Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah - Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way
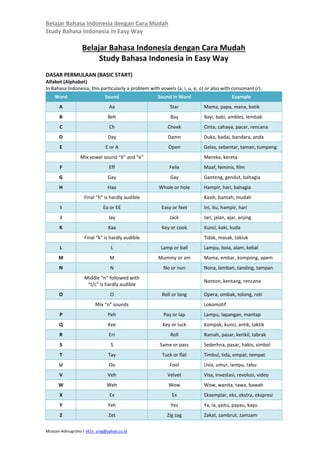
- 1. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way DASAR PERMULAAN (BASIC START) Alfabet (Alphabet) In Bahasa Indonesia, this particularly a problem with vowels (a, i, u, e, o) or also with consonant (r). Word Sound Sound in Word Example A Aa Star Mama, papa, mana, batik B Beh Bay Bayi, babi, ambles, lembab C Ch Cheek Cinta, cahaya, pacar, rencana D Day Damn Duka, badai, bandara, anda E E or A Open Gelas, sebentar, taman, tumpeng Mix vowel sound “ë” and “e” Mereka, kereta F Eff Felix Maaf, feminis, film G Gay Gay Ganteng, gendut, bahagia H Haa Whole or hole Hampir, hari, bahagia Final “h” is hardly audible Kasih, bantah, mudah I Ea or EE Easy or feet Ini, itu, hampir, hari J Jay Jack Jari, jalan, ajar, anjing K Kaa Key or cook Kunci, kaki, kuda Final “k” is hardly audible Tidak, masak, takluk L L Lamp or ball Lampu, bola, alam, kebal M M Mummy or am Mama, embar, kompong, apem N N No or nun Nona, lamban, tanding, tampan Middle “n” followed with “t/c” is hardly audible Nonton, kentang, rencana O O Roll or long Opera, ombak, tolong, roti Mix “o” sounds Lokomotif P Peh Pay or lap Lampu, lapangan, mantap Q Kee Key or luck Kompak, kunci, antik, taktik R Err Roll Ramah, pasar, kerikil, tabrak S S Same or pass Sederhna, pasar, habis, simbol T Tay Tuck or flat Timbul, tida, empat, tempat U Oo Fool Usia, umur, lampu, tabu V Veh Velvet Visa, investasi, revolusi, video W Weh Wow Wow, wanita, tawa, bawah X Ex Ex Eksemplar, eks, ekstra, ekspresi Y Yeh Yes Ya, ia, yaitu, payau, kayu Z Zet Zig zag Zakat, zambrut, zamzam
- 2. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id Beberapa Pengucapan (Some prononciation) Diptong (Diptong) Diptong Sound Example ai sounds like “y” in “supply” sampai, capai, pakai, ramai in closed syllabus it is pronounced separate “a-i” lain, baik, main au same sound as in “cow” pulau, kerbau, pisau Colloquially, you will often hear ‘ai’ pronounced like ‘a’ in English, instead of ‘y’ “sampai” is pronounced “sampe” Konsonan (Consonants) Consonants Sound Example kh occurs in loanwords, mostly of Arabic origins, sounds like “ch” like in “Lochnest” khusus , khawatir ng sounds like “ng” in “singing” tingkat, datang, dengar ngg sounds like “ng” in “finger” anting, tinggal, tunggu, ganggu ny sounds like “ni” in “Spaniard” tanya, nyanyi, nyonya s the sound of “s” always pronounced sharply sapi, suka, pas, susu sy occurs in loanwords of Arabic, sounds like “sh” in “push” and “shrimp” masyarakat, musyawarah, syarat Penekanan Kata / Aksen (Word Stress / Accent) Bahasa Indonesia is normally spoken rhythmically, with little or even no stress. In words of two or more syllabus, the penultimate syllables is somewhat stressed. But for a beginner, simply make an effort to keep an even, unstressed tone, and the slight stress will come naturally eventually. You will develop a feel as you learn. Maaf Pronounced ma’af not maf Jumat pronounced jum’at not jumat Perusahaan pronounced perusaha’an not perusahan Saya pronounced sa’ya not say’a Kemarin pronounced kema’rin not kemar’in Jemaat pronounced jema’at not jemat
