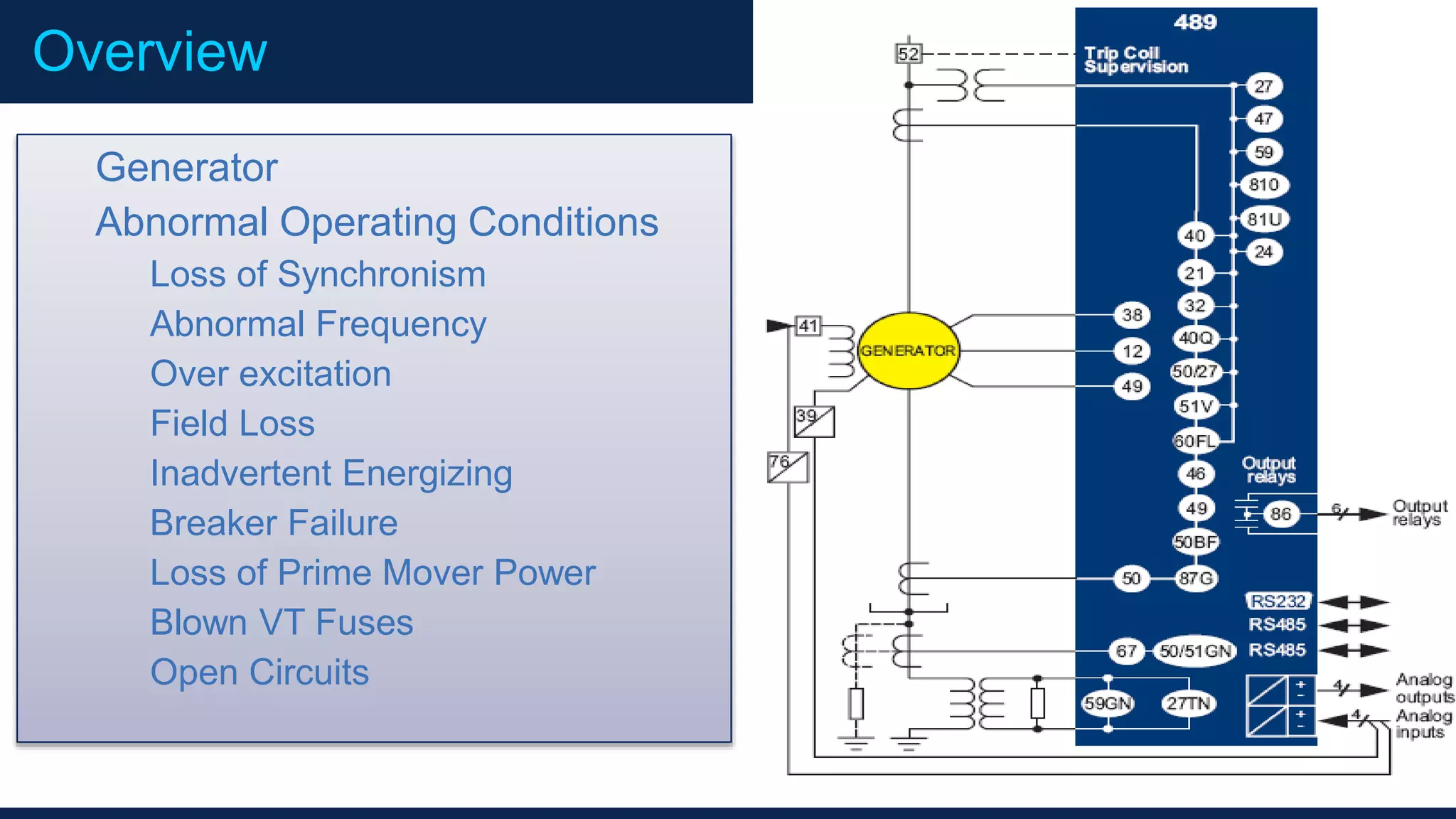
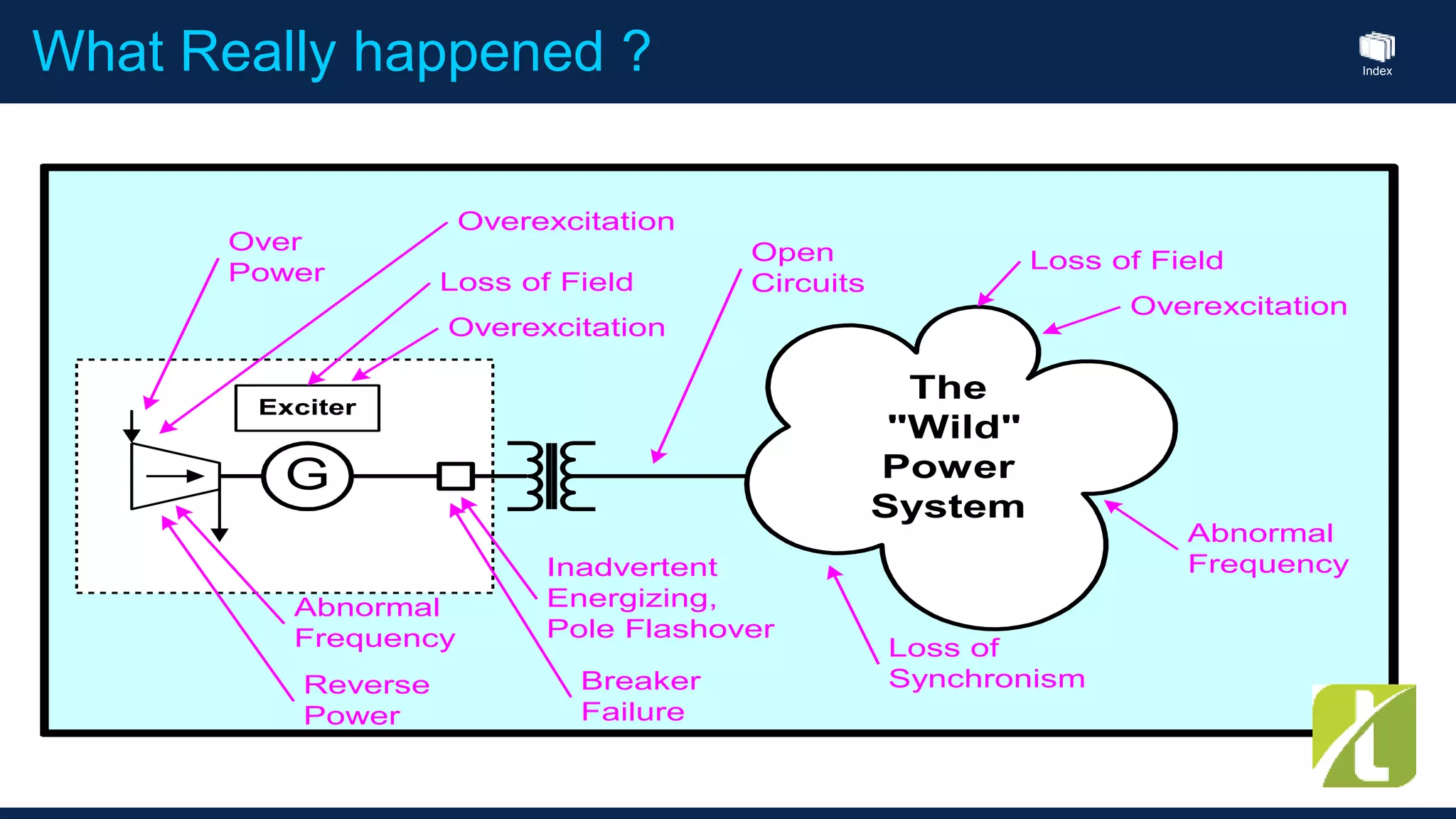
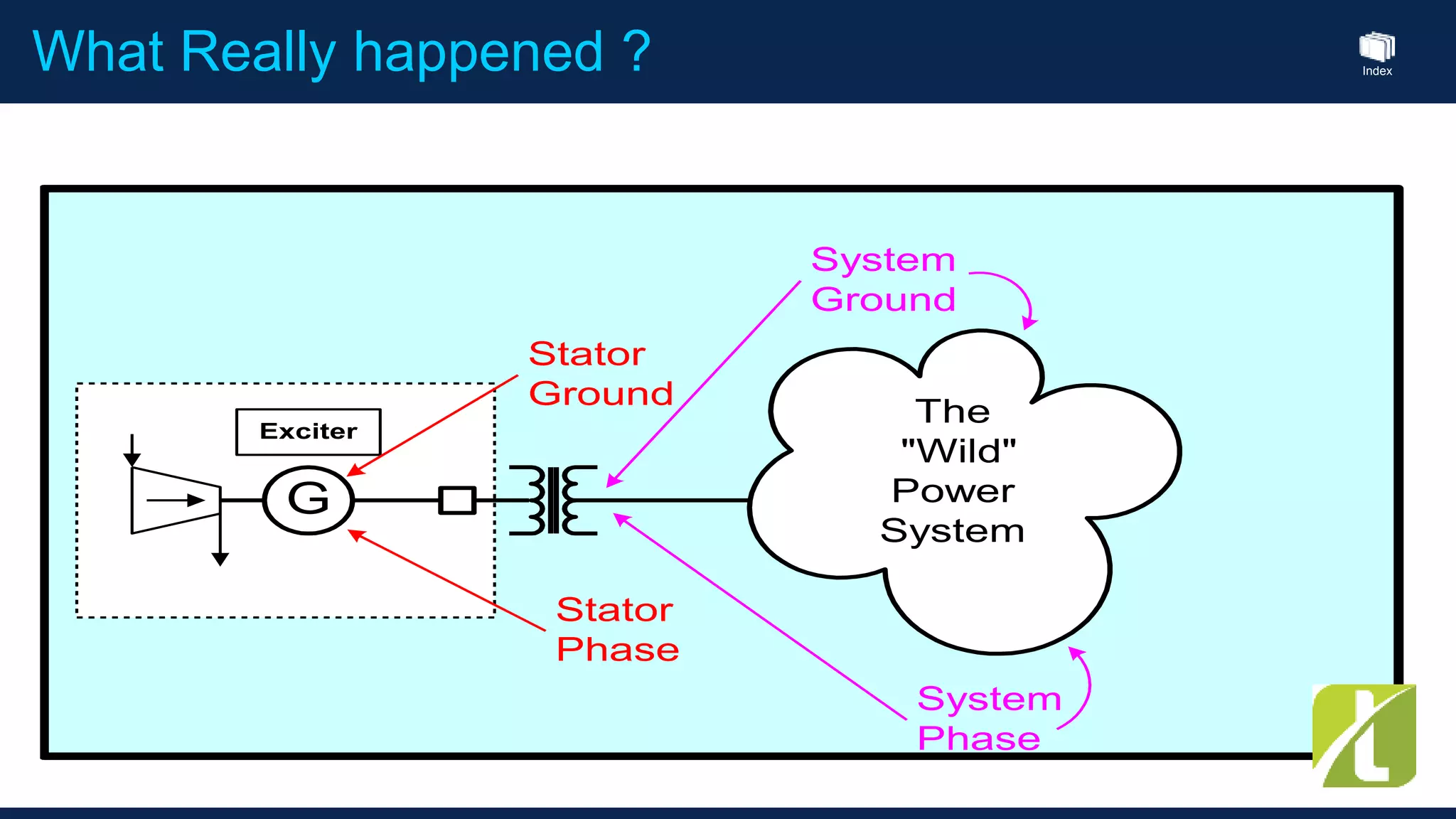
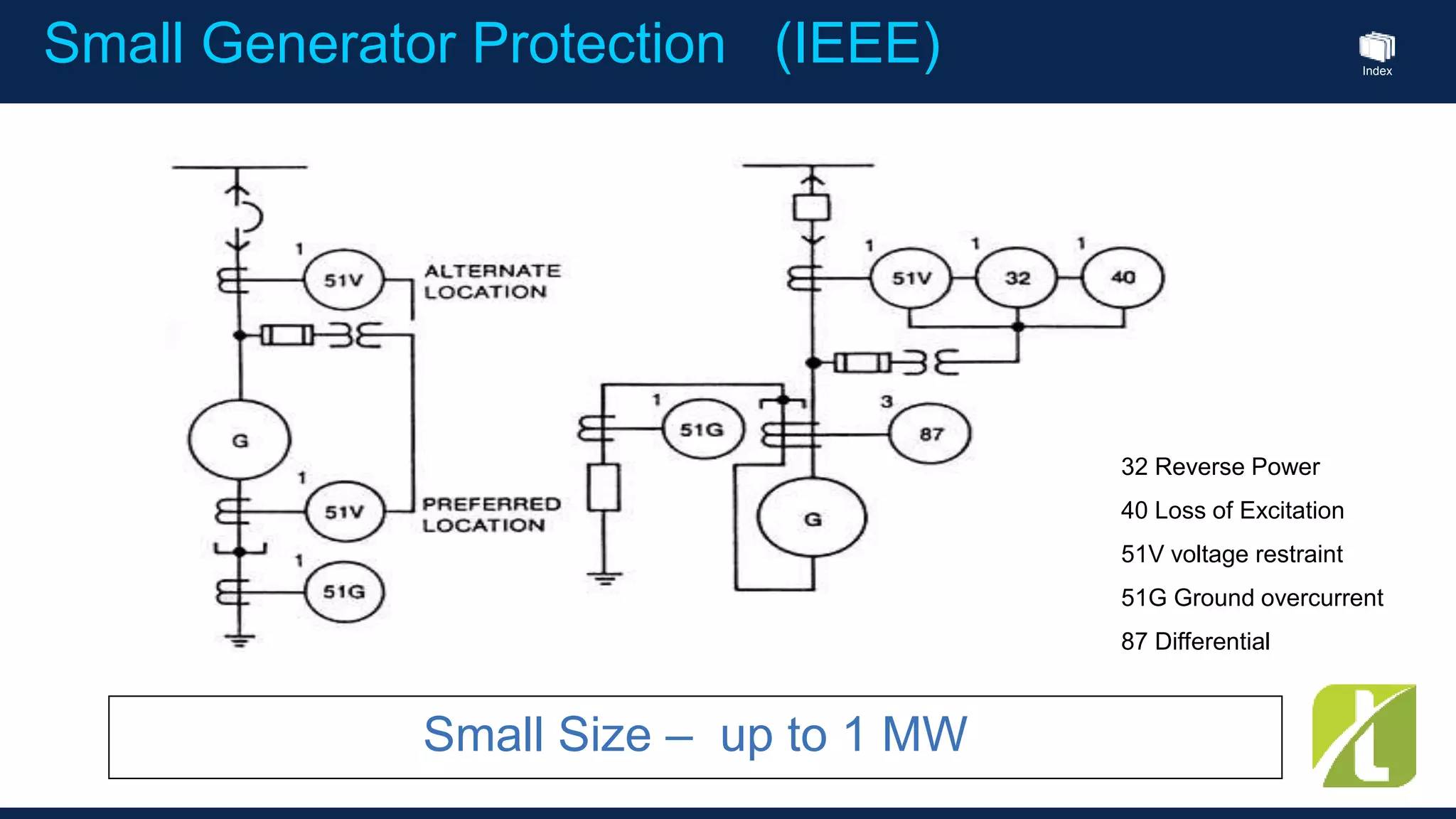
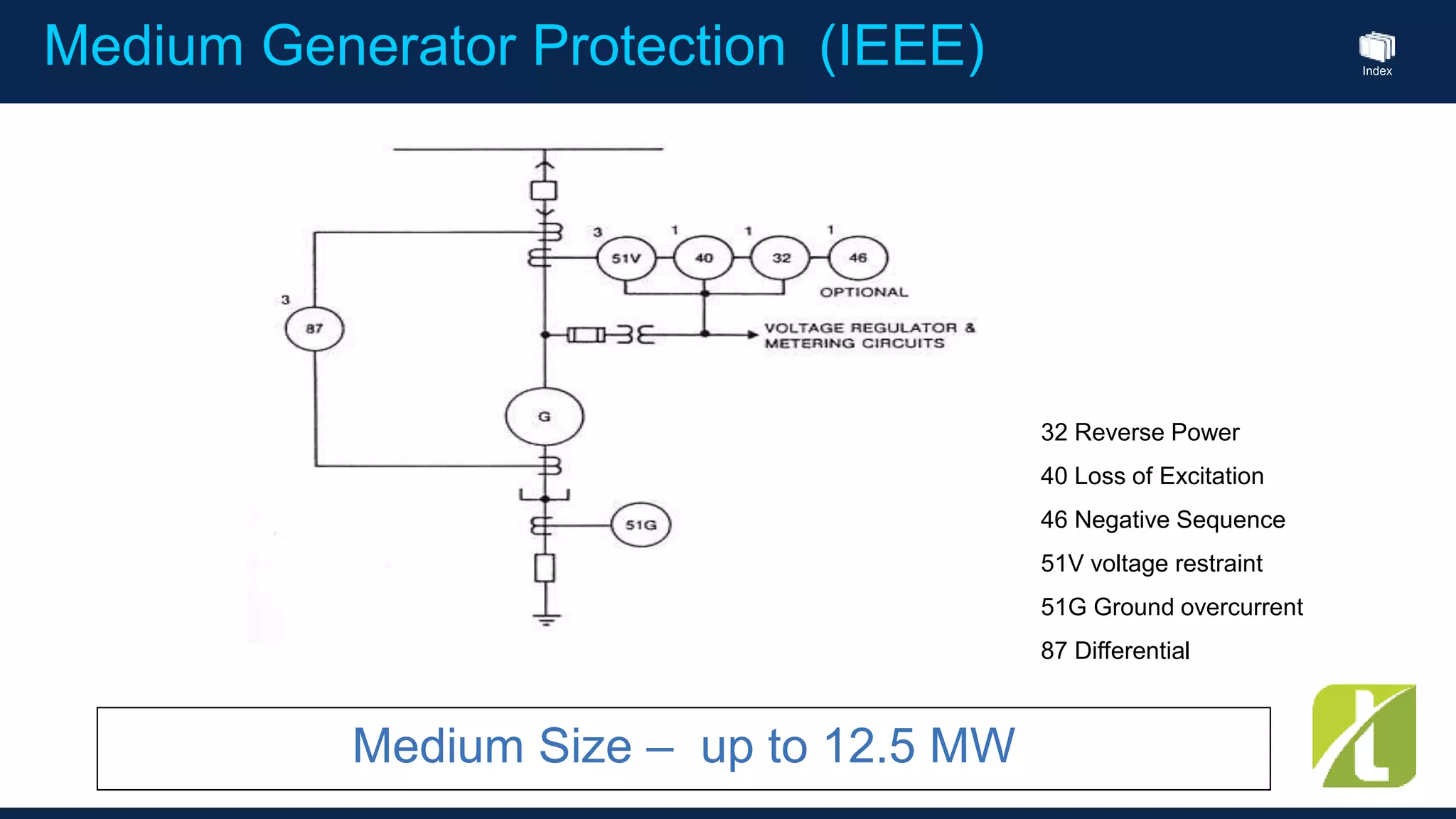
