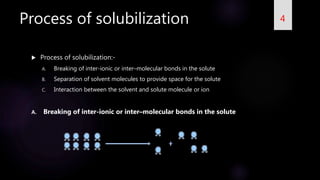
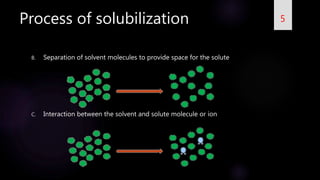
This document summarizes a seminar on solubilization presented by Gajanan V Naik. It defines solubility and provides expressions to describe solubility. It discusses the importance of solubility and problems with poor solubility. Solubilization is defined as preparing an isotropic solution of a normally insoluble substance using components or methods. The process of solubilization involves breaking bonds in the solute, separating solvent molecules, and interactions between solvent and solute. Various methods to increase solubility are described, including addition of co-solvents, pH changes, reducing particle size, temperature changes, hydro-trophy, addition of surfactants, complexation, solid dispersions, polymorphism, and other techniques.