Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

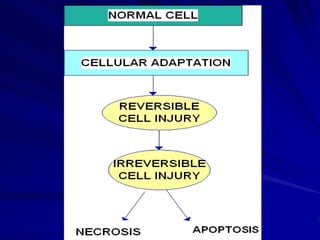






























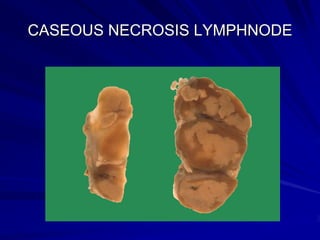

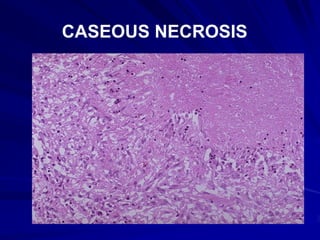


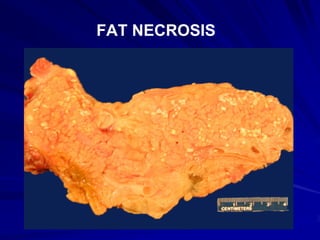


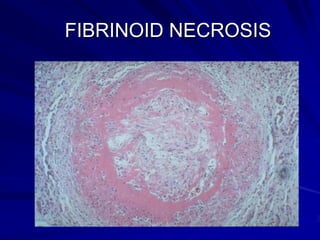

Necrosis is the morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissues. It can be caused by ischemia, physical agents, chemical agents, or immunological injury. The main types of necrosis include coagulative necrosis, liquefactive necrosis, caseous necrosis, fat necrosis, and fibrinoid necrosis. Coagulative necrosis preserves tissue architecture with denatured proteins and enzymatic digestion of cells. Liquefactive necrosis results in a liquid viscous mass. Caseous necrosis is a type of coagulative necrosis seen in tuberculosis that leaves cheesy white tissue.








































