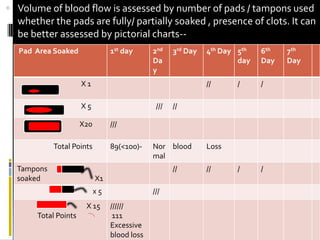
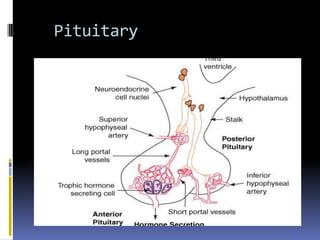
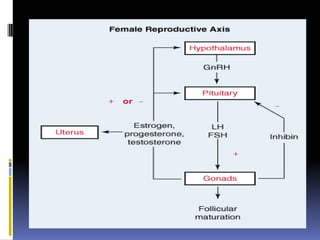
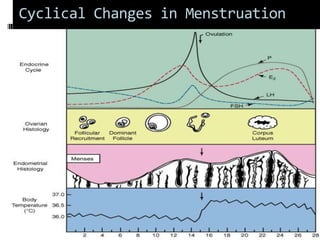
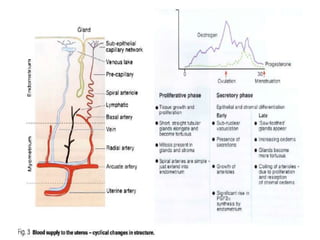
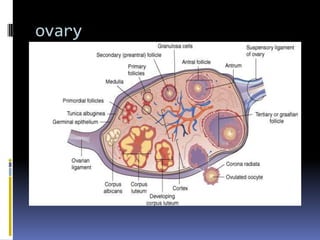
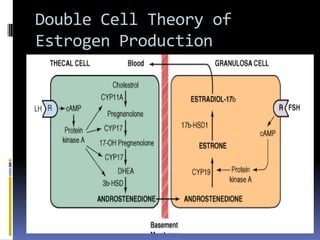
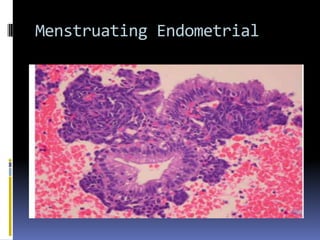
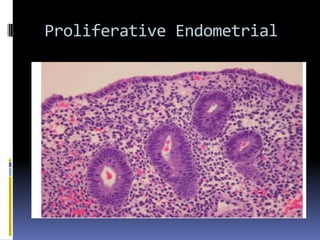
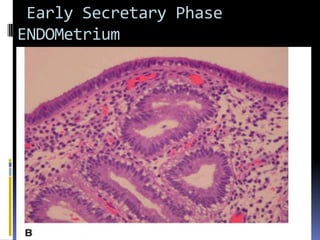
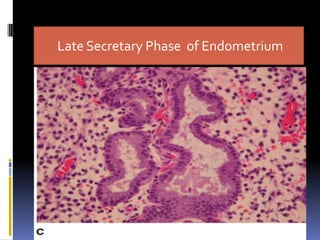
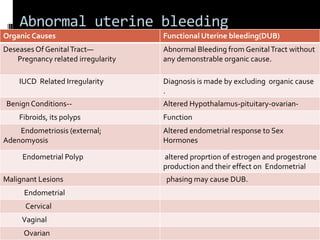
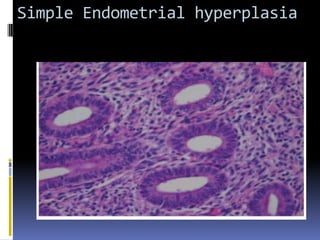
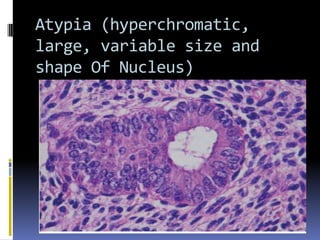
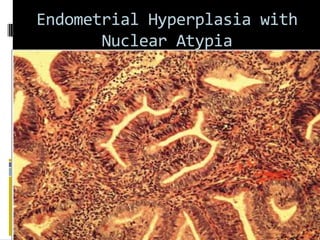
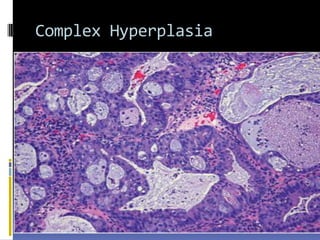
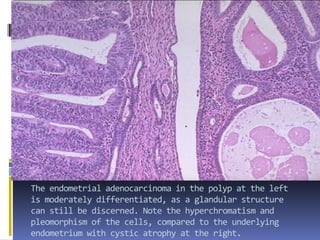
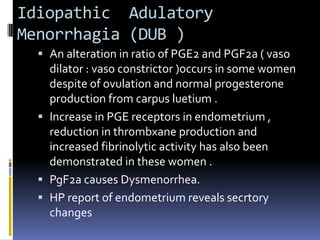
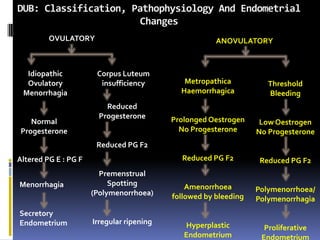
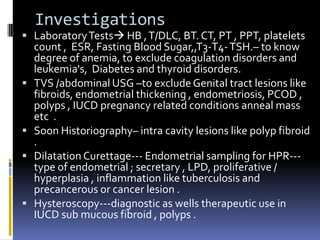
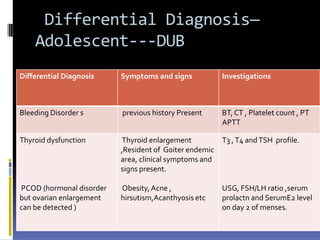
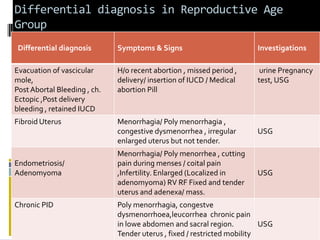
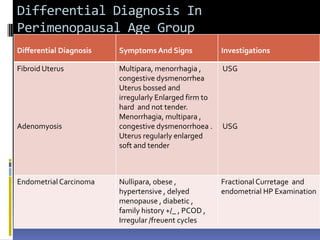
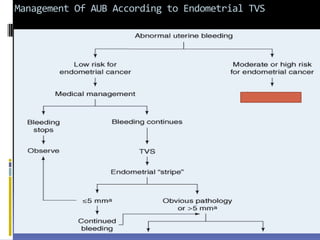
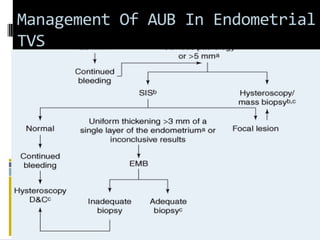
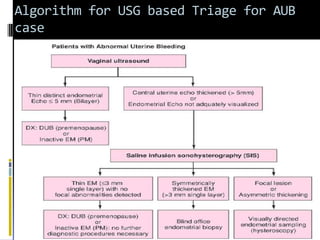
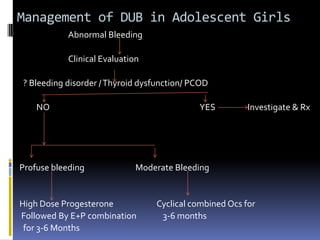
