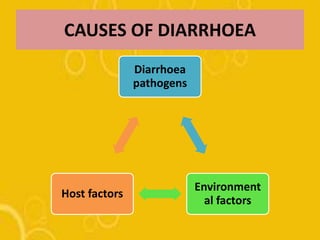
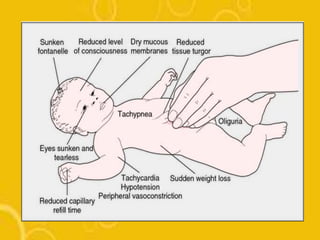
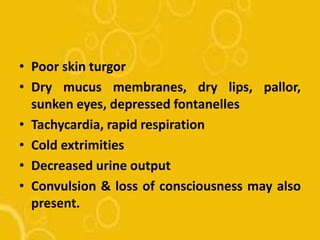
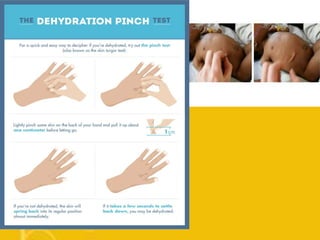
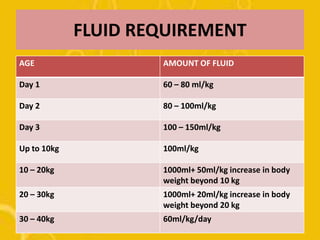
The document discusses diarrhoea, defining it as loose or watery stools more than 3 times per day. It outlines the main causes as diarrhoeal pathogens like viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungi, as well as host factors like young age and environmental factors like season. The types of diarrhoea are described based on pathogens, duration, mechanism and clinical presentation. Management involves rehydration therapy with oral rehydration solution or intravenous fluids based on the degree of dehydration. Nursing care focuses on fluid replacement and monitoring for signs of dehydration.