This document presents an overview of Apache Cassandra, a distributed NoSQL database system, discussing its underlying principles, installation requirements, and key features like high performance, elastic scalability, and fault tolerance. It covers the Cassandra Query Language (CQL) and data modeling concepts, as well as the strengths and weaknesses of using Cassandra in various use cases. Additionally, it highlights the similarities and differences between Cassandra and relational databases, providing examples and comparisons throughout.




























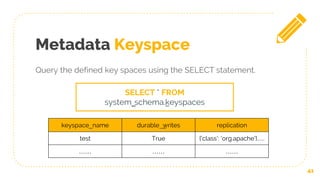

![Logging with System.log
45
INFO [main] 2018-11-08 23:48:36,960
MigrationManager.java:302 - Create new Keyspace:
KeyspaceMetadata {name=system_traces,
params=KeyspaceParams {durable_writes=true,
replication=ReplicationParams
{class=org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleStrategy,
replication_factor=2 }
Here is an Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandrappt-190109122946/85/Cassandra-Database-45-320.jpg)
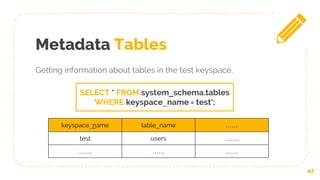
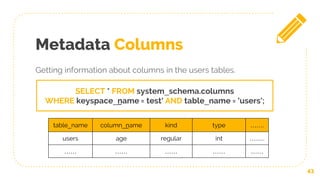
![Logging with Tracing
46
TRACING [ ON | OFF]
It’s an option to activate in the Cassandra database
The result will be on different keyspace called system__traces. In
a table called events
USE system_traces;
SELECT * FROM events;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandrappt-190109122946/85/Cassandra-Database-46-320.jpg)