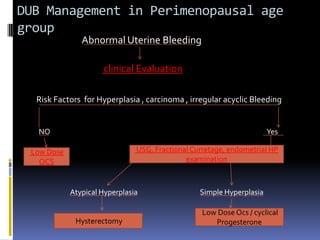
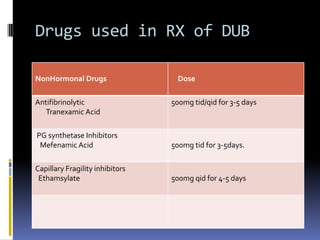
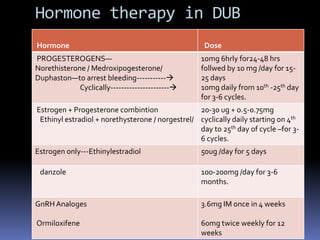
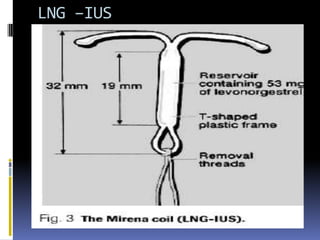
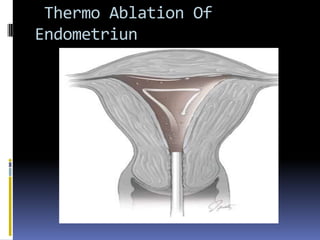
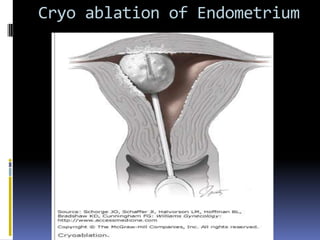
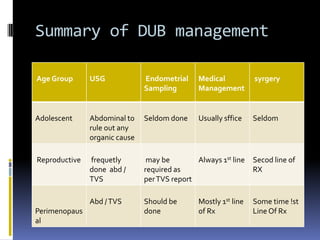
This document discusses abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). It begins by defining normal menstrual cycles and explaining the hormonal regulation of menstruation. It then describes different types of abnormal bleeding patterns seen in AUB, including menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, and oligomenorrhoea. Organic and functional causes of AUB are outlined. The document focuses on the pathophysiology, endometrial changes, and management of anovulatory and ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Diagnostic tests for AUB and differential diagnoses for adolescents and reproductive-aged women are also reviewed. Treatment options for AUB include medical therapies like hormones and lifestyle modifications, as well as surgical interventions.