- 3. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id BAGAIMANA MEMBUAT KALIMAT (HOW TO MAKE SENTENCES) To make sentence in Indonesian is very easy and simple. We just put word by word. Formula of Sentence + - Subject - Predicate Object Adverb - - Subject “bukan” or “tidak” Predicate Object Adverb ? Question Word Subject - Predicate Object Adverb For yes/no question Apa/Apakah Subject - Predicate Object Adverb Note Subject Noun or Joko, Ismi, Tain, Dewi (person name) Pronoun Aku, Dia, Kamu, Mereka (I, He/She, You, They) Predicate Verb or Makan, Tidur, Berenang (Eat, Sleep, Swimming) Adjective Cantik, Manis, Tinggi (Beautiful, Sweet, Tall) Object Noun Roti, Susu, Mobil, Buku (Bread, Milk, Car, Book) Adverb (Kata Keterangan) Place or Jakarta, Warung, Sekolah, Jalan Raya (Jakarta, Restaurant, School, Street) Time Siang, Malam, Jam 6, 4 jam yang lalu (Afternoon, Evening, At 6 o’clock, 4 hours ago) Question Word (Kata Tanya) Who Whom Where When Which What Whose How Siapa Dengan Siapa / Siapa Dimana Kapan Manakah / Yang mana Apa Milik siapa Bagaimana “Tidak” and “Bukan” Tidak is used to negate verbs, adjectives and prepositions Dia bukan mahasiswa (He is not a student) Bukan is to negate a noun Dia tidak belajar di UNDIP (He is not study in UNDIP) Both tidak and bukan can appear in one sentence Dia bukan pelajar dan dia tidak belajar di UNDIP (He is not a student and he is not study in UNDIP)
- 4. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id No past, present and future tenses (simply add the adverb of time to show tense) Formula Subject + Predicate (+ Object) + Adverb of Time Simple Saya makan I eat. I ate. I will eat Past Saya makan sekarang I eat now Present Saya makan kemarin I ate yesterday Future Saya akan makan nanti I will eat later But we can indicate tenses by word in sentence Kata Penunjuk Waktu Indicate Tenses Example Sudah Past Saya sudah makan (I ate) Sedang Present Saya sedang makan (I am eating) Akan / Mau Future Saya mau makan (I will eat) Indicate Past Telah, sudah Have, already Sejak Since Semalam / kemarin malam / tadi malam Last night, yesterday night Kemarin Yesterday Kemarin dulu / 2 hari yang lalu The day before yesterday / 2 days ago (3,4…) hari <yang> lalu (3,4…) days ago (1,2,3,…) minggu <yang> lalu (1,2,3, …) weeks ago (1,2,3,…) bulan <yang> lalu (1,2,3, …) months ago (1,2,3,…) tahun <yang> lalu (1,2,3, …) years ago Indicate Present Tengah, sedang Indicate something is currently happening Sekarang, saat ini Now Biasanya Usually Akhir-akhir ini, baru-baru ini Lately, recently Indicate Future Akan Will Besok Tomorrow Lusa The day after tomorrow Masa yang akan datang, mendatang In the coming future Dalam waktu dekat In the near future (3,4…) hari lagi (3,4…) days later / next (3,4…) days. (1,2,3,…) minggu lagi / minggu depan (1,2,3,…) weeks later / next (1,2,3,…) weeks. (1,2,3,…) bulan lagi / bulan depan (1,2,3,…) months later / next (1,2,3,…)months. (1,2,3,…) tahun lagi / tahun depan (1,2,3,…) tahun lagi / next (1,2,3,…) years.
- 5. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id TATANAN / URUTAN KATA (WORD ORDER) Word order is reversal from English: adjective comes after noun Indonesia: Noun-Adjective English: Adjective-Noun Rumah besar Big house Mobil baru New car Gunung tinggi High mountain Air panas Hot water In case that noun have more than 1 adjective, it simply put adjective after noun Noun + Adj1 + Adj2 + Adj3 ... etc Buku besar hitam mahal (Expensive black big book) Word order exceptions for indicating number precedes the noun Indonesia: Adjective-Noun English: Noun-Adjective Banyak uang Lots of money Sedikit gula A little sugar Semua orang All people, everyone Seluruh kota The whole town In colloquial, the grammar rules are mostly broken Aku memberi kamu uang. I give you money ( ) Aku beri kamu uang. I give you money ( x ) **this is what normally people say colloquially. The sentence pattern is still the same, but morphologically the suffix “me(m) “ which forms (me(m) + beri = memberi) is not used.
