The document discusses several key aspects of professional nursing concepts and practices:
- Nursing aims to promote health and well-being by caring for individuals, families, and communities. It focuses on care of the physical, mental, social, and spiritual aspects of a person.
- Professional nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care across all ages and settings. It includes health promotion, illness prevention, and care of those who are ill, disabled, or dying.
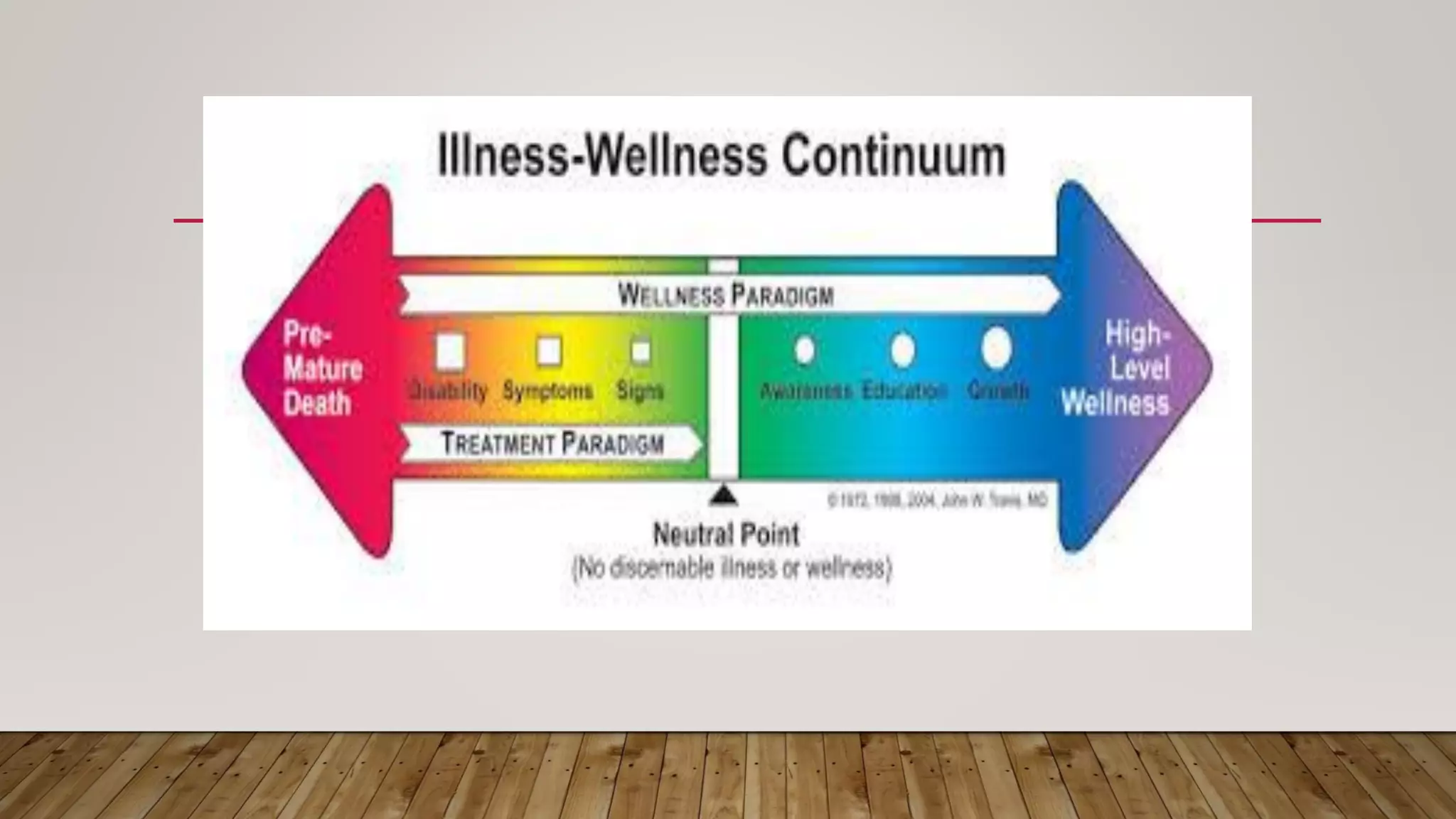
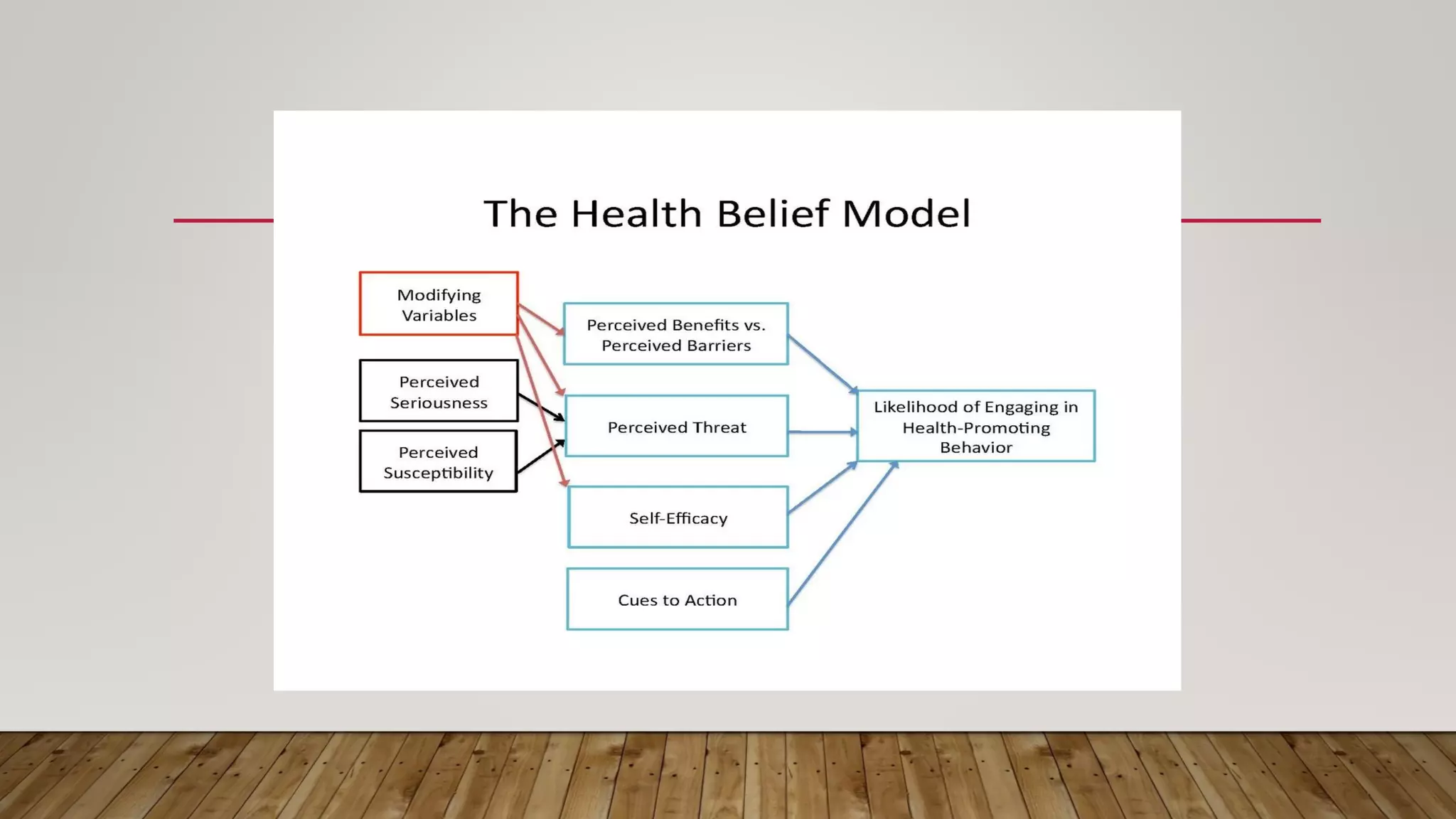
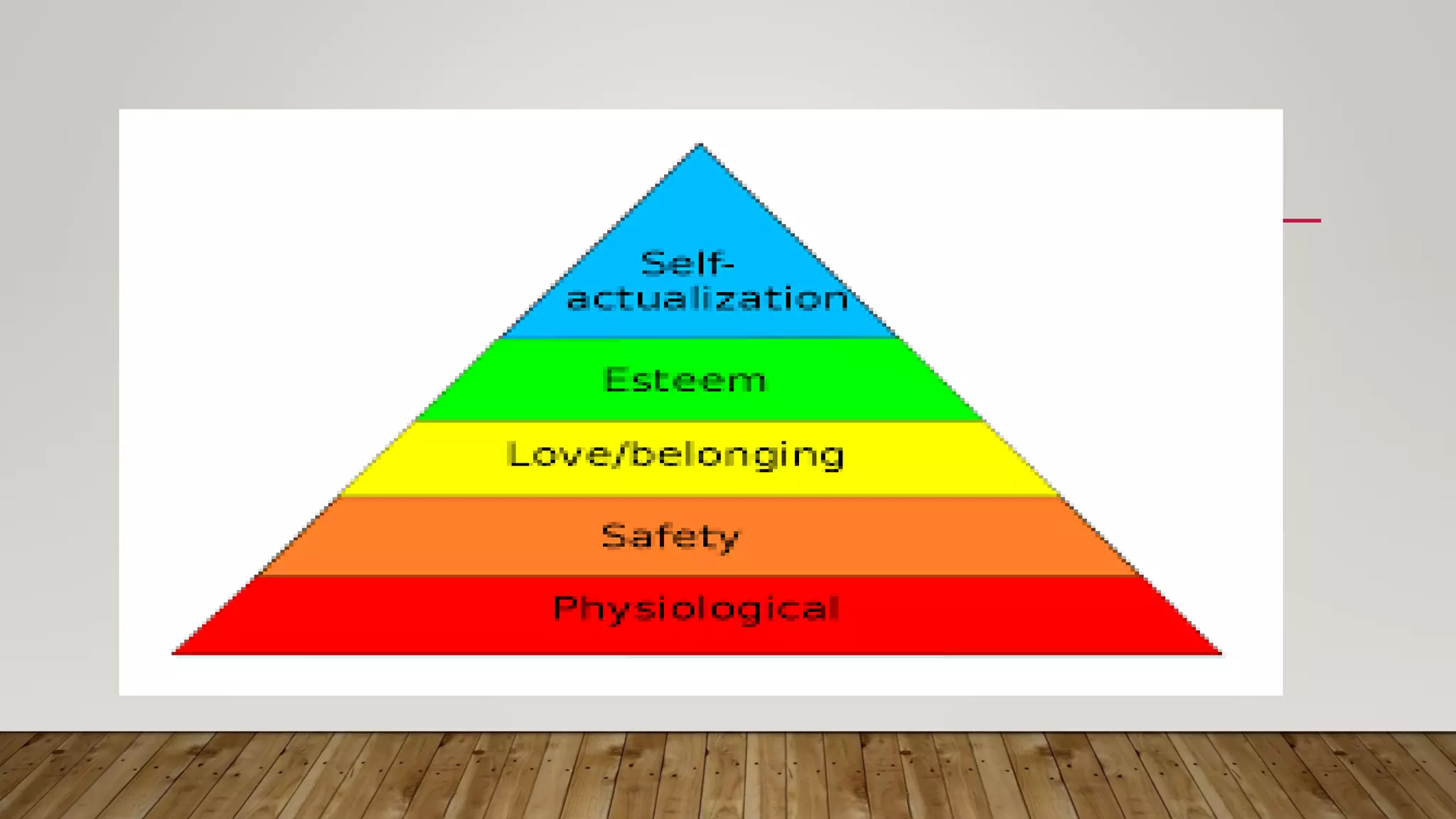
- Several models of nursing are described, including the health-illness continuum model, health belief model, health promotion model, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and holistic health model. These provide theoretical frameworks for understanding health and delivering nursing care.