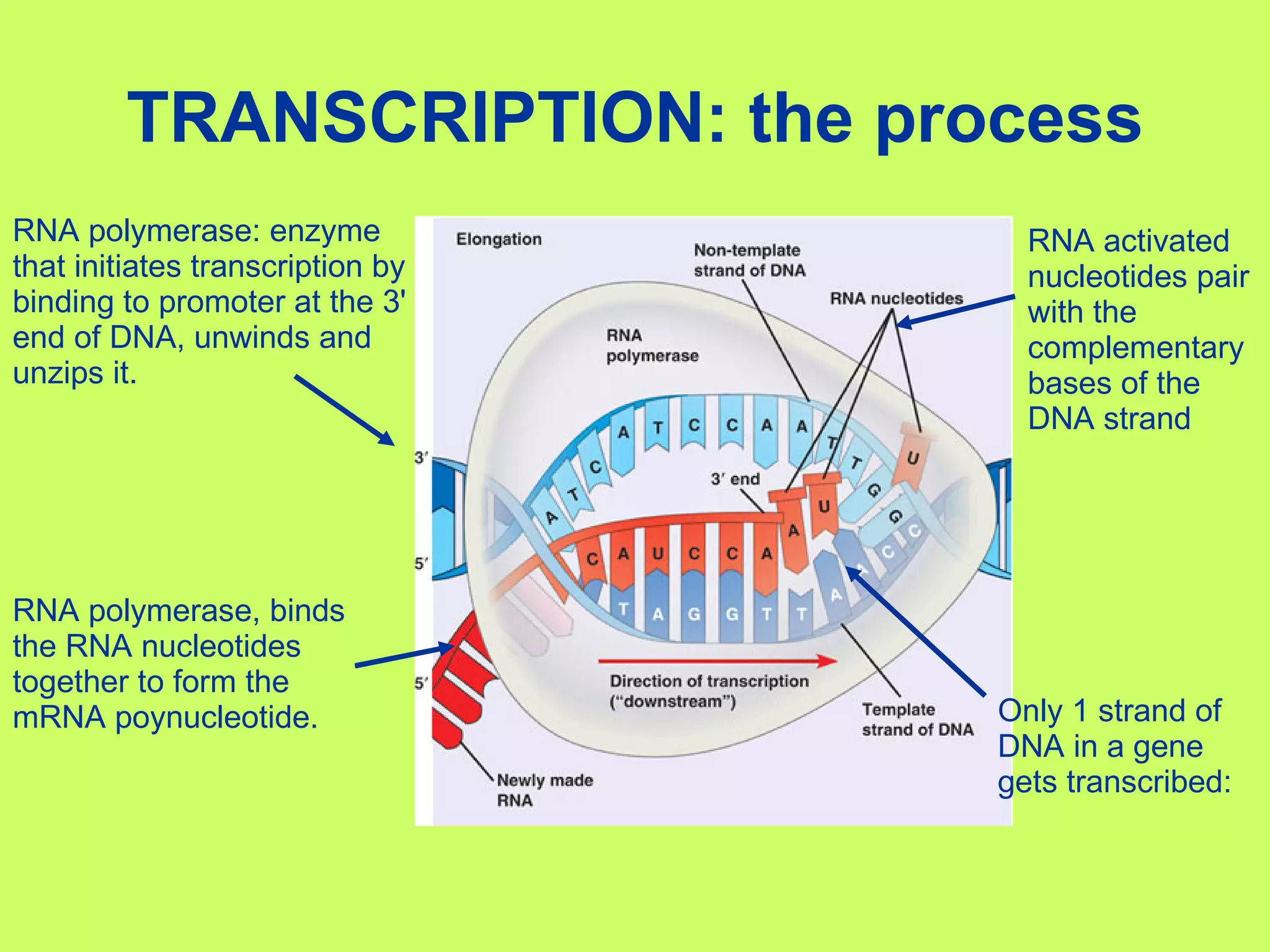
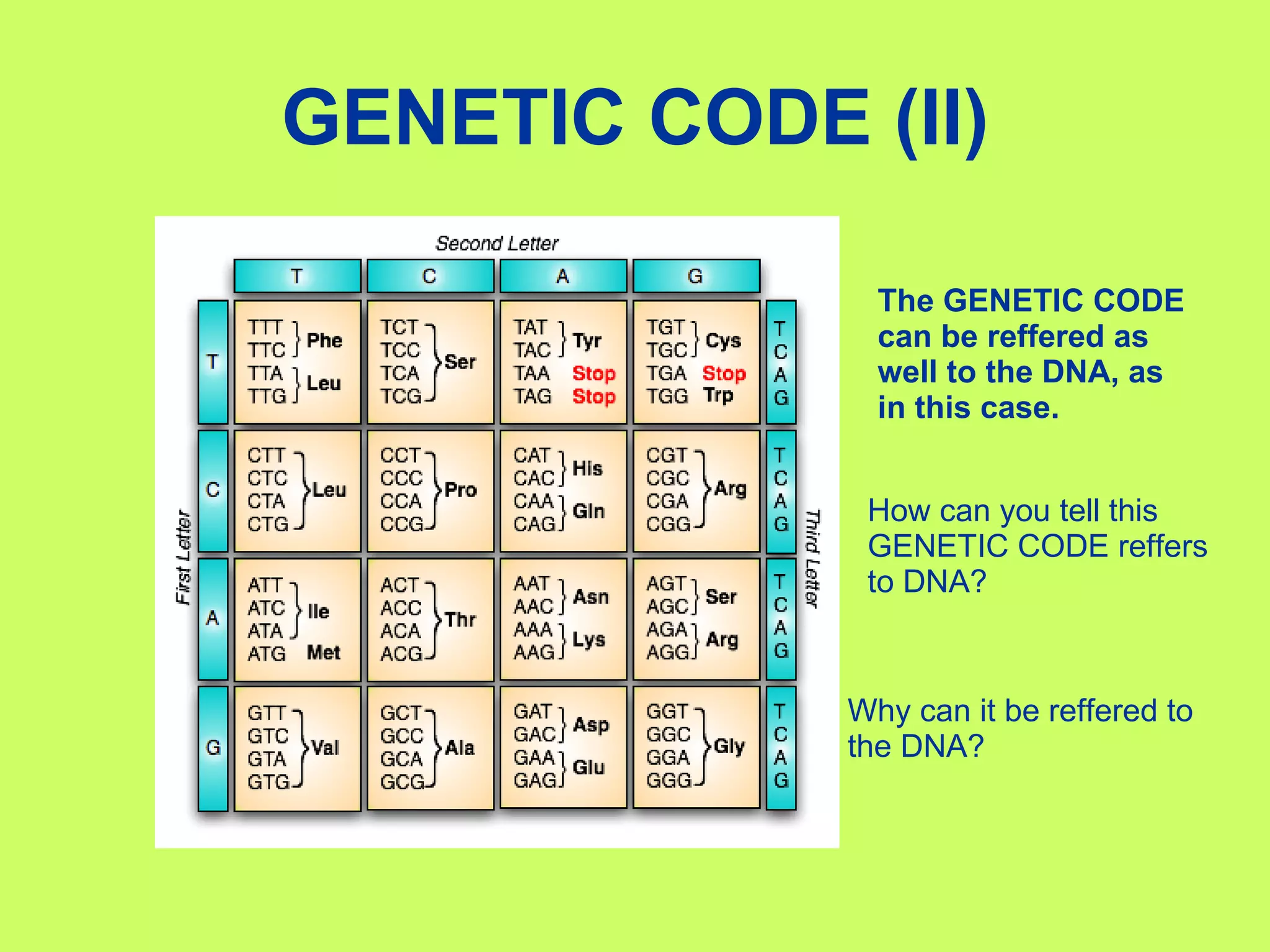
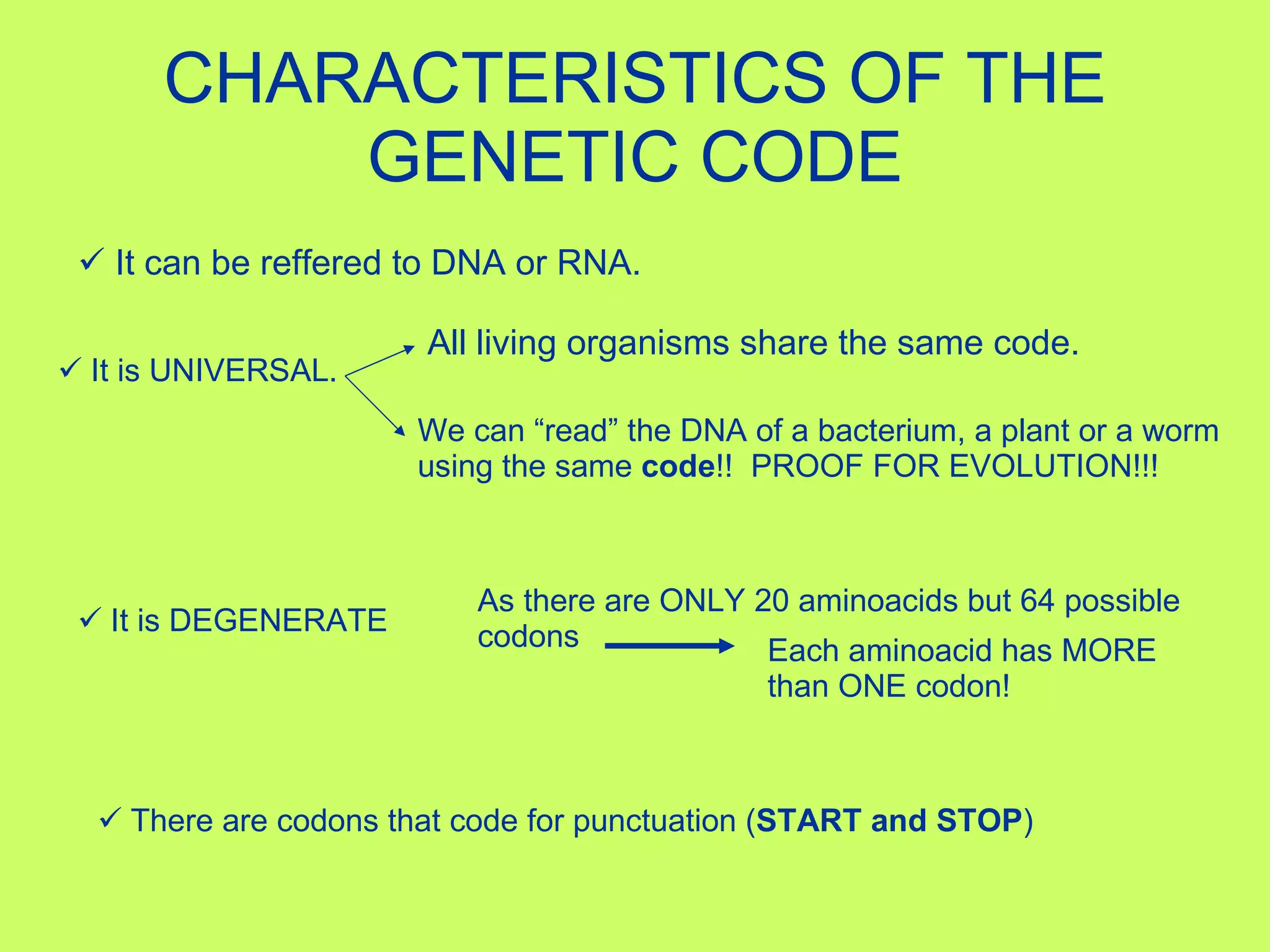
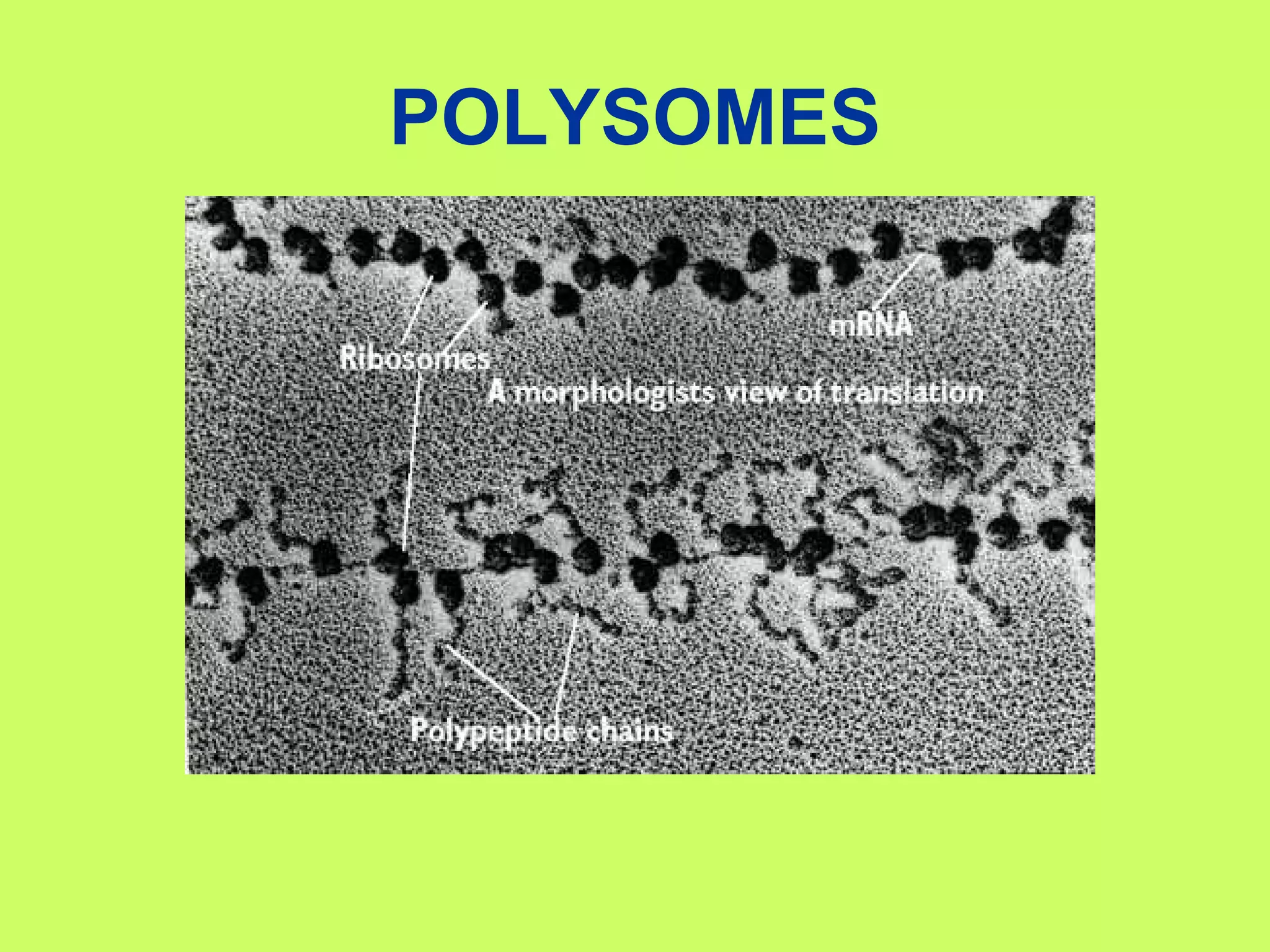
The document summarizes the central dogma of molecular biology and the processes of protein synthesis - transcription and translation. It explains that DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus, and mRNA is then translated into proteins by ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Transcription involves RNA polymerase copying the DNA code into mRNA. Translation involves tRNAs matching their anticodons to the mRNA codons and adding the corresponding amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. The genetic code is universal and degenerate, with multiple codons coding for each amino acid.