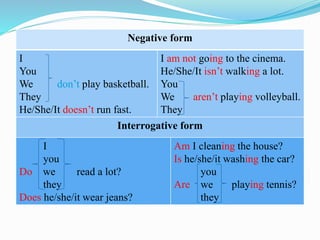
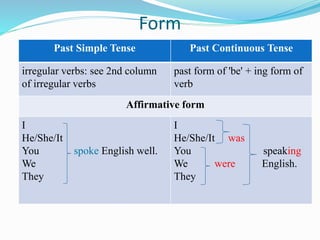
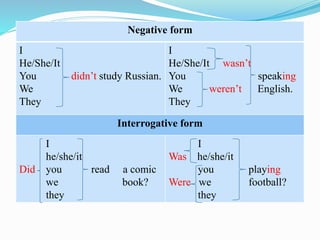
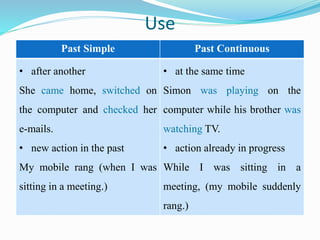
This document provides information on different verb tenses in English including present simple, present continuous, past simple, past continuous, and present perfect. It outlines the forms, uses, and exceptions for each tense. Key points covered include when to use each tense to talk about completed past actions, ongoing actions, habits, schedules, and experiences that are still relevant to the present. Examples are provided to illustrate the different tenses.