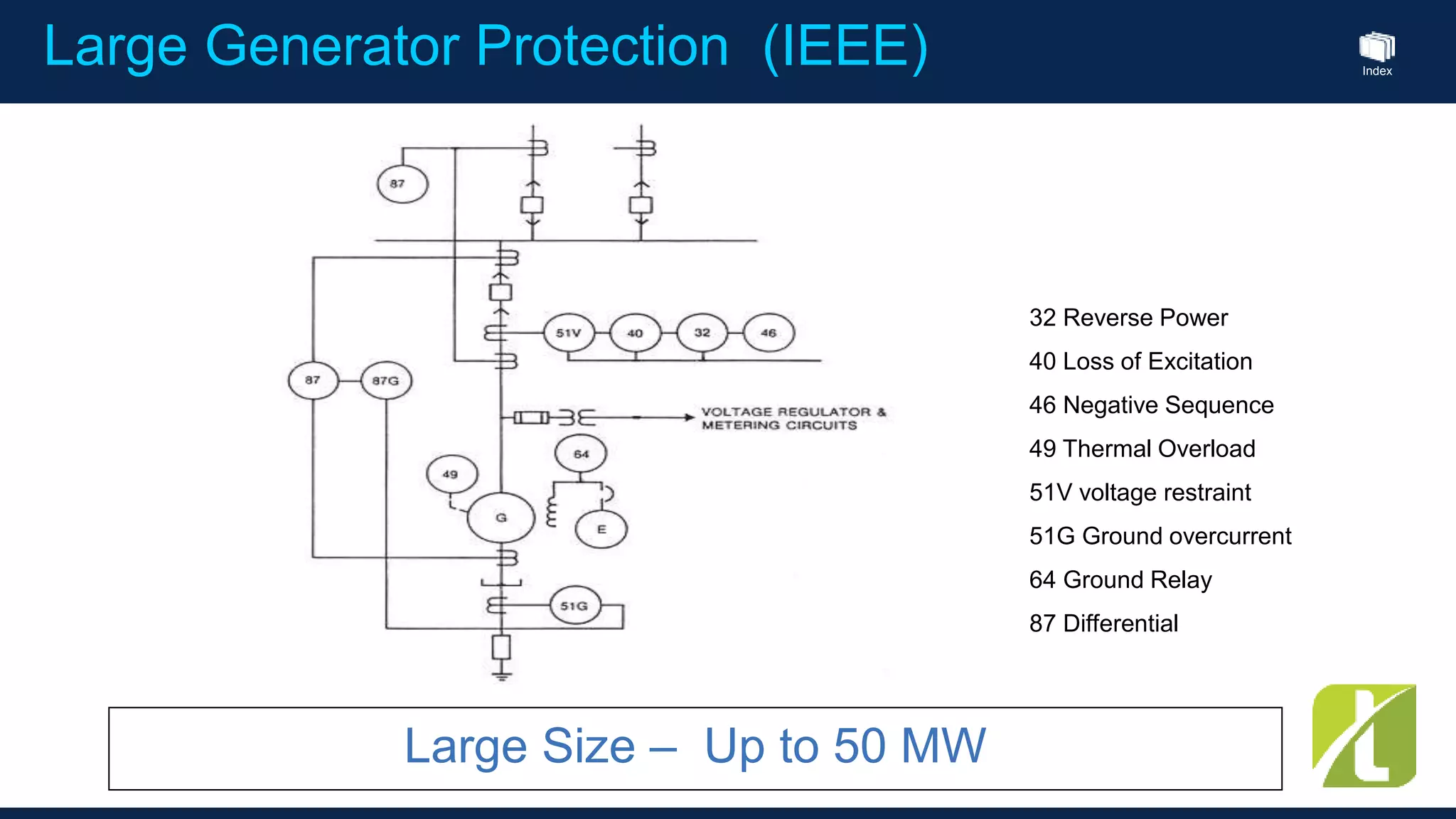
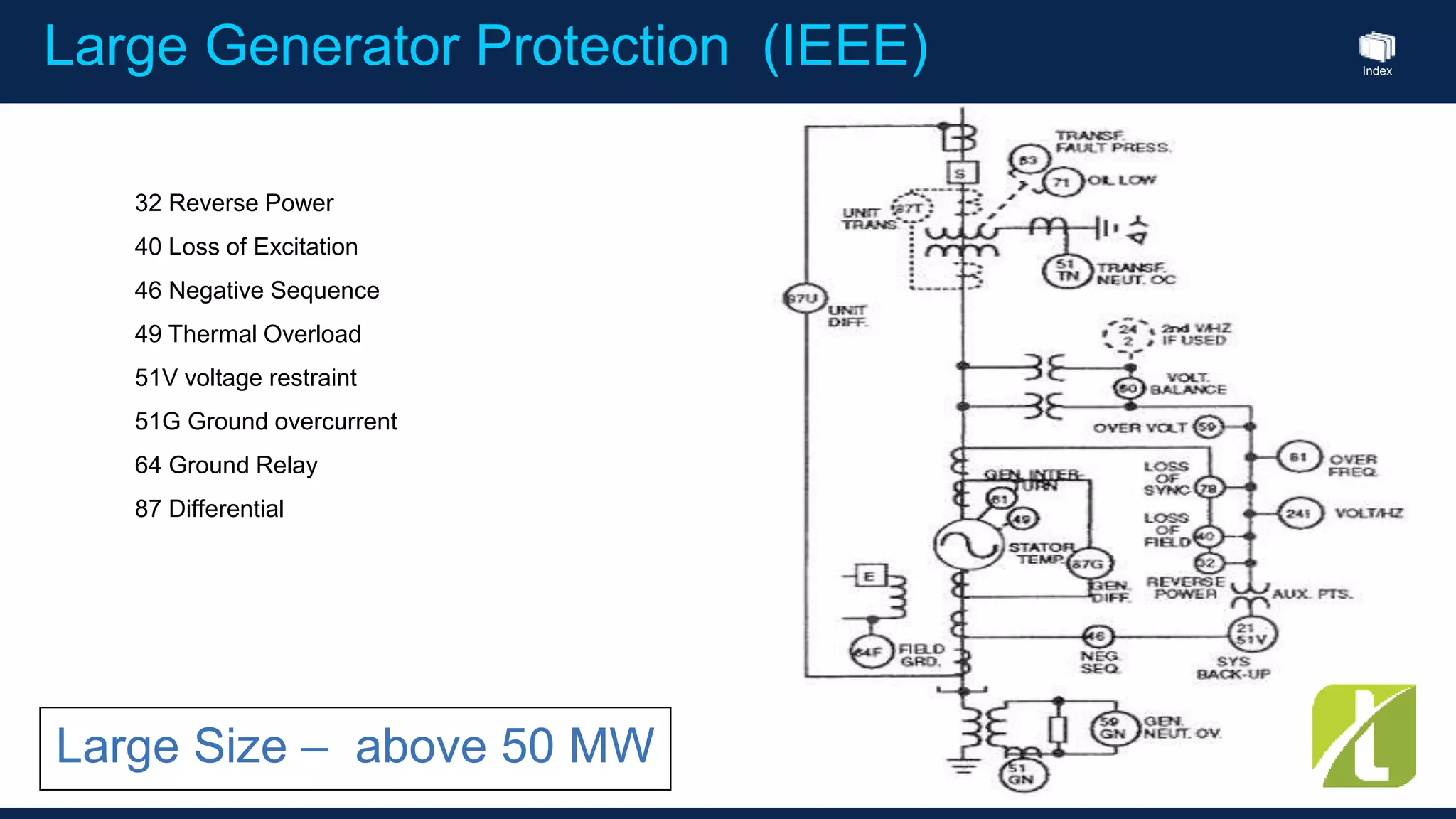
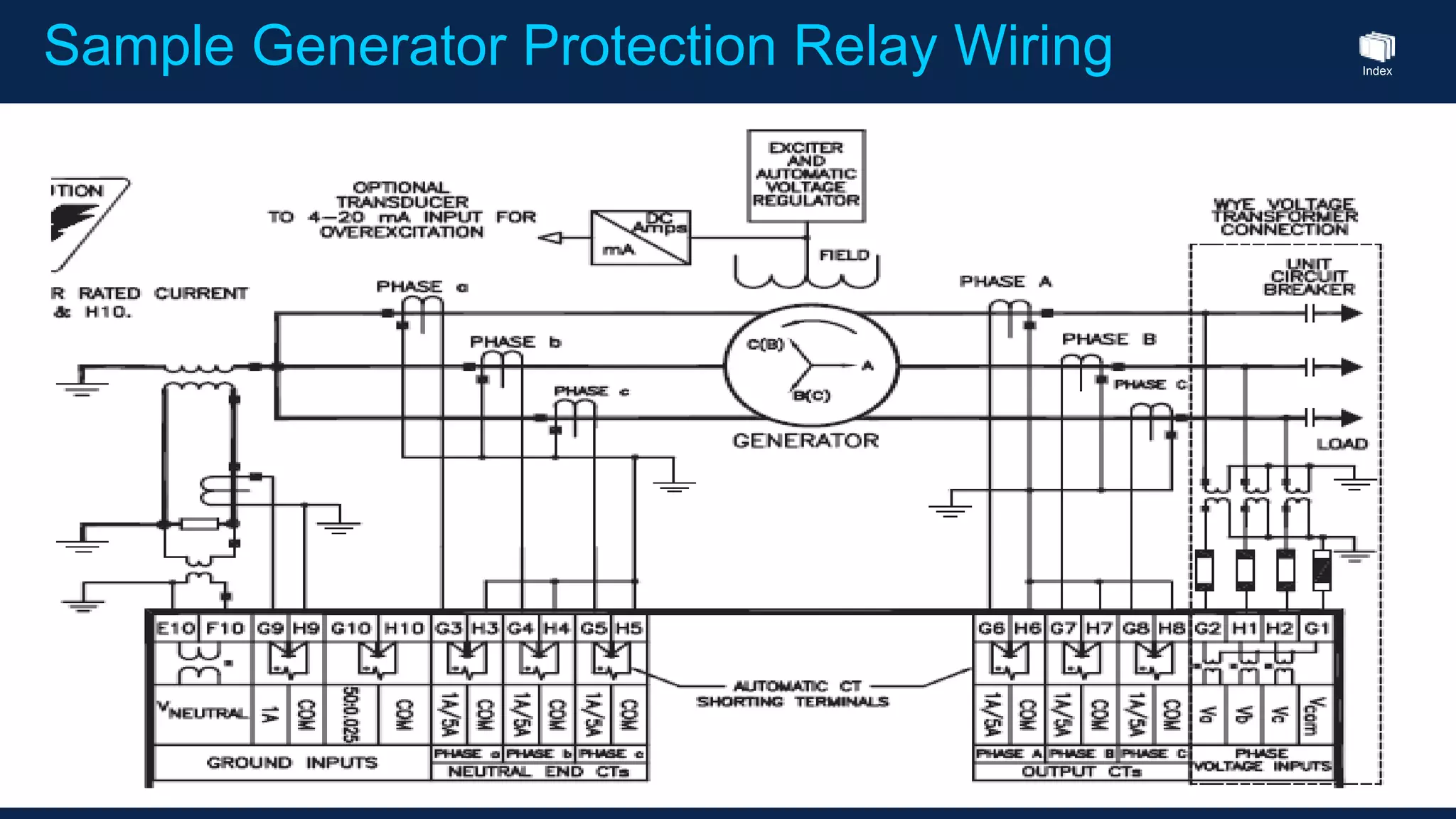
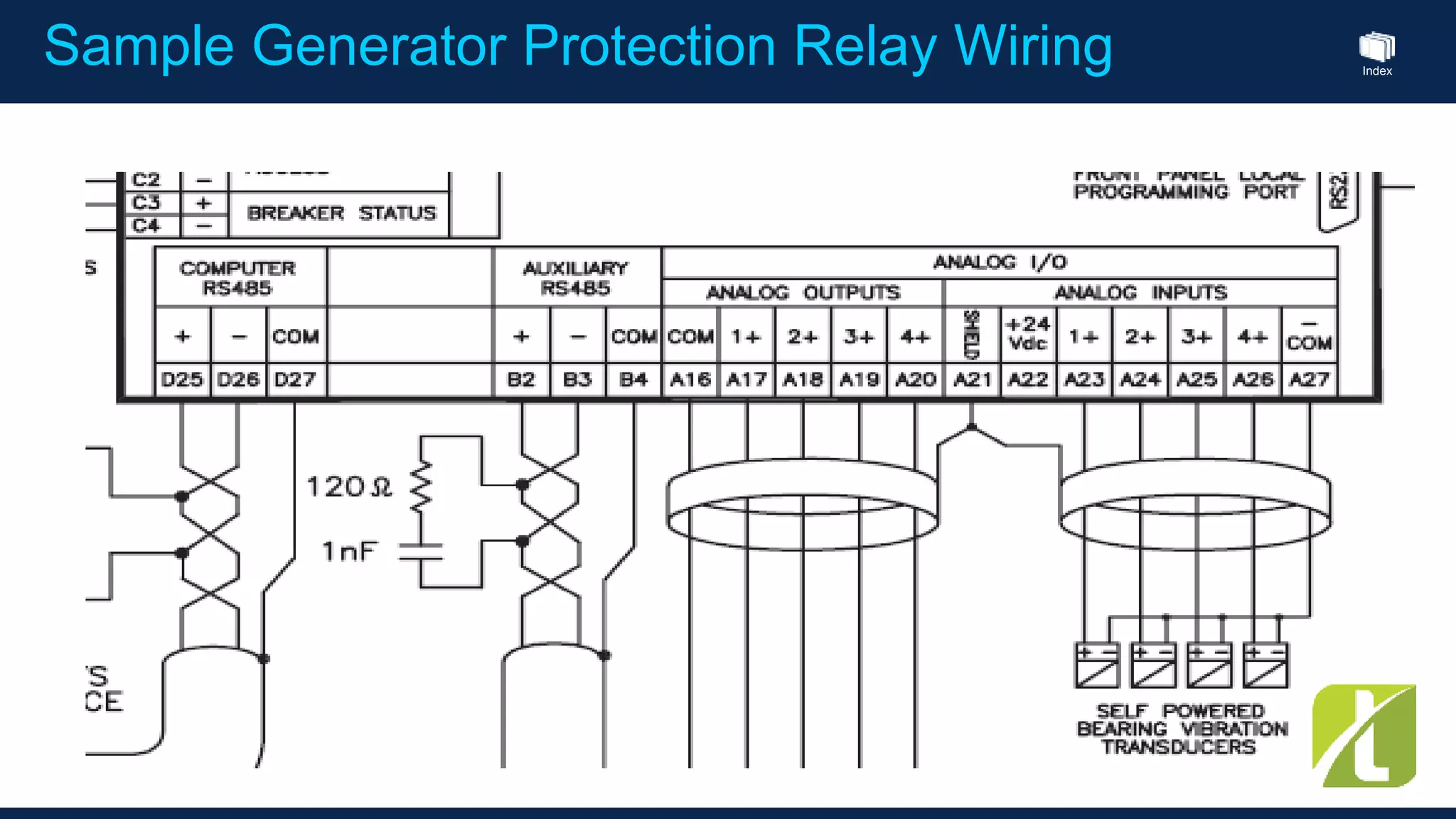