- 6. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id KATA GANTI (PRONOUN) There is very few changes in the form of personal pronouns in Indonesian language. There is no gender difference to address third person pronunciation, gender identity are mostly on contextual basis. Person Singular Plural Pertama First 1. Saya: to address oneself formally, politely 2. Aku: to address oneself informally, less politely (between friends or with younger person); in possessions sometimes “aku” is shortened as “-ku” 1. Kita: to address first persons both for “us or we” when second person is included 2. Kami: to address first persons both for “us or we” when second person is not included Meaning: I, me, my Meaning: we, us, our Saya setuju dengan anda = I agree with you Kamu setuju dengan aku = You agree with me Anda setuju dengan pendapat saya = You agree with my opinion Buku itu adalah bukuku = That book is my book Kami pergi ke pasar = We go to market (“kami” means you aren’t included) Dia mengundang kita makan malam. = She invites us for a dinner (“kita” means you & I) Itu rumah kita = That is our house Ini adalah mobil kami = This is our car Person Singular Plural Kedua Second 1. Engkau/kau : to address a second person in poetic way (normally mentioned in literature), sometimes still to be used in colloquially but not commonly 2. Anda : to address a second person formally, politely 3. Kamu : to address people informally, less politely (between friends or with younger person); in possessions sometimes “aku” is shortened as “-mu” 1. Kalian : to address second persons informally 2. Kamu (sekalian) : to address second persons informally Meaning: you, your Meaning: you, all of you, your Engkau adalah cintaku = You are my love Saya setuju dengan anda = I agree with you Kamu setuju dengan aku = You agree with me Anda setuju dengan pendapat saya = You agree with my opinion Buku itu adalah milikmu = That book is your book Kalian mau ke mana? = Where are you going? Aku kirim surat untuk kalian = I send a letter for you. Surat ini milik kalian = This letter is your letter. Ada pengumuman untuk kamu sekalian = There’s an announcement for all of you.
- 7. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id No gender difference, on contextual basis Ketiga Third 1. Ia: normally used in fiction writing 2. Dia : normally used both in writing and colloquial 3. Beliau: normally used both in writing and colloquial, in formal situation or to address a respectful person (older person, boss, etc) 4. -nya : in possessions sometimes it is shortened as “-nya” 1. mereka: to address third persons both formally and informally, politely and less politely 2. -nya: to address third persons, both formally and informally, politely and less politely. In possessions sometimes it is shortened as “- nya” Meaning: he/she, his/her, it/its Meaning: they, them, their Beliau sedang pergi = He is away Ia/Dia suka kamu = She or he likes you Buku ini miliknya / Buku ini milik dia = This book is his/her book Mereka sedang belajar = They are learning Aku akan belajar bersama mereka = I will study together with them. Ini adalah kelas mereka = This is their class. Pronoun Substitutes The use of second and third-person pronouns is very tricky. Engkau, kau and kamu can only be used to address a younger person, one’s subordinate or among good friends. Because of this kinship terms are used as pronoun substitutes. The following are the pronouns that usually be used to address people by its title. Indonesian English Usage Bapak or Pak Sir/Mister Literally means father Its to address an adult of marriageable age, to be used in a formal and very polite usage Ibu or Bu Ma’am/Mrs Literally means mother Its to address middle age woman and above, to be used in a formal and very polite usage Nona Miss Formal and polite Tuan Mister Formal and polite, like to use it to subordinate Nyonya Madam/Mrs Formal and polite Saudara “you” male To address people of one’s own age or younger, generally used towhom the speaker is not well acquainted withSaudari “you” female
