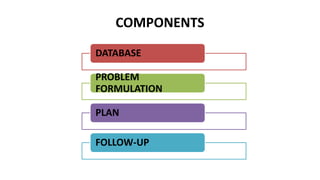
This document discusses holistic nursing and problem-oriented nursing. Holistic nursing aims to heal the whole person, including their physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects. It recognizes the interconnectedness of these dimensions. In contrast, traditional medicine focuses only on decreasing physical symptoms. Holistic nursing may incorporate alternative and complementary therapies alongside conventional treatment. Problem-oriented nursing organizes a patient's care around their identified health problems, with plans developed and progress tracked for each problem.