpora and integrating corpus activities into English language and content-based instruction.









































![66
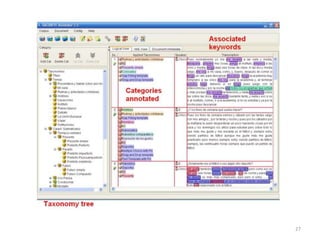
What is a Keyword?
• “… [a] keyword is a stretch of language (a
word, more than one word or a whole
paragraph) that the annotator associates to a
category…”
Pérez-Paredes and Alcaraz, ReCALL, Jan. 2009
Vol 21. (1) (Forthcoming)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingpedagogiccorporainelteurocall2013def1-130917034355-phpapp02/85/Using-pedagogic-corpora-in-ELT-66-320.jpg)