- 8. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id SALAM (GREETINGS) Salam or greeting ussually use in the begining and ending of conversation English Indonesian Good morning Good afternoon Good afternoon Good evening Good evening Good night Bon appetit Selamat pagi Selamat siang Selamat sore Selamat petang Selamat malam Selamat tidur Selamat makan Hey How are you? Fine Great I am fine Thank you You are welcome Good bye Good bye / bon voyage Bye Take care Halo/Hai (informal) Apa kabar? Kabar baik. Saya baik-baik saja. (saya sehat) Terima kasih. Sama-sama/terima kasih kembali Selamat tinggal Selamat jalan Dadah… Hati-hati Hati-hati di jalan. Not / No Not / No Don’t Yes / OK Tidak / Nggak Bukan Jangan Iya Other Greetings Selamat tinggal Good bye! (to be said to person we leave) Selamat jalan Good bye! (to be said to person who departs) Sampai jumpa lagi See you again! Sampai nanti See you later! Selamat dating Welcome! Selamat datang kembali Welcome back! Selamat ulang tahun Happy birthday Selamat tahun baru Happy new year Selamat hari raya Natal Merry Christmas
- 9. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id PERKENALAN DIRI (INTRODUCTION) What to normally say in an introduction: 1. Nama (Name) 2. Pekerjaan (Occupation) 3. Usia (Ages) 4. Asal daerah/Negara (From) 5. Tinggal di mana (Living/Staying) Introducing your self Introducing yourself in another way A: Siapa nama anda? B: Nama saya Novi. A: Nama anda? B: Saya Novi. A: What is your name? B: My name is Novi. A: Your name? B: I am Novi. A: Apa pekerjaan anda? B: Saya seorang dokter A: Apakah anda bekerja atau masih kuliah? B: Saya belum bekerja. Saya masih kuliah A: What do you do? B: I am a doctor A: Are you worker or student? B: I havent got job yet. I am still student. A: Anda bertugas di mana? B : Di rumah sakit Kariyadi, Semarang A: Kuliah apa? B: Kuliah jurusan kedokteran. Semester delapan. A: Where do you work? B : I work at Kariyadi Hospital, Semarang City A: What do you study? B: I study in medical program. Semester eight A : Berapa usia/umur anda ? B : Usia/umur saya 25 tahun. A : Usia/umur anda berapa? B : Usia/umur saya 19 tahun A : How old are you? B : I am 25 years old A : How old are you? B : I am 19 years old A: Dari mana asal anda? B: Saya berasal dari Semarang? A: Anda orang mana? (Anda asli mana?) B: Saya orang Semarang. (Saya asli Semarang) A: Where do you come from? B: I am from Semarang? A: Where do you originaly from? B: I am from Semarang A : Di mana anda tinggal ? B : Saya tinggal di Semarang Barat A : Anda tinggal di mana? B : Di Semarang Barat A : Where doo you live? B : i live in West Semarang A : Where do you live? B : West Semarang *you can use the sentences in Italics to introduce yourself formally in new community/office.
- 10. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id Example: Halo, nama saya Novi. Saya seorang dokter berasal dari Semarang. Usia saya 25 tahun. Saya tinggal di Semarang Barat. Senang bisa berkenalan dengan anda = Hi, my name Novi. I am a doctor from Semarang. I am 25 years old. I live in West Semarang. Nice to meet you Introducing others (only 1 st and 2 nd person involved) Introducing others (when the 3 rd person is also there) Dian : Siapa dia? Neni : Dia teman saya. Namanya Ruth. Neni : Dian, Perkenalkan, ini teman saya, Ruth. Dia berasal dari Semarang. Dan Ruth, ini adalah teman kerja saya, Dian. Dian : Who is she? Neni : She is my friend. Her name is Ruth. Neni : Dian, let me introduce, this is my friend, Ruth. She is from Semarang. And Ruth, this is my co-worker, Dian. Dian : Apa pekerjaannya? Neni : Dia tidak bekerja. Dia seorang ibu rumah tangga. Ruth dan Dian : Halo, apa kabar? Dian : What does she do? Neni : She doesnt work. She is a housewife. Ruth dan Dian : Hi, how are you? Dian : Oya? Berapa usia/umur dia? Neni : Dia berusia 30 tahun. NenI : Dian, saya ingin mengenalkan kamu kepada teman saya, Ruth. Dia berasal dari Semarang. Dan Ruth, ini teman kerja saya, Dian. Dian : Really? Ho old is she? Neni : She is 30 years old. Neni: Dian, i want to introduce my friend, Ruth. She is from Semarang. And Ruth, this is my co- worker, Dian. Dian: Dari mana? Neni : Dari Semarang. Dian : Dimana dia tinggal? Neni : Dia tinggal di Semarang Barat. Ruth dan Dian : Halo, senang berkenalan dengan anda. Dian : Where is she come from? Neni : She is from Semarang. Dian : Where is she live? Neni : She lives in West Semarang. Ruth dan Dian : Hi, nice to meet you.