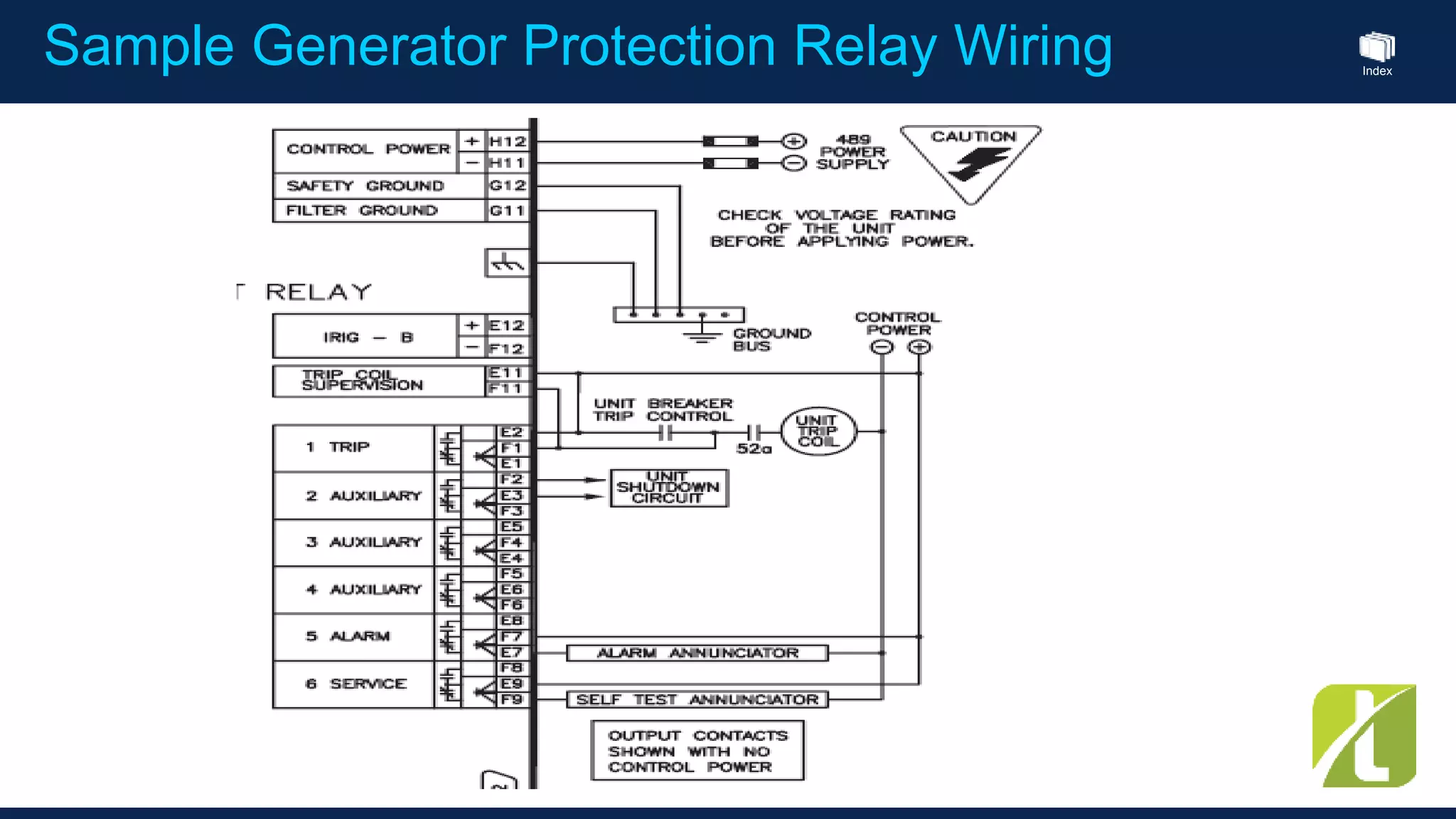
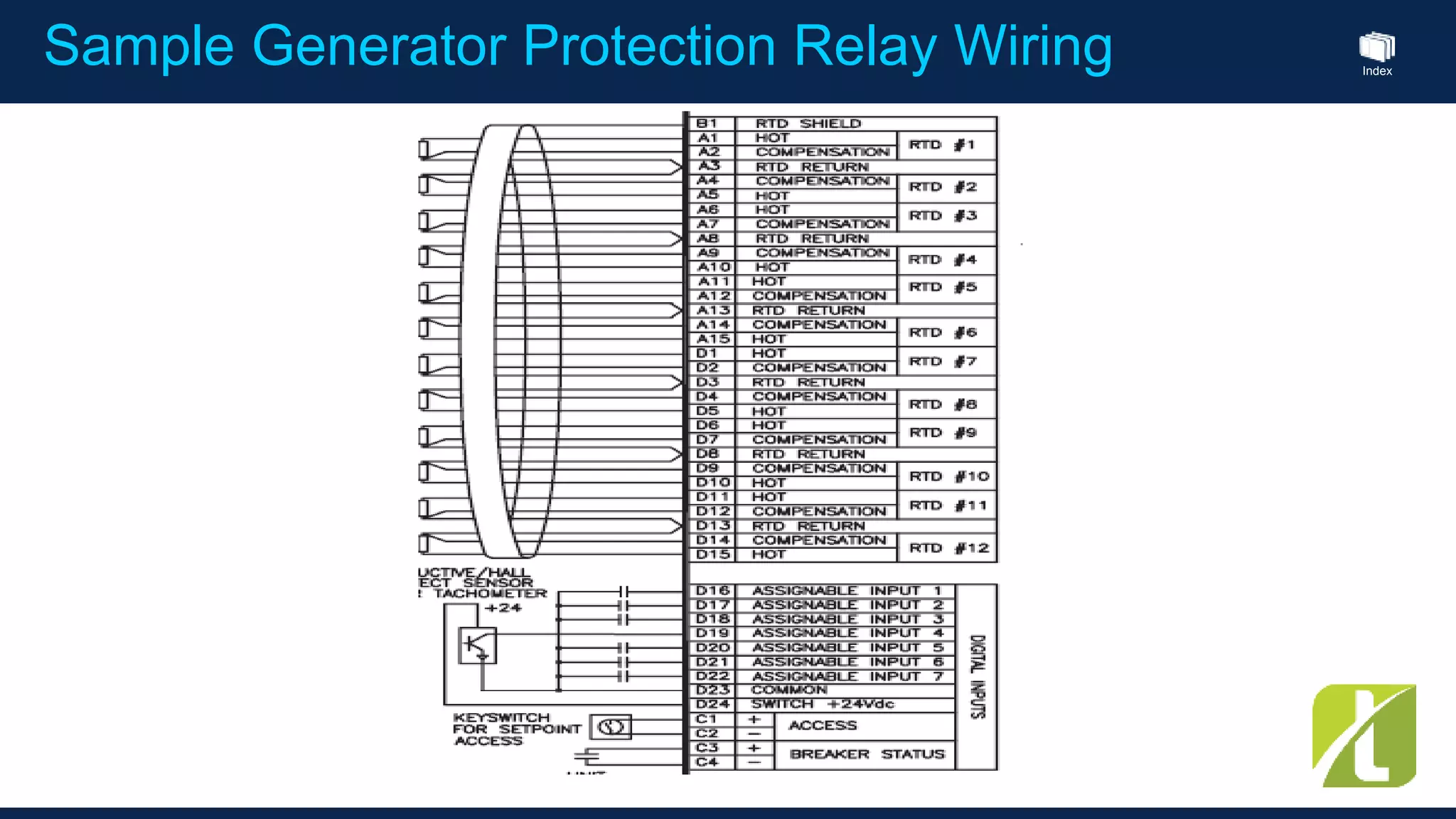
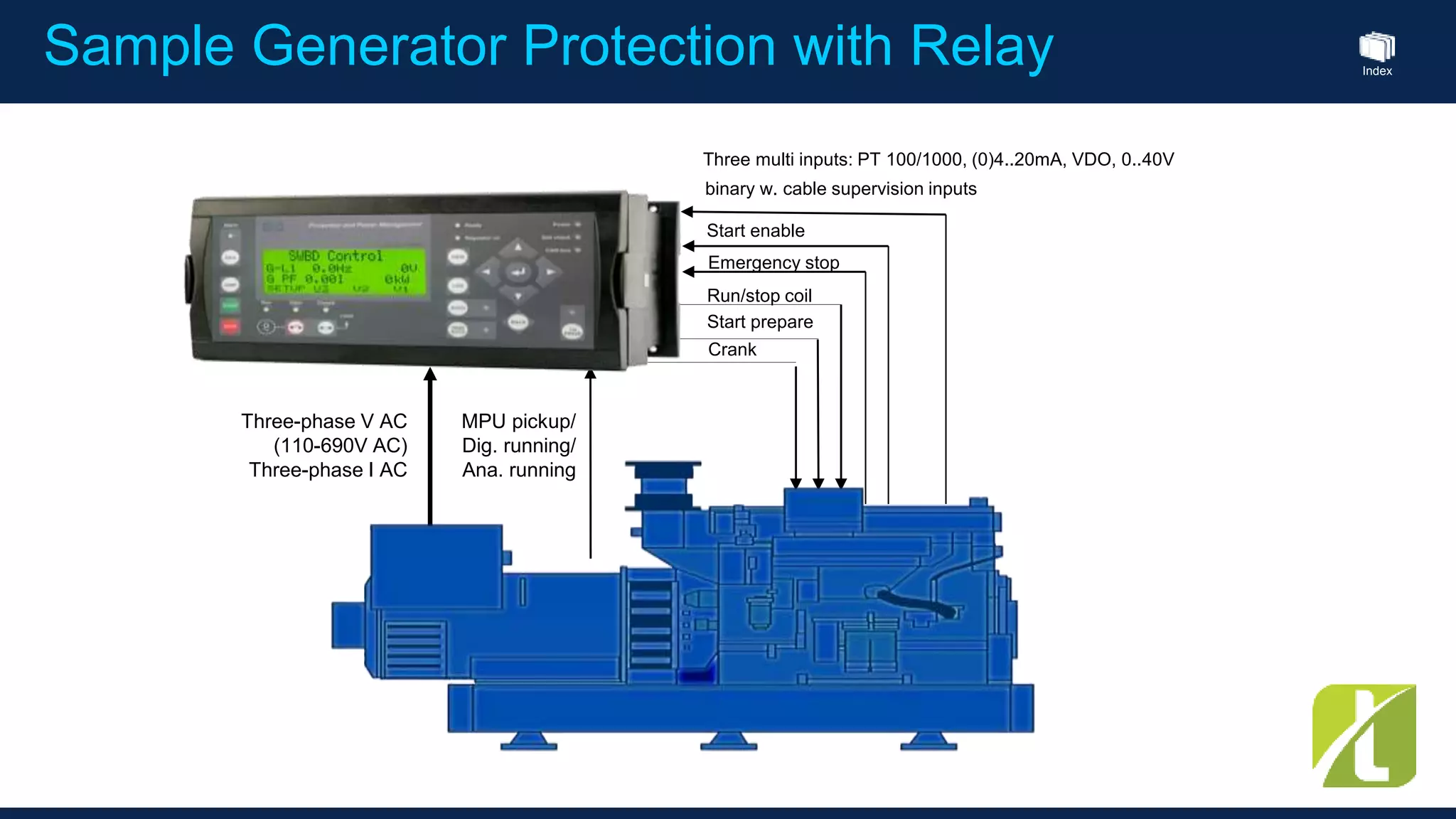
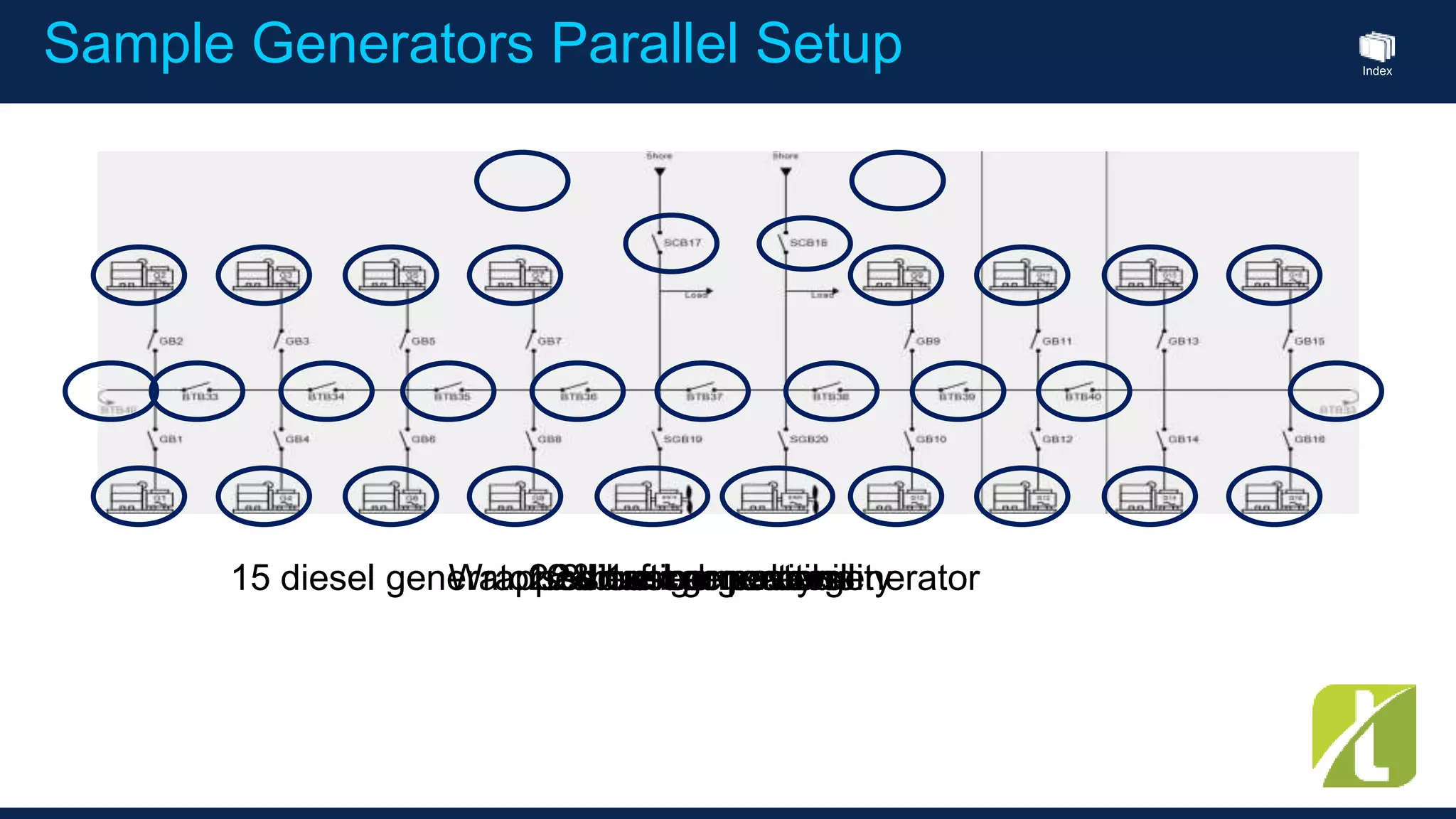
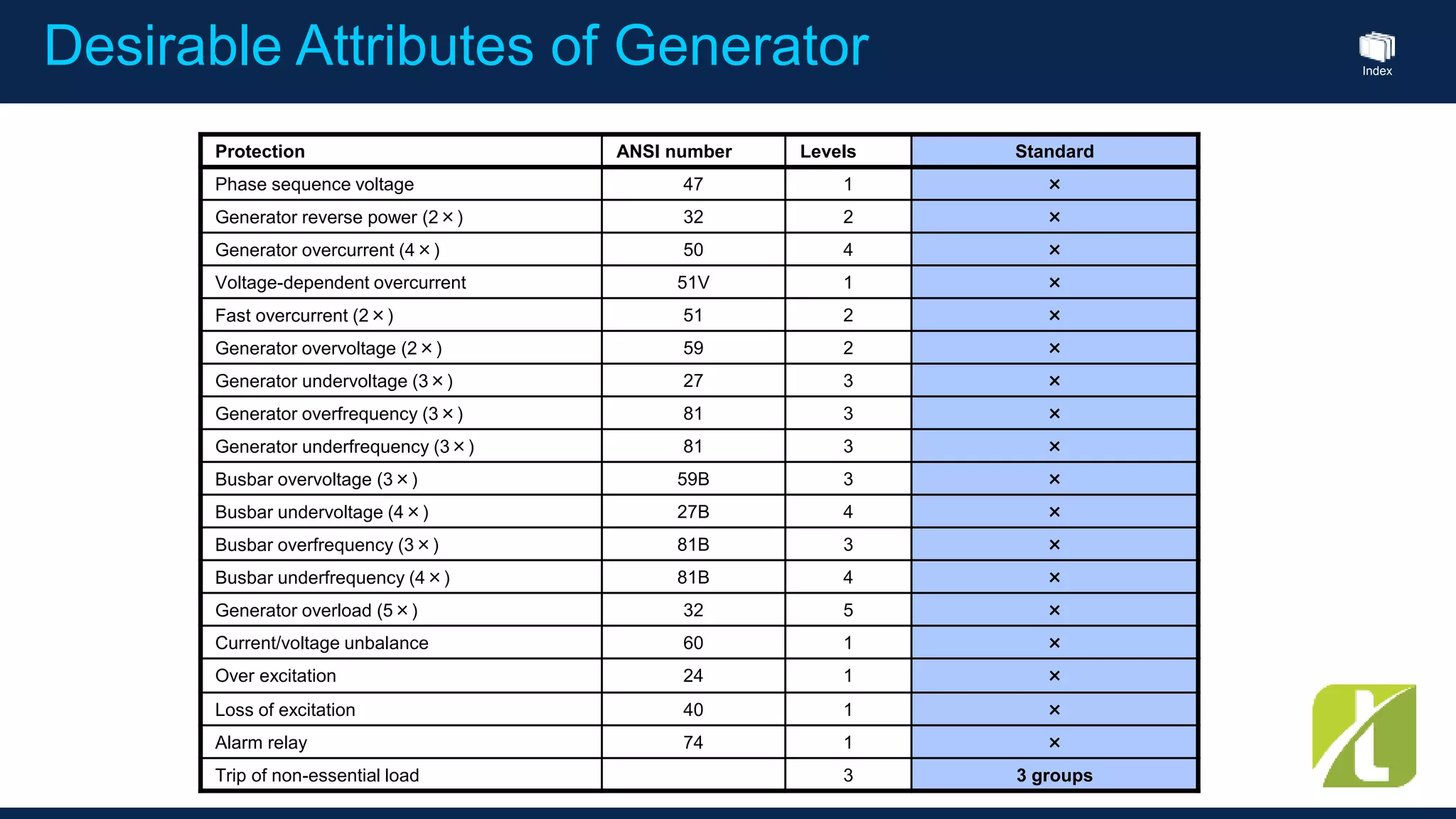
