1) Statistics play an important role in medical research by describing diseases, making estimates from samples, determining significance of differences and associations, and making forecasts.
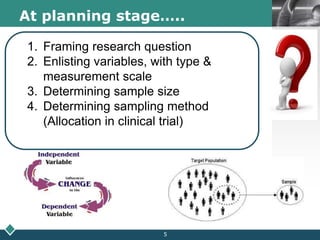
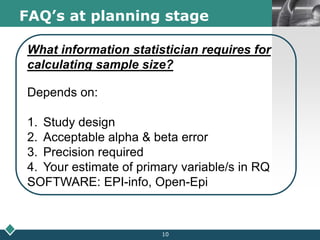
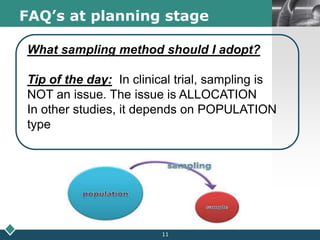
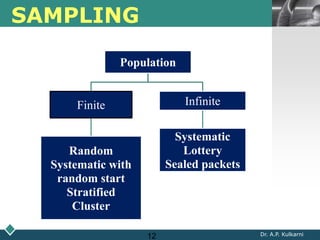
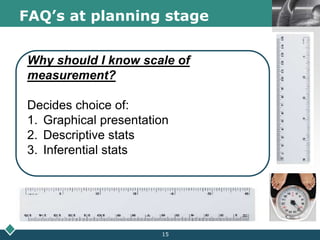
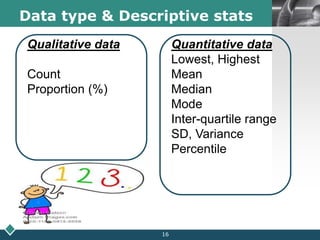
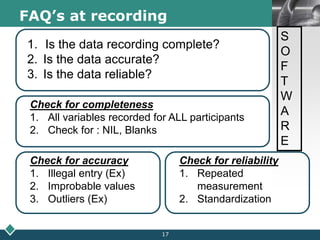
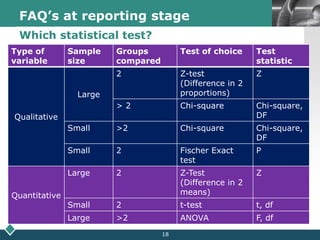
2) A statistician should be consulted at the planning, data collection, and reporting stages of research. At planning, they can help frame questions, determine sample size and sampling methods, and identify variables and scales of measurement.
3) It is important to utilize statisticians properly in research by involving them in the entire process and communicating effectively between clinical and statistical perspectives.