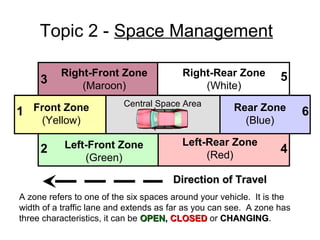
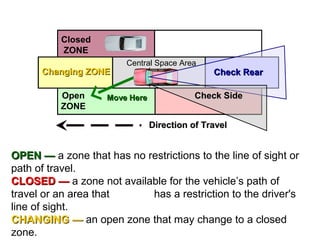
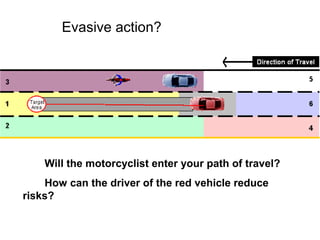
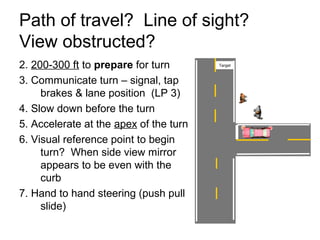
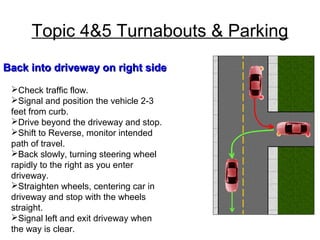
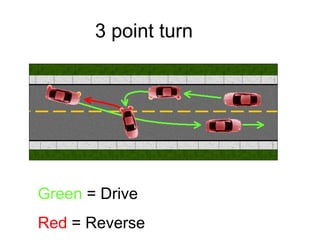
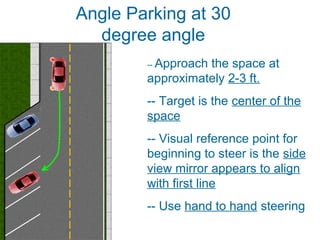
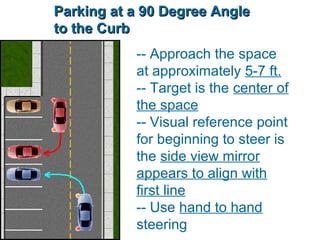
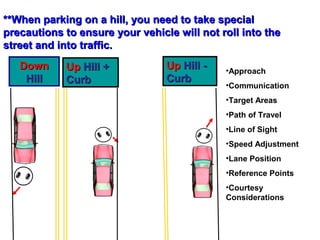
This document discusses risk assessment and space management strategies for driving. It defines risk as the chance of injury, damage or loss from a crash, and identifies behaviors that increase risk like speeding and distracted driving. It describes how to assess open, closed and changing zones around your vehicle to manage space. The document provides guidance on turning, lane changes, parking and turnabouts including techniques for path of travel, reference points, signaling and reducing risks.