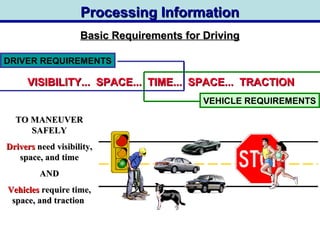
Drivers must consider visibility, space, time, and traction when maneuvering their vehicle. They need to search for potential hazards by scanning their field of vision from 4-30 seconds ahead. When passing, drivers must determine if they are in a legal passing zone, calculate the time and space needed to pass safely based on vehicle speeds, and check for oncoming traffic to ensure adequate distance to complete the maneuver. Failing to properly process roadway information and plan maneuvers can lead to unsafe driving situations.