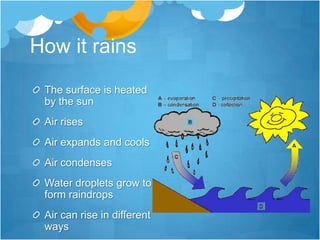
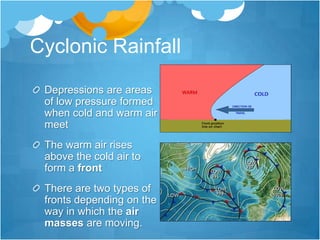
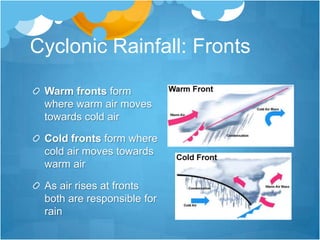
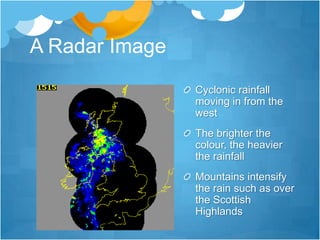
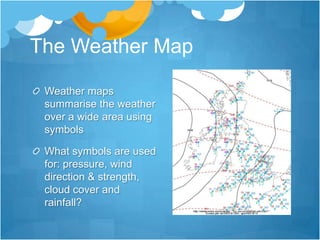
This document provides an overview of weather and climate concepts. It discusses how weather is measured using instruments in weather stations, including temperature, precipitation, wind, pressure, sunshine, and cloud cover. It then explains different weather phenomena like how rainfall occurs through convection, relief, cyclonic systems, and fronts. Climate patterns in Britain are influenced by latitude, proximity to the sea, and ocean currents. Weather is now forecast using computer models and satellite/radar images to analyze conditions over wide areas.