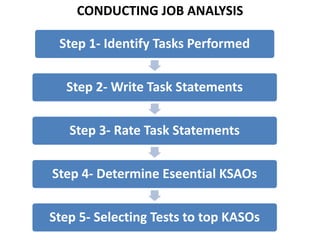
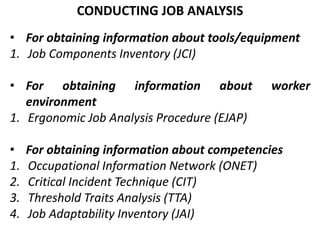
Job analysis is the process of gathering and analyzing information about the components, characteristics, and requirements of a job. It involves analyzing the duties, conditions of work, and the knowledge, skills, and abilities needed to effectively perform the job. A thorough job analysis forms the foundation for human resource planning activities like employee selection, training, performance appraisal, and job design. Conducting job analysis involves identifying tasks, writing task statements, determining essential skills, and selecting tests to measure those skills. Structured questionnaires can also be used to efficiently obtain job analysis information.