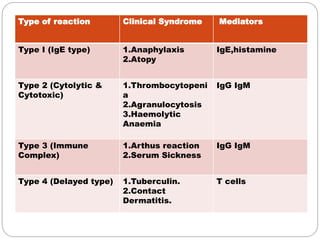
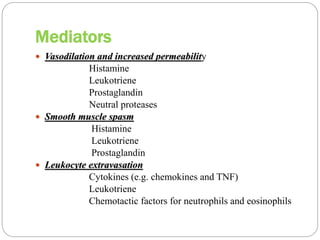
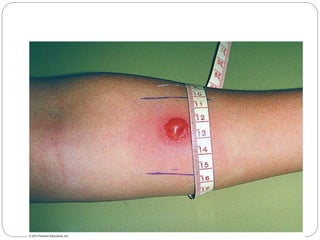
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when the immune system responds in an exaggerated or inappropriate manner following contact with an antigen. There are four main types of hypersensitivity reactions:
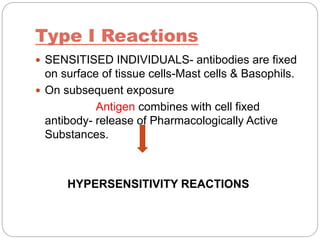
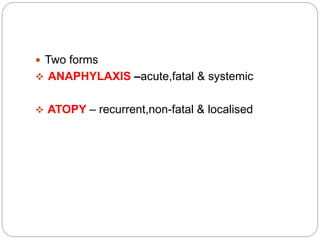
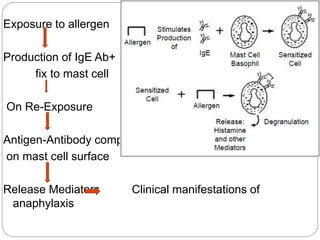
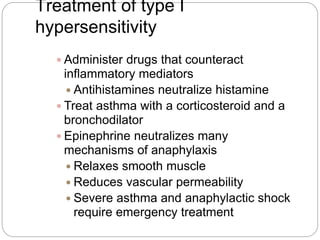
1. Type I reactions are mediated by IgE antibodies and mast cells, causing immediate reactions like anaphylaxis.
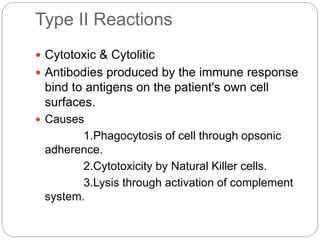
2. Type II reactions involve IgG and IgM antibodies binding to antigens on a person's own cells, leading to cell damage or lysis.
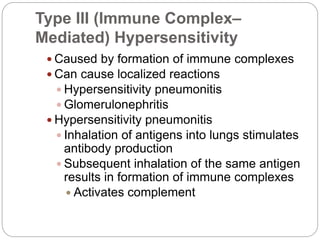
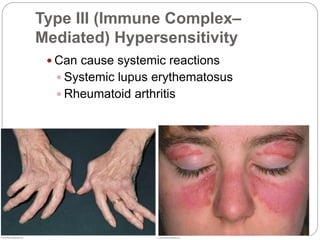
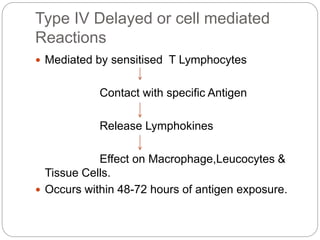
3. Type III reactions involve immune complex deposition in tissues, complement activation, and inflammatory cell infiltration causing tissue damage.
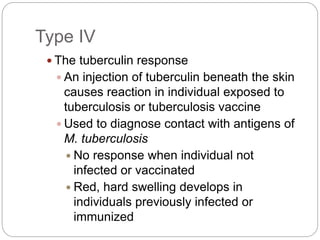
4. Type IV delayed reactions are mediated by T cells and involve responses like contact dermatitis and tuberculin reactions occurring 1-3 days after