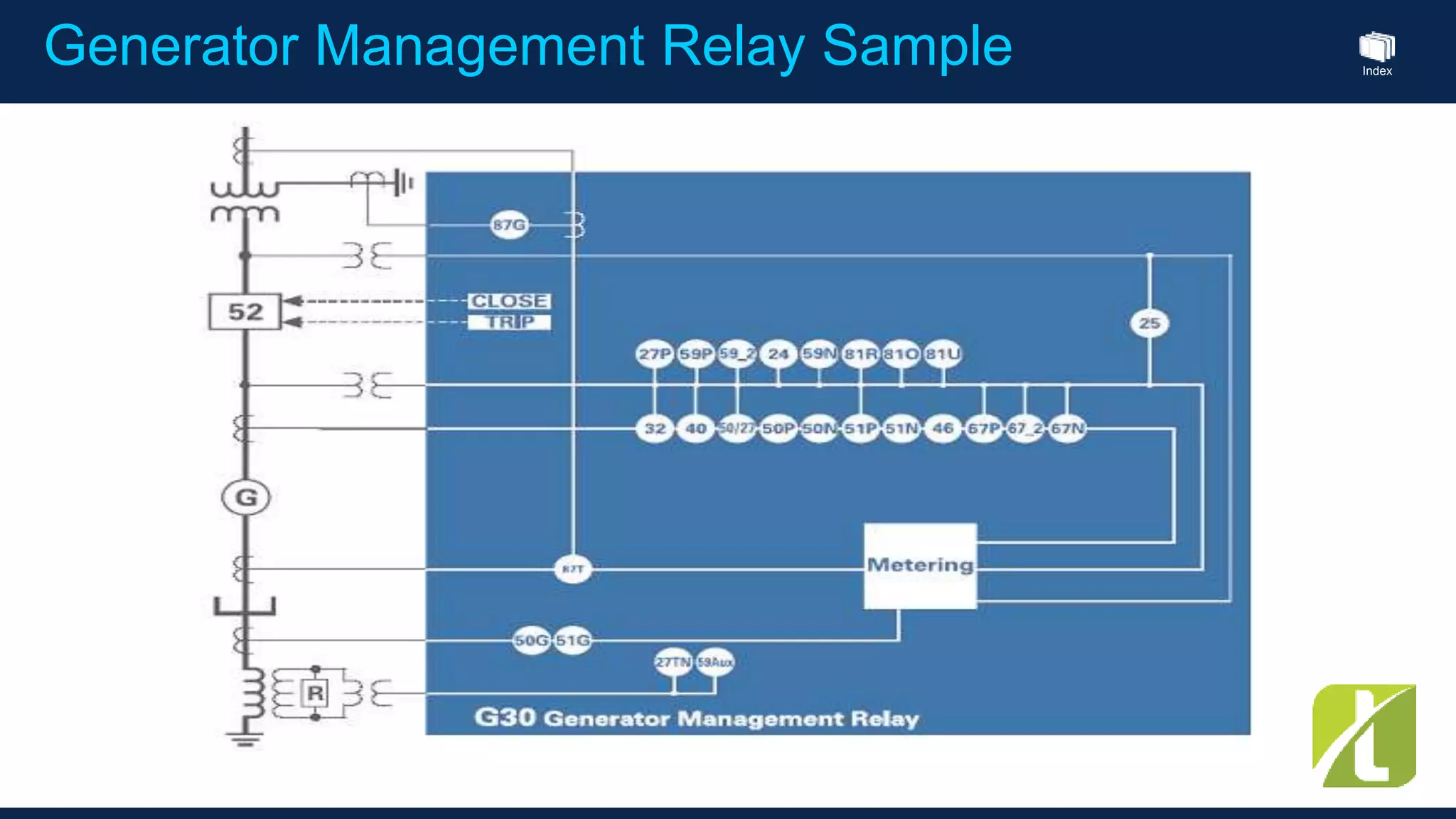
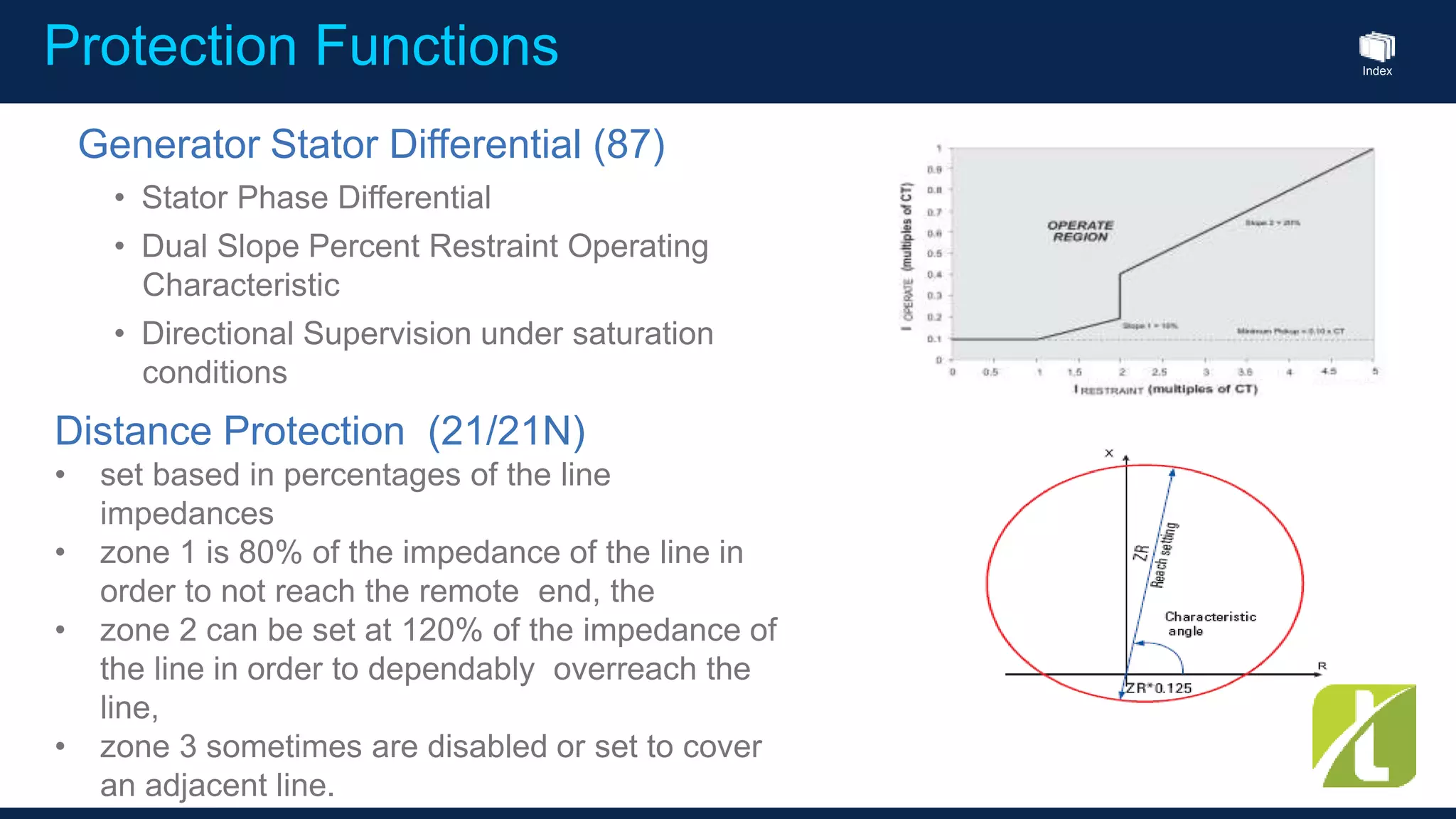
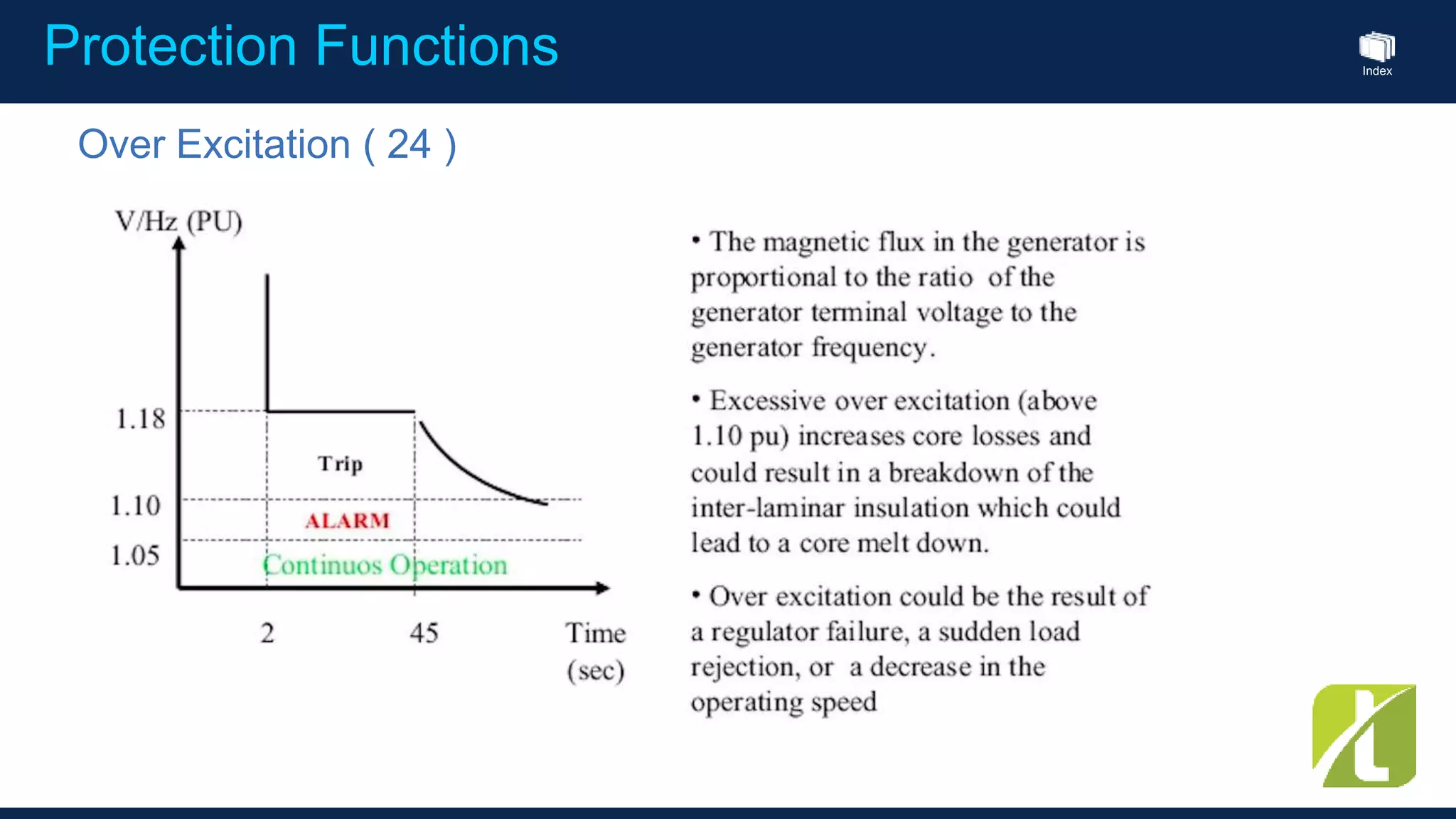
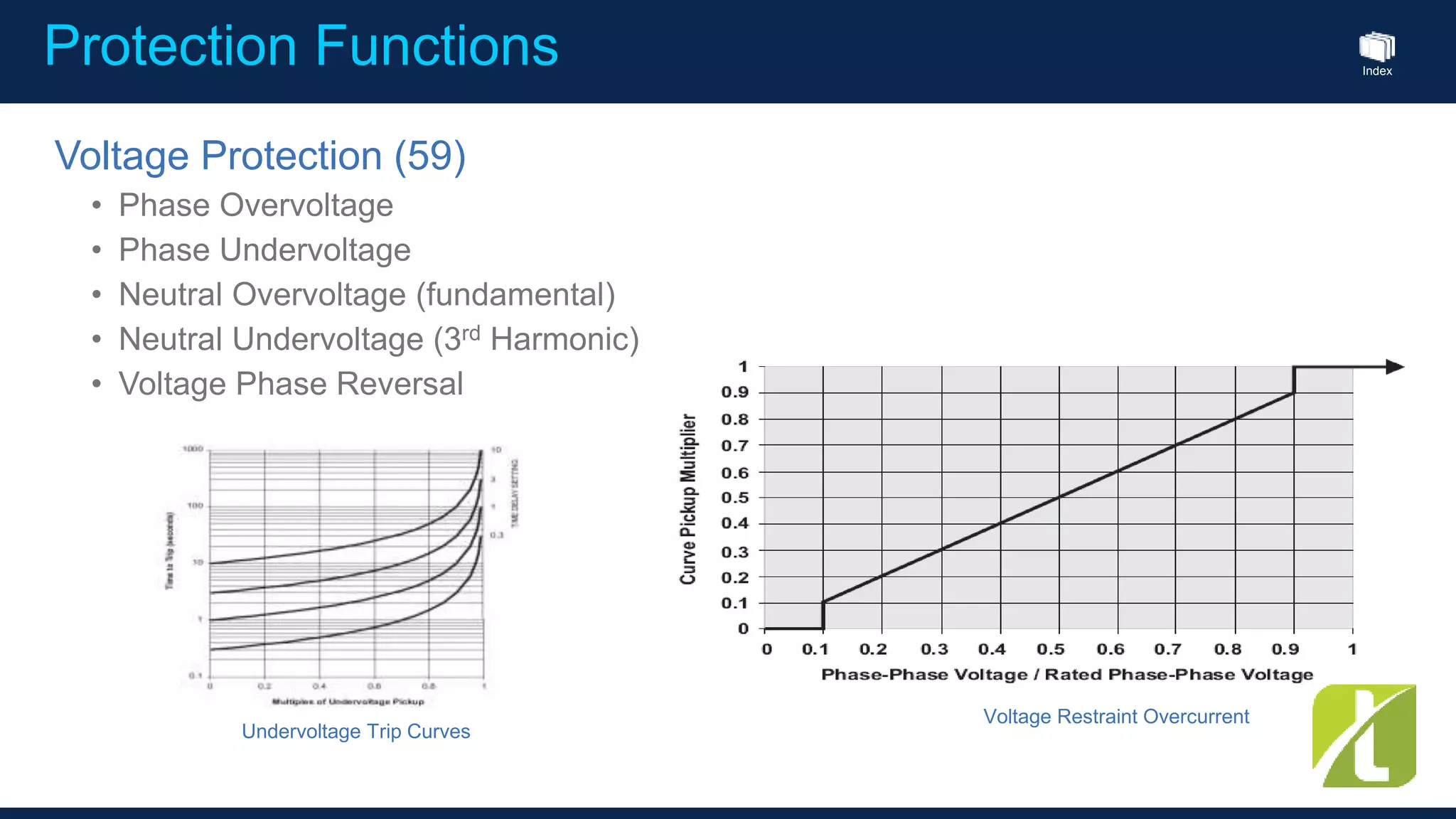
