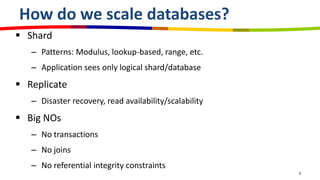
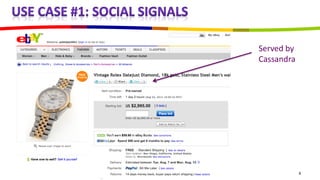
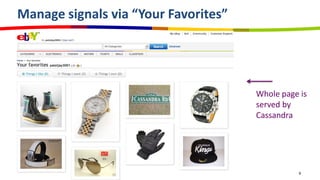
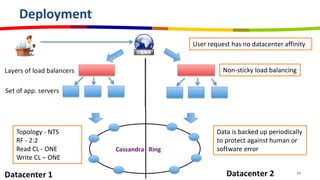
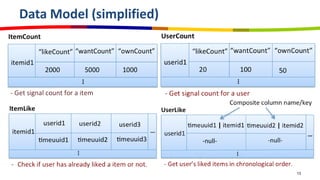
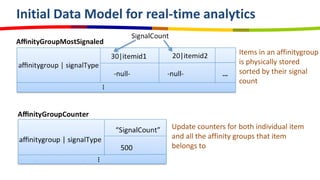
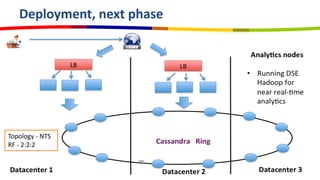
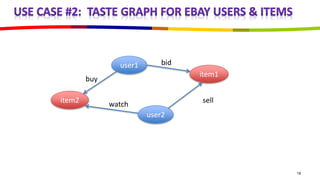
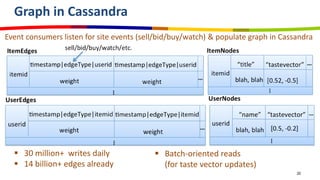
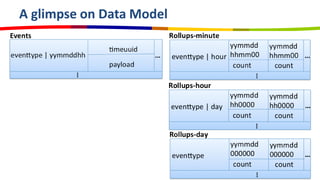
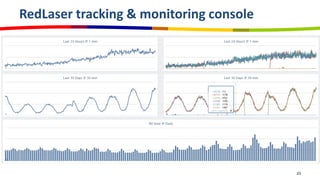
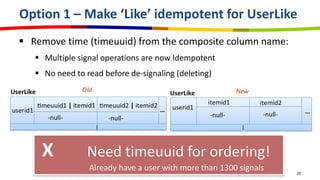
eBay utilizes Cassandra for its database needs, supporting 97 million active users and handling over 2 billion page views daily. The deployment includes multiple clusters with significant storage and write/read volumes, focusing on real-time analytics for social signals and various other use cases. Key considerations involve choosing proper replication and consistency levels, alongside managing the data model based on query patterns.