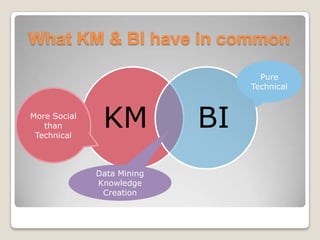
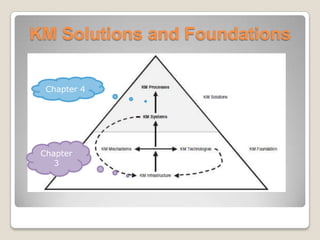
The document outlines the foundations of knowledge management, including its infrastructure, mechanisms, and technologies necessary for enhancing organizational goals through effective knowledge utilization. It highlights the roles of organizational culture, structure, and information technology in supporting knowledge processes such as discovery, capture, sharing, and application. Additionally, it contrasts knowledge management with business intelligence, providing insights into their similarities and differences.