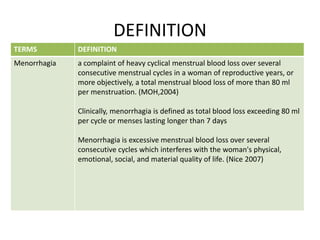
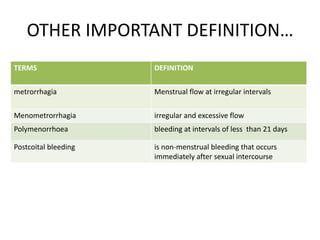
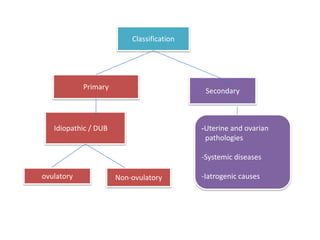
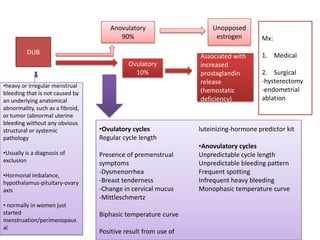
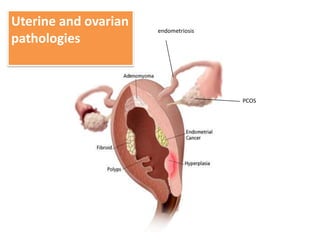
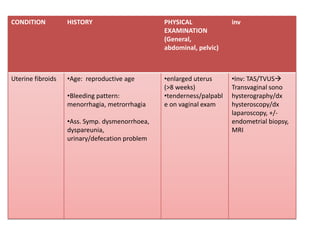
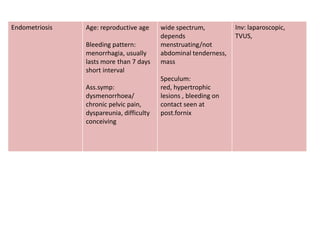
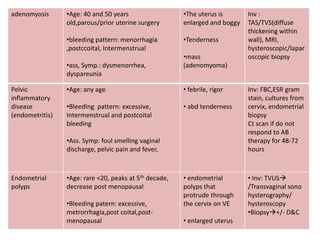
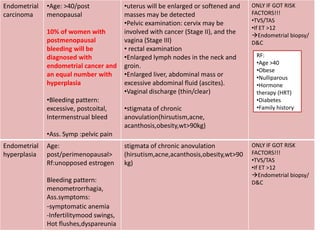
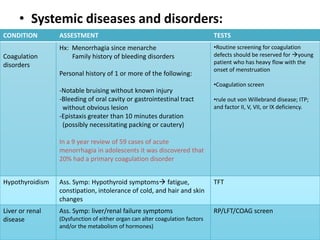
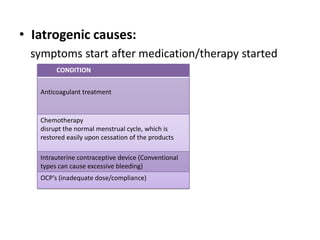
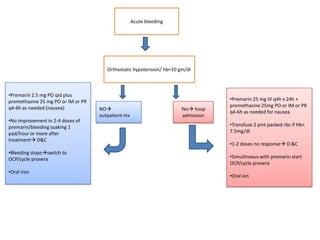
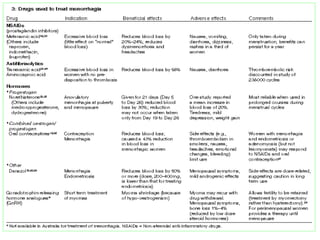
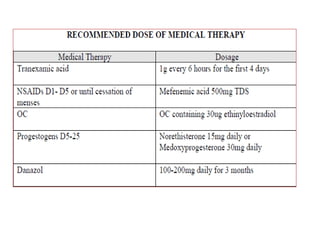
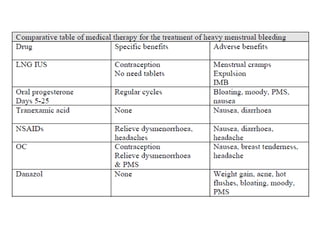
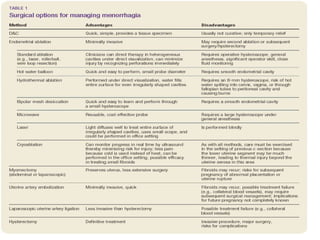
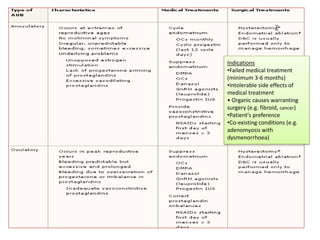
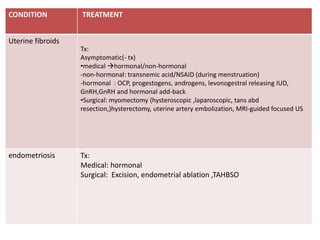
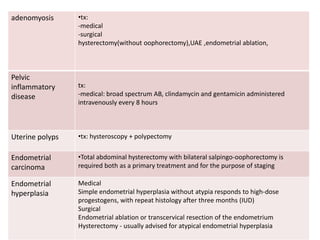
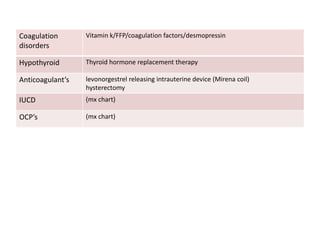
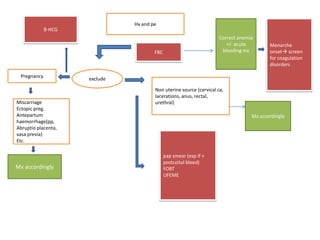
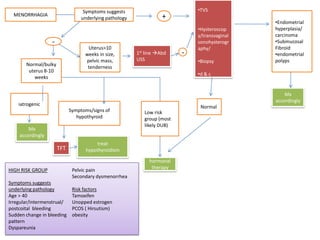
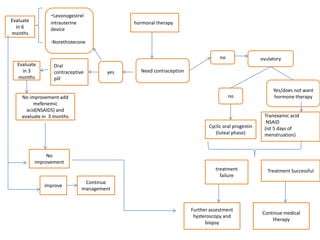