- 11. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id NOMER / ANGKA / NUMERAL (NUMBER) Satuan Belasan 1 Satu 11 Sebelas 2 Dua 12 Dua belas 3 Tiga 13 Tiga belas 4 Empat 14 Empat belas 5 Lima 15 6 Enam 16 7 Tujuh (Tuju) 17 8 Delapan 18 9 Sembilan 19 10 Sepuluh 20 Puluhan Ratusan / Hundreds 10 Sepuluh 100 Seratus 20 Dua puluh 200 Dua ratus 30 Tiga puluh 300 Tiga ratus 40 400 50 500 60 600 70 700 80 800 90 900 100 Seratus 1.000 Seribu Ribuan / Thousands Jutaan / Million 1.000 Seribu 1.000.000 Satu juta / Sejuta 2.000 Dua ribu 2.000.000 Dua juta 3.000 Tiga ribu 3.000.000 Tiga juta 4.000 4.000.000 5.000 5.000.000 6.000 6.000.000 7.000 7.000.000 8.000 8.000.000 9.000 9.000.000 10.000 Sepuluh ribu 10.000.000 Sepuluh juta 1.000.000.000 Satu Milyar 1.000.000.000.000 Satu Trilyun
- 12. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id ORDINAL NUMBER To make ordinal number, its simple. Just put “ke-“ in front on number Ke-1 Ke satu Ke-11 Ke-sebelas Ke-2 Ke dua Ke-12 Ke dua belas Ke-3 Ke tiga Ke-13 Ke tiga belas Ke-4 Ke empat Ke-14 Ke empat belas Ke-5 Ke lima Ke-20 Ke dua puluh Ke-6 Ke enam Ke-30 Ke tiga puluh Ke-7 Ke tujuh (tuju) Ke-100 Ke seratus Ke-8 Ke delapan Ke-200 Ke dua ratus Ke-9 Ke sembilan Ke-1.000 Ke seribu Ke-10 Ke sepuluh Ke-100.000 Ke seratus ribu * In case for date or month, you dont need to put “ke” to telling the date. Example: 7th January 2015, in Bahasa Indonesia it will be “tanggal tujuh Januari dua ribu lima belas” or 7 Januari 2015.
- 13. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id WAKTU (TIME/JAM) In Indoneisa, to describe time there are formal and informal way. Normally in formal way we use 24 hours format. And for informal way we use 12 hours format. Dini hari 12.00 am – 05.00 am / 00.00 – 05.00. Pagi 05.01 am – 12.00 pm / 05.01 – 12.00. Siang 12.01 pm – 03.00 pm / 12.01 – 15.00. Sore 03.01 pm – 06.00 pm / 15.01 – 18.00. Petang 05.01 pm – 06.00 pm / 17.01 – 18.00 (during sunset time, normally said by TV anchor) Malam 06.01 pm – 12.00 am / 18.00 – 00.00 Questions about hour / time Kapan? When? Pukul/jam berapa? What time? Sekarang jam berapa, ya? What time is it now? Jam berapa sekarang? What time is it now? Permisi, boleh tahu sekarang jam berapa? Excuse me, may I know what time is it now? NOTE: Different Word Order will be different the meaning Jam berapa? What time? Berapa jam? How many hours? ON THE HOUR AM: Sekarang jam dua belas malam PM: Sekarang jam dua belas siang General: Sekarang jam dua belas tepat AM: Sekarang jam lima pagi PM: Sekarang jam lima sore General: Sekarang jam lima tepat
- 14. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id ON 15 MINUTES / A QUARTER PAST AM: Sekarang jam dua lewat lima belas malam/ Sekarang jam dua seperempat malam PM: Sekarang jam dua lewat lima belas siang/ Sekarang jam dua seperempat siang General: Sekarang jam dua lewat lima belas AM: Sekarang jam enam lewat lima belas malam/ Sekarang jam enam seperempat malam PM: Sekarang jam enam lewat lima belas pagi/ Sekarang jam enam seperempat pagi General: Sekarang jam enam lewat lima belas ON 30MINUTES / HALF PAST AM: Sekarang jam dua lewat tiga puluh malam/ Sekarang jam setengah tiga malam PM: Sekarang jam dua lewat tiga puluh siang/ Sekarang jam setengah tiga siang General: Sekarang jam dua lewat tiga puluh AM: Sekarang jam delapan lewat tiga puluh malam/ Sekarang jam setengah sembilan malam PM: Sekarang jam delapan lewat tiga puluh pagi/ Sekarang jam setengah sembilan pagi General: Sekarang jam enam lewat tiga puluh ON FIFTEEN / A QUARTER TO AM: Sekarang jam dua lewat empat puluh lima malam/ Sekarang jam tiga kurang seperempat malam PM: Sekarang jam dua lewat empat puluh lima siang/ Sekarang jam tiga kurang seperempat siang General: Sekarang jam dua lewat empat puluh lima AM: Sekarang jam lima lewat empat puluh lima pagi/ Sekarang jam enam kurang seperempat pagi PM: Sekarang jam lima lewat empat puluh lima sore/ Sekarang jam enam kurang seperempat sore General: Sekarang jam enam lewat empat puluh lima
