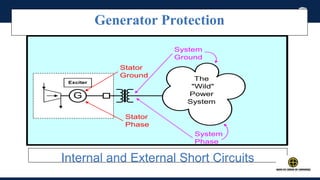
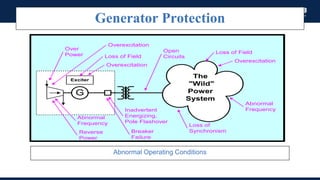
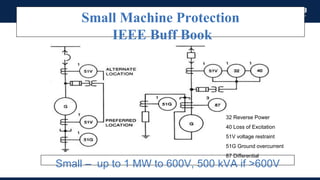
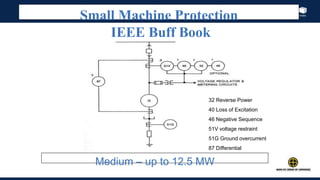
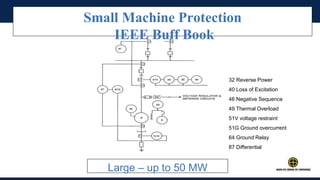
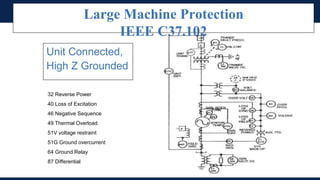
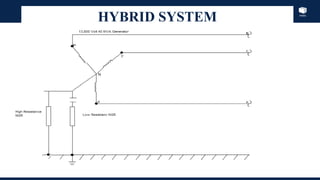
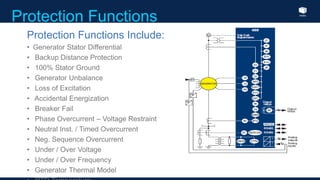
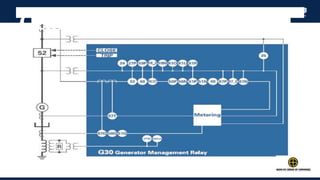
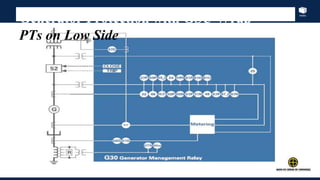
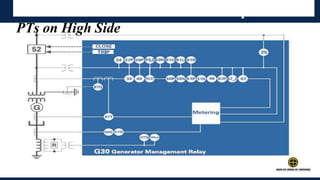
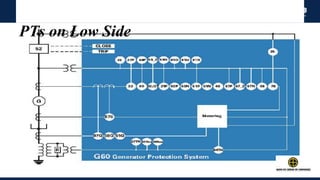
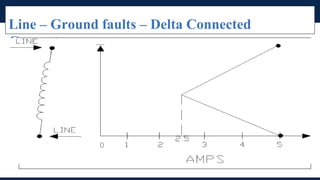
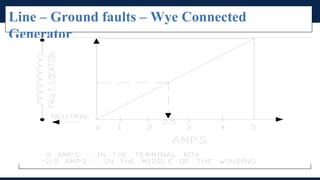
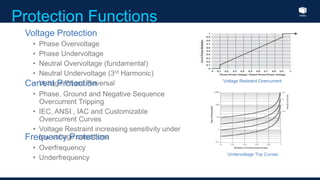
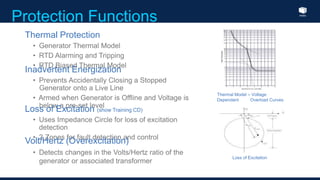
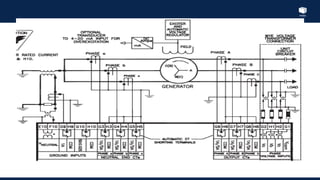
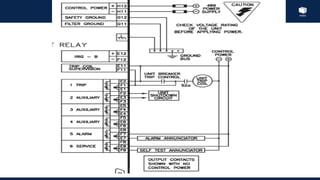
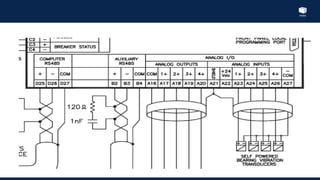
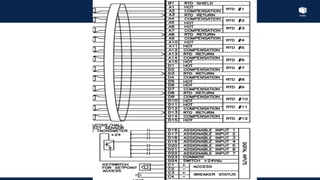
The document outlines an agenda for a presentation on protection systems for power generators held by AGCC from 1-3pm on November 1, 2014. The agenda includes: a welcome speech at 1pm, introduction of the speaker at 1:10pm, a fault analysis detail session at 1:15pm, a tea break at 1:50pm, a presentation on generator protection systems from 2-2:40pm, a question and answer section from 2:40-3pm, and ending the presentation at 3pm. The rest of the document provides details on generator protection including common protection functions, wiring diagrams, and an example.