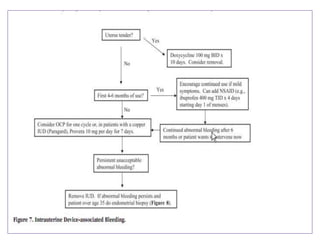
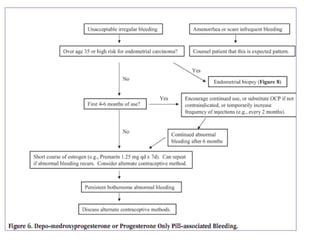
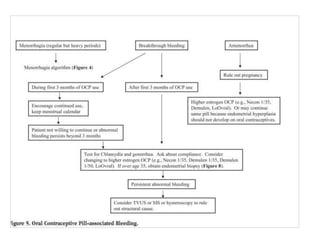
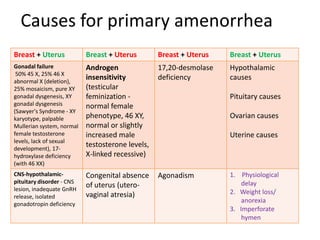
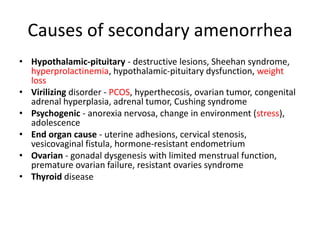
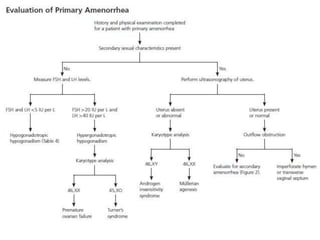
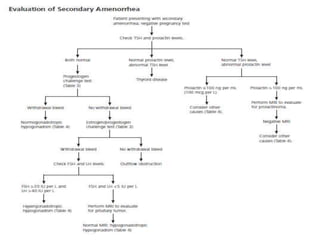
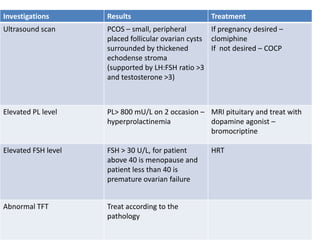
Menorrhagia, or heavy menstrual bleeding, is defined as a total blood loss of more than 80 ml per menstrual period. It can be classified as primary, caused by conditions like dysfunctional uterine bleeding, or secondary, caused by underlying pathologies of the uterus, ovaries, or systemic diseases. Common causes of secondary menorrhagia include uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometriosis, and less commonly, endometrial polyps or cancer. A thorough history, physical examination, and targeted investigations are needed to diagnose the cause of menorrhagia.