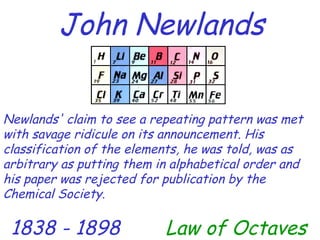
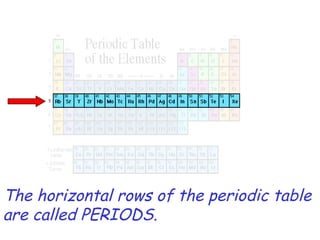
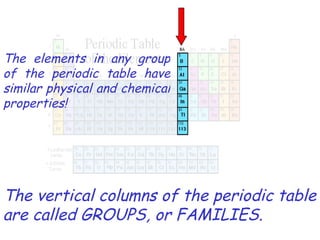
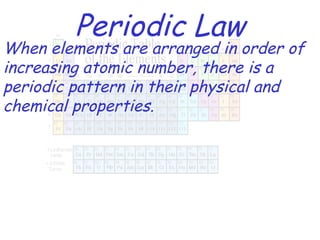
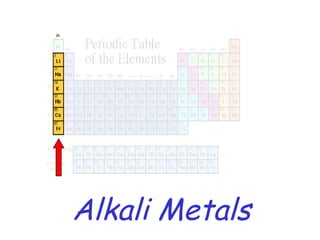
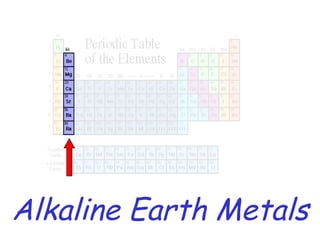
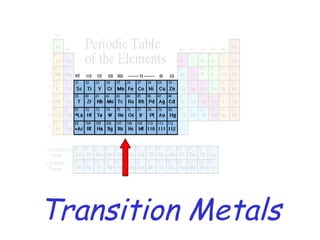
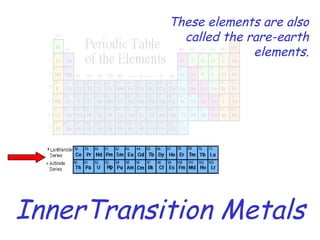
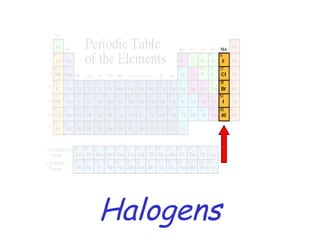
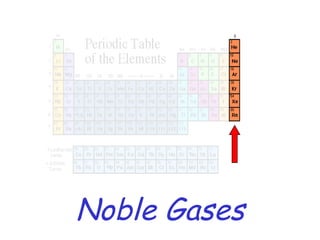
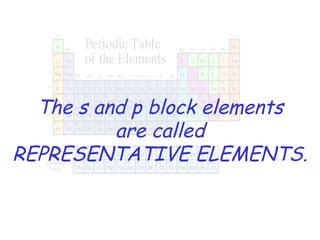
The modern periodic table developed from early 19th century attempts by chemists to organize the known elements. Johann Dobereiner first classified elements into triads based on their properties. John Newlands proposed an early version of the periodic law, arranging elements in order of atomic mass and noticing repeating patterns every eighth element. However, his work was ridiculed. Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer independently published periodic tables in 1869 arranging elements by atomic mass and leaving gaps for undiscovered elements. Mendeleev's predictions for properties of unknown elements were more accurate, earning him recognition as the father of the periodic table. Henry Moseley later rearranged elements by atomic number, resolving inconsistencies and establishing the