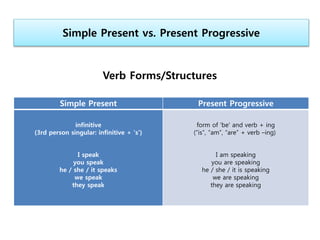
The document summarizes the differences between the simple present and present progressive tenses in English. It provides examples of when each would be used, such as the simple present for general or habitual actions, and the present progressive for temporary actions or those happening now. It also lists exceptions and certain verbs that are usually only used in one tense form.