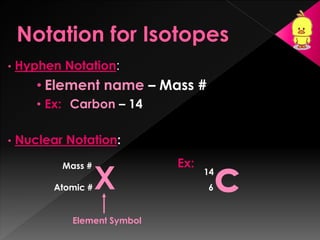
This document discusses atomic structure, isotopes, and how atomic masses are reported on the periodic table. It explains that each element has a unique number of protons, while isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. It provides examples of common isotopes of oxygen, carbon, calcium, and lithium and explains that the atomic masses reported on the periodic table represent weighted averages accounting for the relative abundances of each isotope.