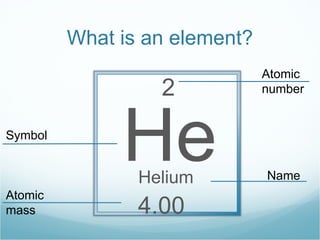
The document discusses atomic structure and the periodic table. It explains that atomic number increases from left to right and top to bottom on the periodic table. Atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Atomic mass values are decimals because they represent weighted averages of naturally occurring isotopes, which can have different numbers of neutrons while maintaining the same atomic number.