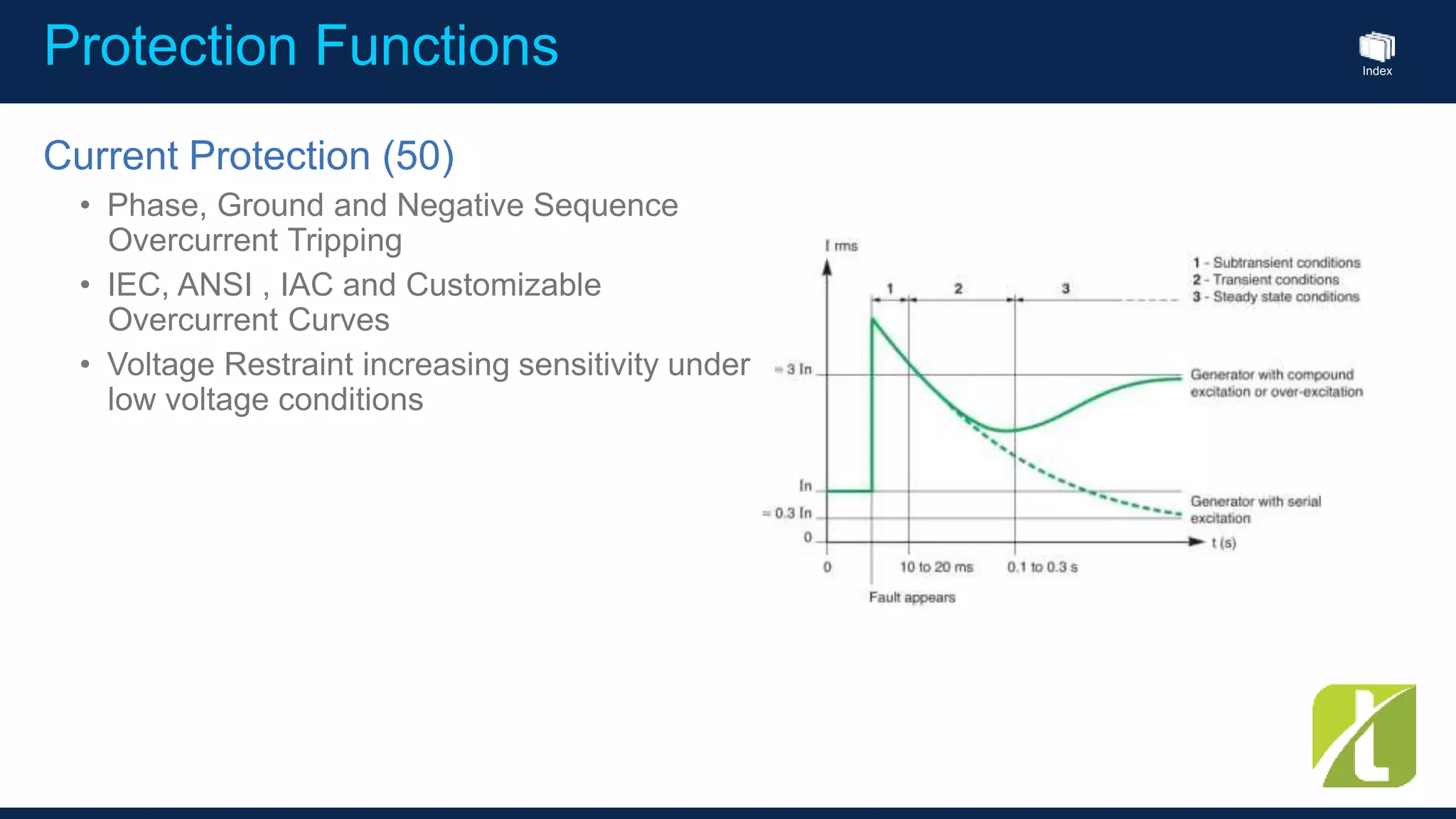
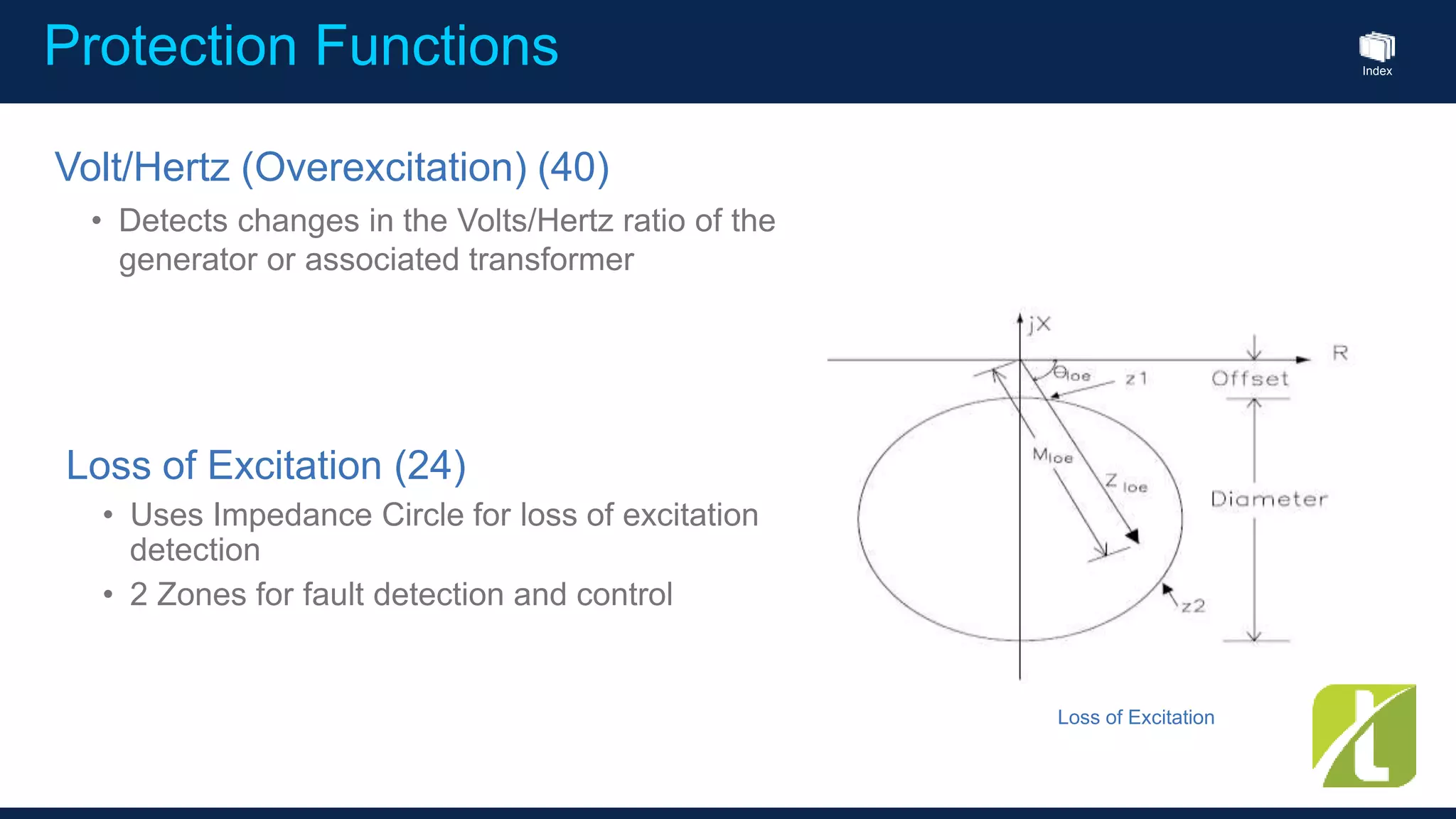
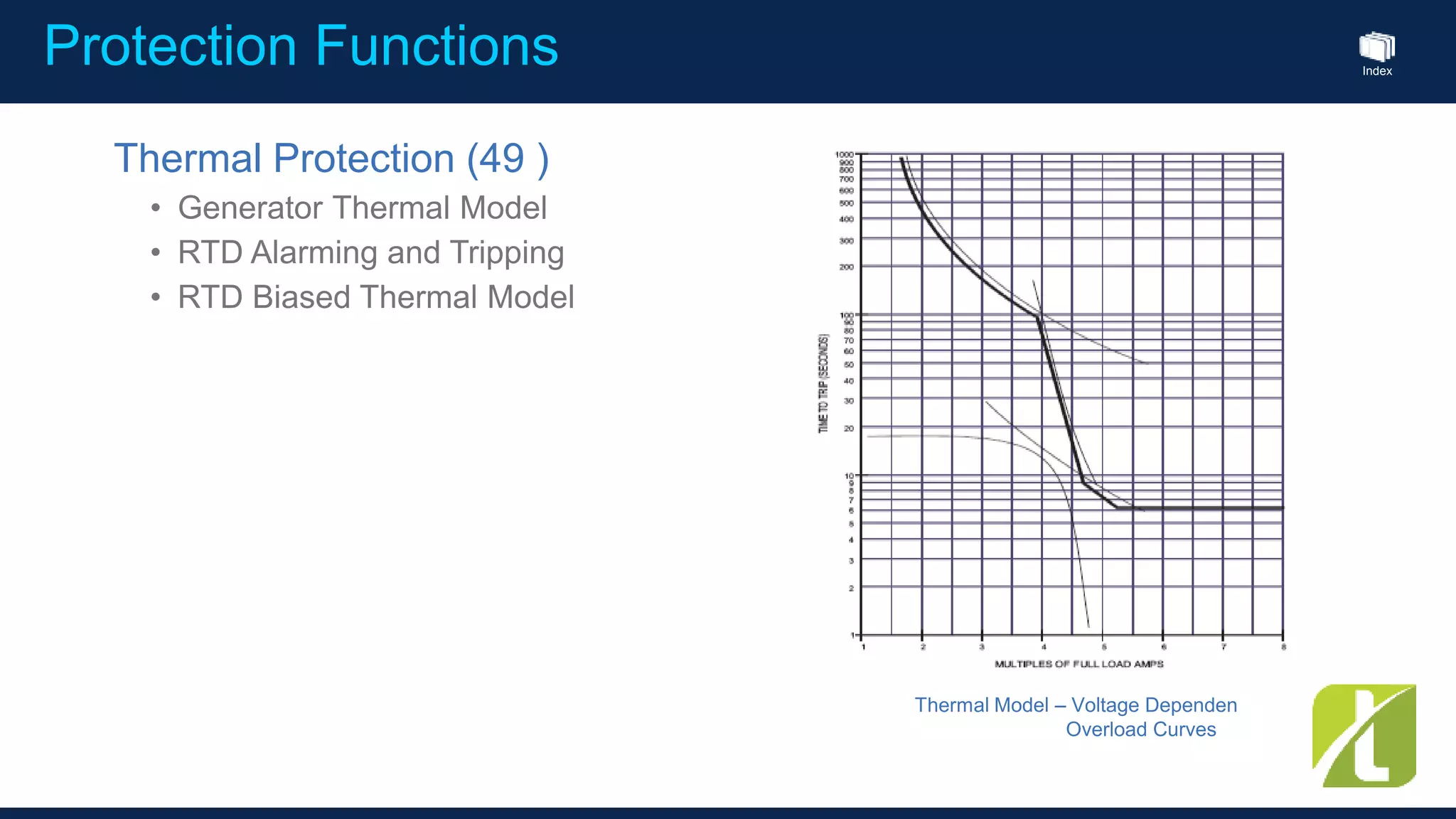
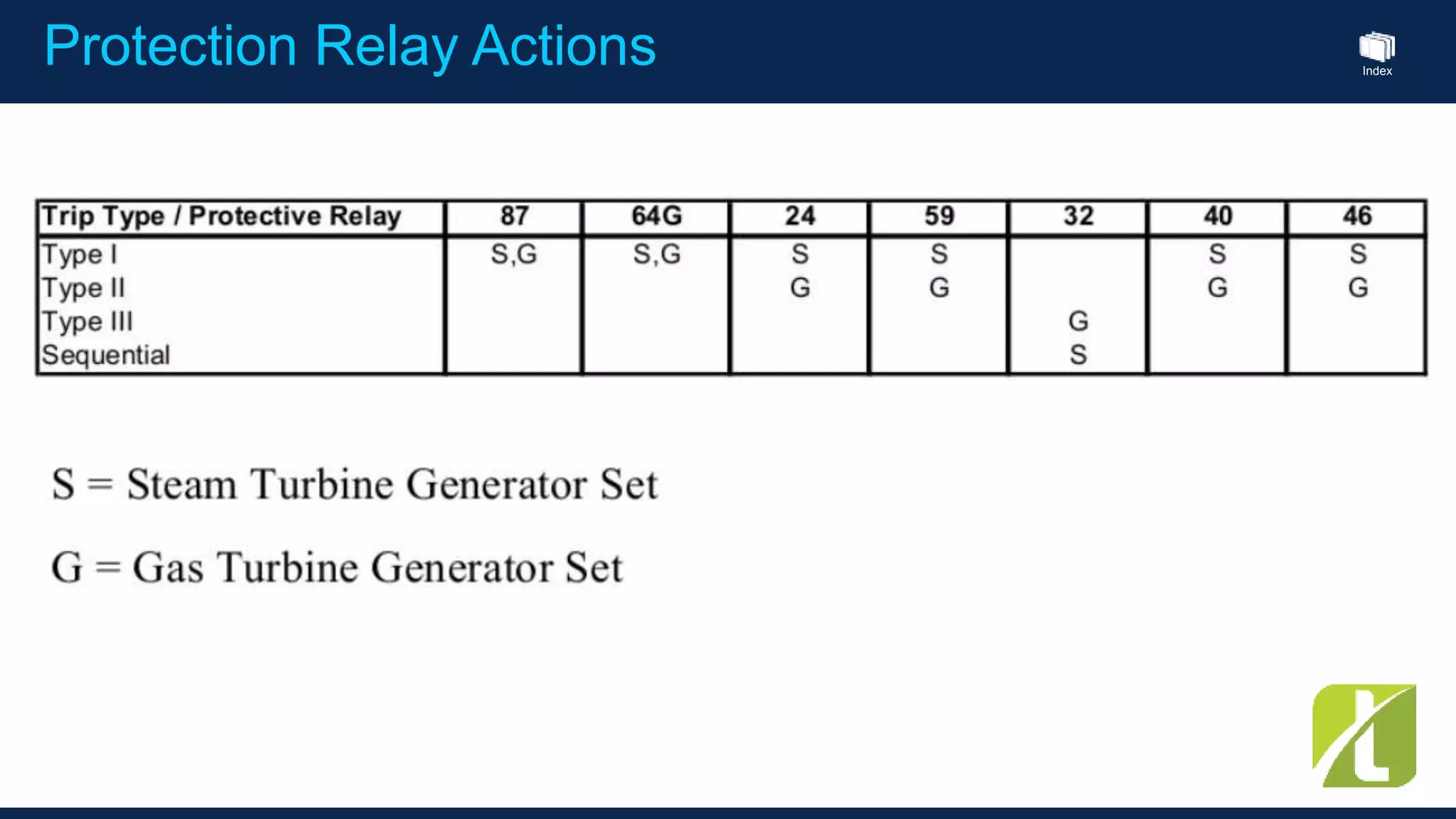
This document outlines the agenda for a generator protection system seminar taking place on January 13, 2016 from 1pm to 3pm at the YTU Electrical Power Department. The agenda includes welcome and introduction sessions followed by a presentation on generator protection systems and their functions. There will then be a tea break followed by more detailed explanations of protection functions and a question/answer section before concluding at 3pm. The document also provides sample generator protection relay wiring diagrams and listings of common protection functions and relay actions.