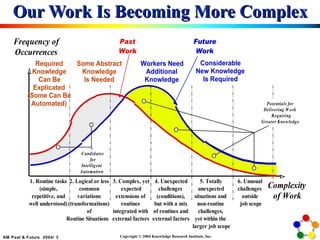
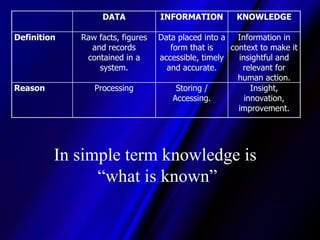
The document discusses knowledge and knowledge management, defining knowledge as justified true belief and emphasizing its role in organizational processes. It differentiates between various types of knowledge, such as explicit and implicit knowledge, and outlines objectives and actions in knowledge management to enhance efficiency and competitive advantage. Additionally, it defines knowledge workers and their crucial role in creating, utilizing, and facilitating knowledge in various industries.