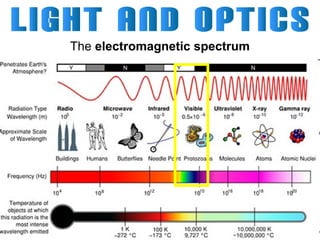
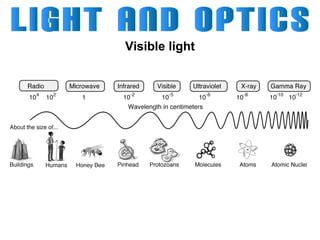
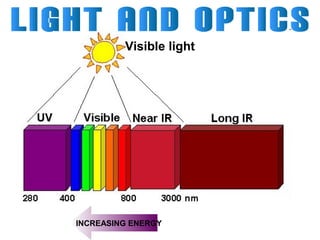
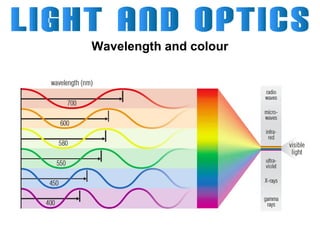
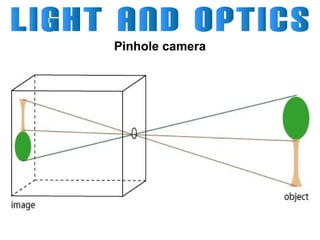
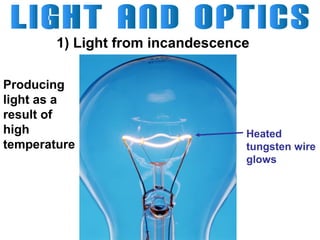
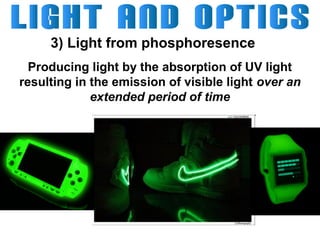
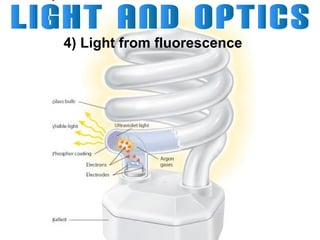
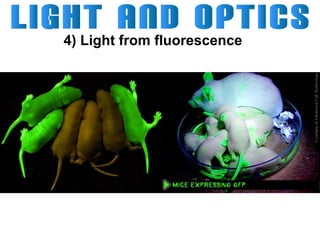
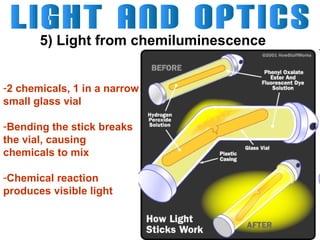
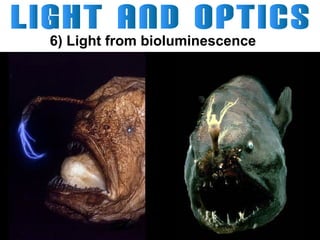
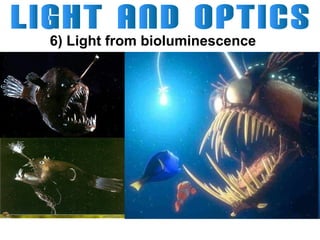
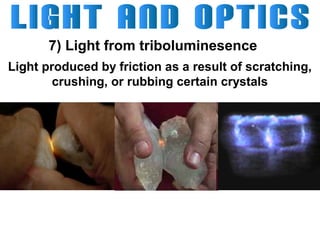
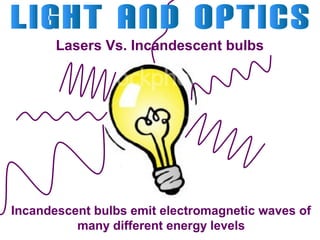
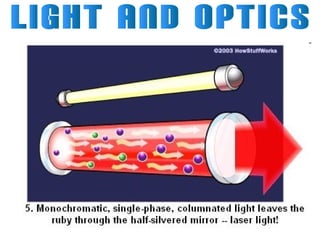
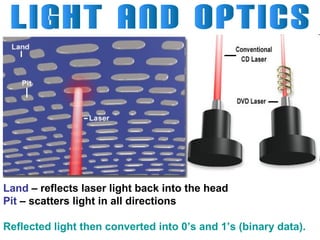
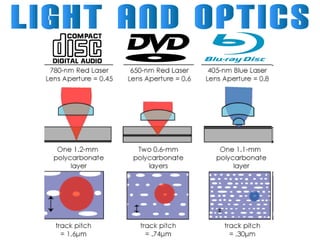
Light can travel through space in straight lines and comes in different forms, including visible light. There are various ways that light can be produced, including incandescence from heated objects, electric discharge through gases, and chemiluminescence from chemical reactions. Lasers produce coherent electromagnetic waves of the same wavelength and phase which travel in parallel, and are used in applications like manufacturing, astronomy, and entertainment due to their precision and focus.