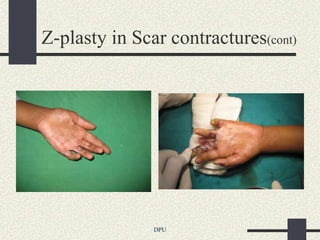
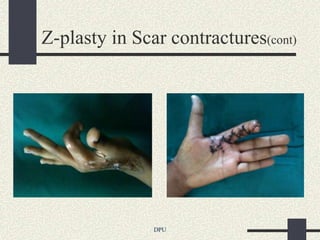
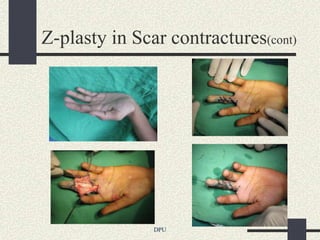
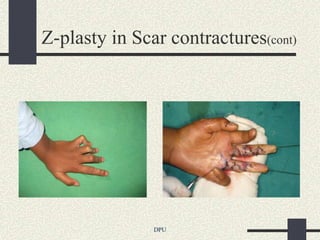
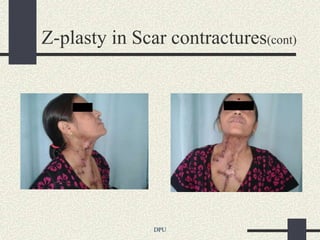
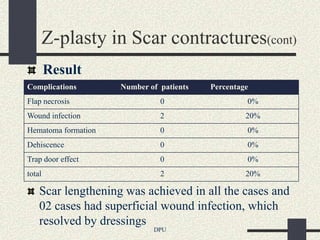
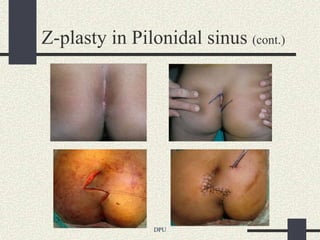
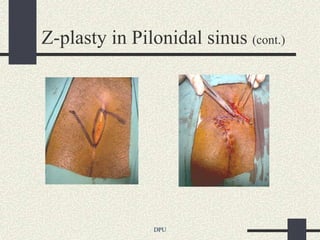
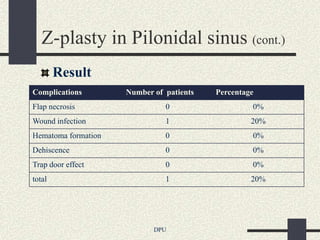
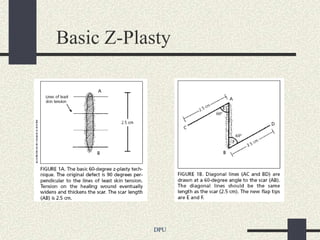
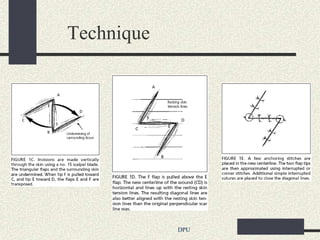
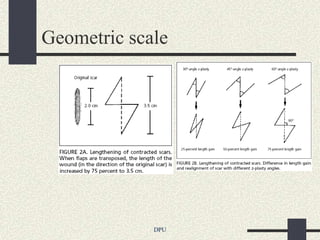
The document discusses using Z-plasty techniques to treat post-burn scar contractures and pilonidal sinus. Z-plasty involves reorienting scar tissue to lengthen it and correct deformities. The author describes using Z-plasty on 10 cases of scar contractures and 5 cases of pilonidal sinus. It resulted in scar lengthening and zero recurrence of pilonidal sinus with less hospital stay compared to other techniques. The document concludes that Z-plasty is a versatile technique for general surgeons to manage linear scar contractures and pilonidal disease.