1) Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
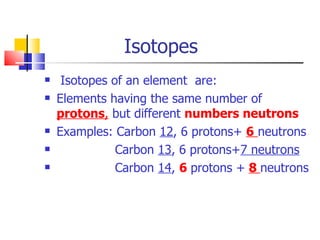
2) The atomic number of an element is the number of protons it contains. Isotopes are elements with the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons.
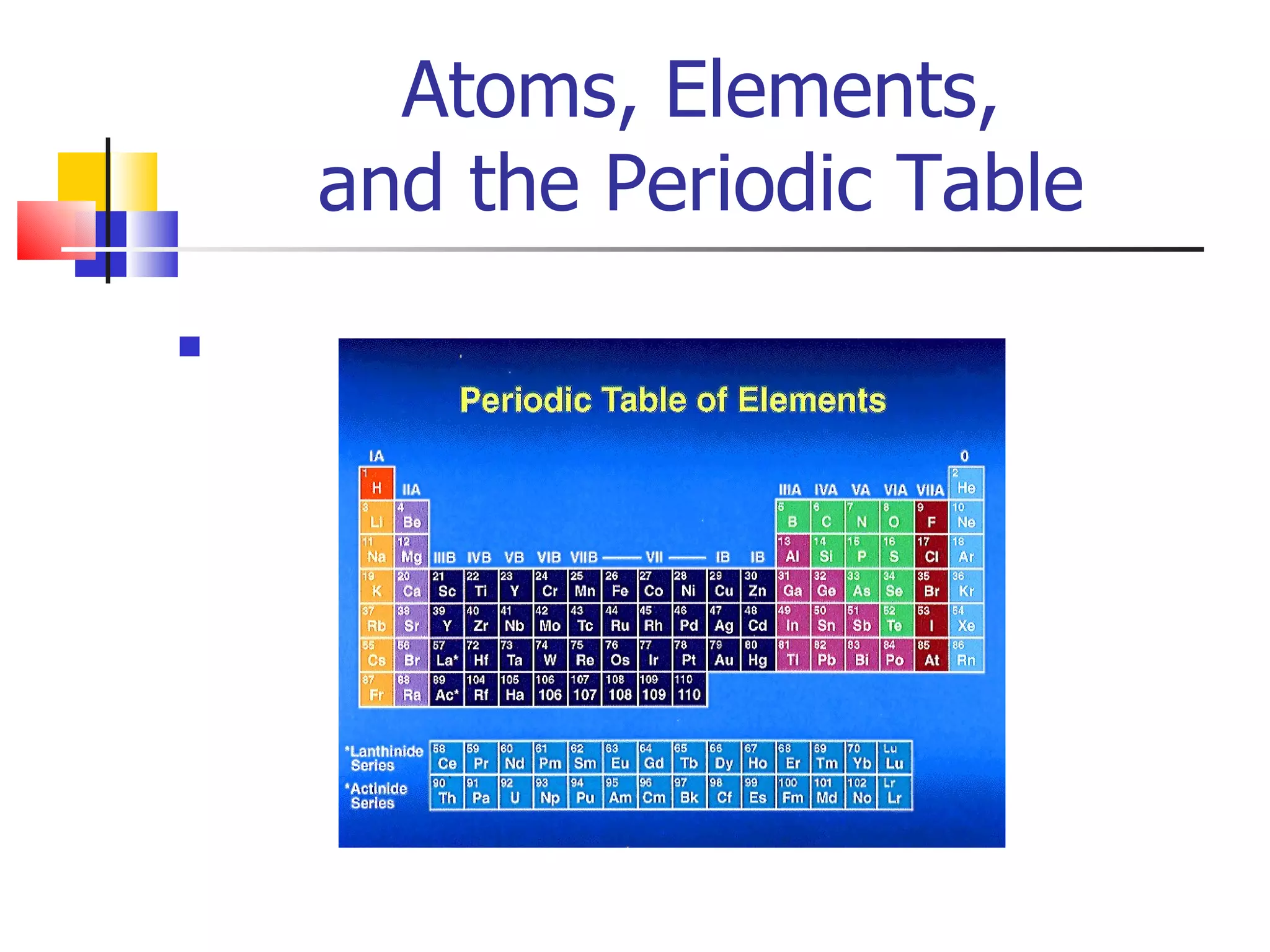
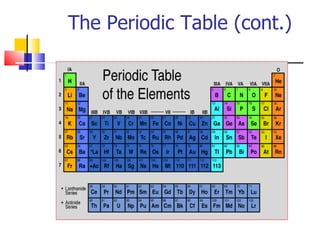
3) Elements are arranged in the periodic table based on their atomic number. The periodic table is organized into rows and columns, with elements in the same column having similar chemical properties.