- 15. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id To make easy in case for telling time, its better to use 24-hours (informal) Formula Jam + (TIME) + Menit 11:20 Jam Sebelas-Dua puluh menit 15:55 Jam Lima belas-Lima lima menit 06:43 Jam Enam-Empat puluh tiga menit 20:35 Jam Dua puluh-Tiga lima menit 10:10 Jam Sepuluh-Sepuluh menit 03:20 Jam Tiga-Dua puluh menit In case of date, normaly word order is following Day-Month-Year. DAY – MONTH – YEAR Correct 7 Januari 2015 Tujuh Januari dua ribu lima belas Incorrect Desember, 20 2015 Desember dua puluh duaribu lima belas Bulan Desember tanggal dua puluh tahun dua ribu lima belas Incorrect 2009 Agustus 13 Dua ribu sembilan Agustus tiga belas Tahun dua ribu sembilan bulan Agustus tanggal tiga belas Incorrect 2000, 1 April Dua ribu satu April Tahun dua ribu tanggal satu bulan April
- 16. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id PETUNJUK ARAH (DIRECTIONS) COMPASS DIRECTIONS - ARAH MATA ANGIN North to the north at the north of… Utara ke arah utara sebelah utaranya/utara dari… South to the south at the south of… Selatan ke arah selatan sebelah selatannya/dari… East to the east at the east of ... Timur ke arah timur sebelah timurnya/timur dari… West to the west at the west of Barat ke arah barat sebelah baratnya/barat dari LOCATIONS – LETAK In front of… Di depan Behind… Di belakang Across the street Di seberang jalan On the right of… Di sebelah kanan dari…/di sebelah kanannya. On the left of… Di sebelah kiri dari…/…di sebelah kirinya. Pertigaan (T junction, Y junction) Lampu merah (traffic light) Perempatan (intersection, cross road) Jembatan (bridge) Bundaran (roundabout) Masjid (mosque) Alun-alun (townsquare/roundabout) Gereja (church) Menara (tower) Toko (shop) UTARA SELATAN BARAT TIMUR TENGGARABARAT DAYA TIMUR LAUTBARAT LAUT
- 17. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id English Indonesian Along/down Go along this street. Go down this street. Lurus/terus saja Jalan ini lurus saja. Ikuti jalan ini. Back Go back. Kembali Putar kembali. in the direction of/towards... …… the train station …… the church …… the hotel Menuju… / Ke arah… …kereta api …gereja …hotel left - to the left – turn left Take the first turn to the left Kiri – ke kiri – belok kiri Ambil belokan ke kiri right - to the right – turn right Take the first turn to the right Kanan – ke kanan – belok kanan Ambil belokan ke kanan. Straight ahead Keep going straight ahead. Lurus saja. Tetap jalan lurus. Up to, until up to the traffic light Sampai…. Sampai di lampu merah Tersesat / Bertanya Dan Memberikan Petunjuk Arah (Getting Lost / Asking And Giving Directions) English Indonesian Addressing: Excuse me, Sir/Mam. Starting questions: Can I ask something? Possible answers: Of course, what do you want to ask? Menyapa: Maaf, Pak/Bu OR Permisi, Pak/Bu Memulai pertanyaan: Boleh saya bertanya? Jawaban: Boleh. Mau tanya apa? Getting lost: How can I go to ...? I want to go to... but I dont know which way We will go to...but I think/it seems we are lost Tersesat: Bagaimana caranya untuk ke.../Saya harus naik apa untuk ke... ? (about transport) Saya ingin pergi ke .... Tapi saya tidak tahu lewat mana? (about directions) Kami mau pergi ke… tapi sepertinya kami tersesat Asking for directions: Do you know where it is? Answers: From here take a bus to... Menanyakan arah: Anda tahu di mana tempatnya/lokasinya? Jawaban: Dari sini naik bis ke... Thanking: Thank you for the directions. Thank’s for the information. Answers: You’re welcome. Berterimakasih: Terima kasih atas petunjuknya / informasinya. Makasih, ya, Pak/Bu/Mas/Mbak. Jawaban: Sama-sama. PERMINTAAN MAAF (APOLOGY)
