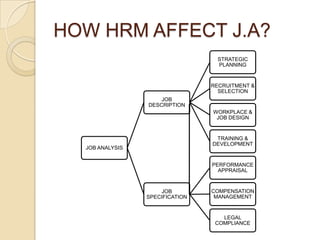
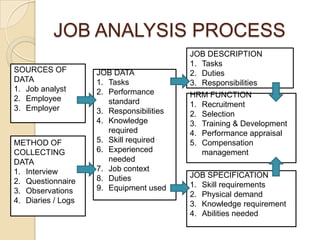
The document discusses job analysis which is the systematic process of collecting information about all aspects of a job. It involves gathering data on responsibilities, skills, physical/mental requirements, and the job description and specification. A job specification outlines the specific knowledge, skills, and abilities required for a position. Human resource management uses job analysis for strategic planning, recruitment/selection, workplace/job design, training/development, performance appraisal, compensation management, and legal compliance. Common data collection methods include interviews, questionnaires, observation, and diaries/logs. The job analysis process involves collecting data, developing job descriptions and specifications, and informing various HRM functions.