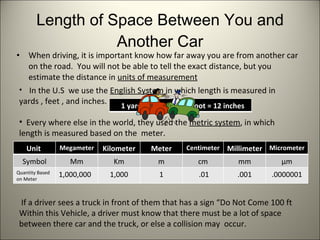
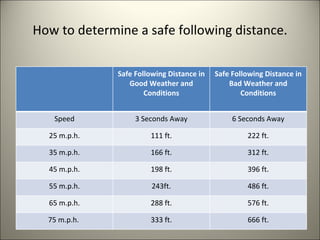
This document discusses several factors that affect driving safety, including reaction time, speed limits, braking distance, and traffic signals. It explains that reaction time is slowed by distractions, drugs, alcohol, fatigue and other factors. Safe driving requires maintaining accurate speeds and safe following distances that take into account braking distances, which increase exponentially with speed. Traffic signals introduce a "dilemma zone" where drivers may not have enough time to stop or proceed safely through an intersection when the light turns yellow.