- 18. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id Indonesian English Saya mohon minta maaf, karena… Kemarin saya tidak datang ke rapat kantor. I would like to apologize, for…. Yesterday, I did not come to the office meeting. Saya menyesal karena… Tidak datang pada konser Bon Jovi. I am sorry for…./ I regret for… Not coming to Bon Jovi concert. Saya minta maaf tentang… Saya datang terlambat hari ini. I want to apologize for… I came late today. Maafkan saya untuk… Forgive me for…. Permisi… (to interrupt conversation, etc) Excuse me… To Response to an Apology / Merespon Permintaan Maaf Formal: Saya memaafkan anda. Anda dimaafkan. (passive sentence) Formal: I forgive you. You are forgiven Informal: Aku maafin kamu. Tidak apa-apa / nggak apa-apa. Informal: I forgive you. It’s alright. / never mind. Maaf… Maaf atas kesalahan kami. Maaf, saya tidak bisa. Sorry… Sorry for our mistakes. Sorry, I can not. Silakan… (as a positive response to Permisi) Yes, please… (as a positive response to Permisi) TENTANG JANJI (ABOUT APPOINTMENT) Indonesian English Formal: Saya ingin membuat janji dengan Bapak/Ibu… Saya sudah ada janji untuk bertemu dengan Bapak/Ibu… Saya sudah membuat janji telepon dengan Bapak/Ibu… Bisakah besok kita rapat lagi? Kapan kita bisa bertemu kembali? Formal: I want to make an appointment with Mr./Mrs…. I have made an appointment to meet with Mr. / Mrs…. I have made an appointment to call Mr./Mrs… Can we have another meeting tomorrow? When will we set a meeting date again? Informal: Aku mau bikin janji sama kamu…. Aku sudah janji sama kamu untuk….jam….(time)….di… (place)… Ayo, janjian lagi di sini! Informal: I want to make an appointment with you… I have made an appointment with you to… at…in… Let’s meet again here! Berkencan (positif): Aku ada kencan dengan cewekku. Aku kencan dengan dia. Dating (positive): I have a date with my girlfriend. I am dating him.
- 19. Belajar Bahasa Indonesia dengan Cara Mudah Study Bahasa Indonesia in Easy Way Mustain Adinugroho | t41n_smg@yahoo.co.id LATIHAN – EXERCISE Put () if the phrase is correct or (x) if incorrect Mandi kamar ( ) Bayi cantik ( ) Besar rencana ( ) Kaki jalan ( ) Nonton bola ( ) Panas teh ( ) Pria tampan ( ) Nasi goreng ( ) Saya nama ( ) Put the following words into correct order 1. Orang – sedikit – pintar ………………………………….. 2. Semua – ganteng – pria ………………………………….. 3. Sayur –banyak – segar ………………………………… 4. Manis – gula – sedikit ……………………………….. 5. Pisang – pohon – banyak …………………………………….. 6. Putri – saya – halo – Indonesia – nama – dari …………………………………………………………............. 7. Mau – pasar – saya –besok – ke ……………………………………………….. 8. Senang – sangat – ini – hari – saya …………………………………………………… 9. Eropa – relawan – dari – saya ……………………………………………. 10. Apotek – ingin – aku – obat – membeli –di ………………………………………………………………… 11. Indonesia – belajar – kalian – kemarin – bahasa ……………………………………………………………………….. 12. Segar – susu – Putri – suka – tidak – minum ………………………………………………………………….. 13. Di – Antonio – Jacopo – bandara – bertemu – dan – akan …………………………………………………………………………………….... 14. Mangga – jus – dia – minum – segelas – ingin ……………………………………………………………………. 15. Relawan – Julia – Mariate dan Michal – dengan – rumah – di – tinggal …………………………………………………………………………………………………………...
